Introduction
In an age where environmental concerns and sustainable practices are at the forefront of global consciousness, the automotive and industrial sectors are undergoing a transformation to address the pressing issue of harmful emissions. Emissions control systems and advanced aftertreatment technologies have emerged as indispensable tools in the quest for cleaner air and a healthier planet. This article delves into the intricate world of emissions control systems and aftertreatment, exploring their inner workings, significance, and their vital role in shaping a more sustainable future.
In the 21st century, as environmental awareness and sustainable practices take center stage on the global agenda, the automotive and industrial sectors find themselves in the midst of a profound transformation. This transformation is driven by an urgent need to confront the pressing issue of harmful emissions and their far-reaching impact on the planet. Within this context, emissions control systems and advanced aftertreatment technologies have emerged as nothing short of indispensable tools in the relentless pursuit of cleaner air and a healthier, more sustainable world. In the following sections, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of these remarkable innovations, unraveling the intricacies of emissions control systems and the significance of advanced aftertreatment technologies. Together, they form the bedrock of our collective efforts to mold a future where environmental preservation is not just a goal but an imperative.
The Environmental Imperative:
The urgency of addressing harmful emissions cannot be overstated. The repercussions of air pollution, global warming, and the degradation of natural ecosystems have become undeniable, calling for immediate and effective action. The automotive and industrial sectors, which have historically been significant contributors to these problems, are now pivotal players in the drive for environmental responsibility.
Emissions Control Systems: The Guardians of Clean Air:
Emissions control systems are the vanguard of this transformation. These ingenious systems are meticulously engineered to reduce the release of harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. At the heart of this endeavor is the catalytic converter, a marvel of modern engineering that employs precious metals to act as catalysts. Through a series of chemical reactions, catalytic converters convert CO, HC, and NOx into less harmful compounds, effectively purifying the exhaust gases before they are released into the air. This technology alone has been instrumental in achieving significant reductions in air pollution.
The Symphony of Components:
Beyond catalytic converters, emissions control systems comprise a symphony of intricately designed components. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems re-circulate exhaust gases to reduce NOx emissions, while evaporative emissions control prevents the release of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. Together, these components harmonize to ensure that harmful emissions are kept to a minimum.
Aftertreatment Technologies: A Second Line of Defense:
However, emissions control systems, impressive as they are, cannot eliminate all pollutants entirely. This is where aftertreatment technologies come into play, particularly in diesel engines and modern vehicles equipped with Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems. Aftertreatment technologies take the cleanup process a step further, employing chemical reduction processes to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water vapor. This second line of defense ensures that emissions are reduced to the absolute minimum, even in the most challenging conditions.
A Symphony of Innovation:
The automotive industry, driven by the imperative to reduce emissions and enhance efficiency, is an epicenter of innovation. Lean-burn engines, direct injection, and state-of-the-art exhaust gas sensors are just a few examples of innovations that are fine-tuning the balance between power and environmental responsibility. These advancements not only reduce the environmental footprint but also improve fuel economy and engine performance, proving that sustainability and efficiency are not mutually exclusive.
A Cleaner, More Sustainable Future:
In the grand narrative of environmental preservation, emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are the unsung heroes, diligently working behind the scenes to mitigate the adverse effects of transportation and industrial activities. Their continuous evolution and integration into various industries are pivotal in the pursuit of a future where cleaner air, a healthier planet, and environmental sustainability are not just aspirations but tangible realities.
As the world collectively embraces a vision of a greener and more sustainable future, emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies will continue to be instrumental. They will ensure that our engines, our industries, and our way of life remain harmoniously aligned with the imperative of environmental stewardship. In the journey toward a world where the air we breathe is cleaner, the ecosystems we cherish are healthier, and the legacy we leave for future generations is one of responsible custodianship, these technologies stand as unwavering sentinels, guarding our path toward a brighter and more sustainable tomorrow.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: ISOR HD Warranty
The combustion processes in internal combustion engines, whether in vehicles or industrial machinery, produce a cocktail of pollutants that contribute to air pollution, climate change, and adverse health effects. Among these emissions are carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). To combat these issues, emissions control systems have become integral components of modern engine design.
The inner workings of internal combustion engines, whether propelling vehicles on the road or driving industrial machinery, are a testament to engineering prowess. These mechanical marvels harness the power of controlled explosions, converting fuel into energy with incredible efficiency. However, lurking within this symphony of controlled chaos are emissions that pose a substantial threat to our environment and well-being.
This emissions medley includes carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM), each playing a distinct role in the environmental drama. Carbon monoxide, the silent and deadly gas, can impair our ability to carry oxygen, posing immediate health risks. Nitrogen oxides contribute to the formation of smog and are a key player in respiratory problems. Hydrocarbons, the precursors to ground-level ozone, can irritate the eyes and respiratory system. Particulate matter, consisting of tiny, inhalable particles, has been linked to a range of health issues, from aggravated asthma to heart attacks.
To combat these multifaceted challenges, the integration of emissions control systems has become an indispensable part of modern engine design. These systems are akin to environmental guardians, diligently working to mitigate the harmful effects of engine emissions. They deploy an arsenal of advanced technologies, from catalytic converters that transform toxic gases into harmless compounds, to diesel particulate filters that trap harmful particles before they escape into the air.
Moreover, these emissions control systems are not static; they continually evolve. Engineers are engaged in a perpetual quest for more efficient, effective, and sustainable solutions. The development of cleaner fuels, such as low-sulfur diesel and biofuels, further complements these efforts, reducing the pollutant content in the combustion process.
As we navigate the intersection of industry, transportation, and environmental stewardship, it’s evident that emissions control systems are not just technological marvels; they represent an ethical imperative. They are tangible manifestations of our commitment to creating a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable world. The challenges may be formidable, but the determination to overcome them is unwavering. In our ongoing endeavor to reduce emissions, we are not just refining engines; we are forging a path toward a brighter and cleaner future for all.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Beyond a One-Time Scandal: Europe’s Onging Diesel Pollution …

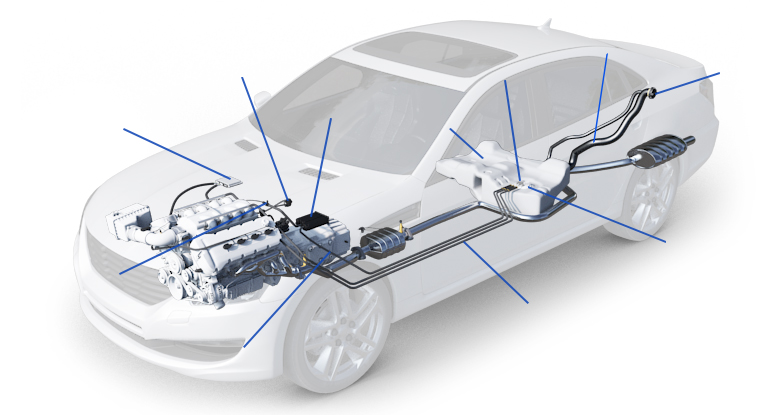
Emissions control systems are engineered to reduce the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. They typically comprise three main components:
Emissions control systems are a testament to the ongoing commitment to environmental stewardship within the automotive industry. These intricate systems are meticulously designed and engineered with a clear purpose: to mitigate the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. To achieve this vital mission, emissions control systems typically comprise three main components, each playing a pivotal role in safeguarding air quality and human health.
Catalytic Converter: At the heart of every emissions control system, the catalytic converter stands as a technological marvel. This ingenious device operates as a chemical catalyst, initiating reactions that convert harmful exhaust gases into less detrimental compounds. By facilitating the transformation of carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into more benign substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), catalytic converters significantly reduce the emission of these pollutants. They represent the frontline defense against the noxious byproducts of combustion, contributing to cleaner air for all.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System: The EGR system is a master of balance in the emissions control arsenal. It functions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold, where they mix with fresh air and fuel. This process serves a dual purpose: first, it lowers combustion temperatures, which reduces the production of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a major contributor to smog and respiratory problems. Second, it optimizes fuel efficiency, striking an eco-friendly balance between performance and emissions reduction.
Air Injection System (Secondary Air Injection): The air injection system plays a crucial role in promoting complete combustion and minimizing harmful emissions. By injecting fresh air into the exhaust stream before it reaches the catalytic converter, this system aids in the further oxidation of unburned hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO). This supplemental oxygen ensures that the catalytic converter operates at its peak efficiency, further reducing the release of these pollutants into the environment.
Together, these three components form a robust and highly effective defense against the environmental impact of internal combustion engines. Emissions control systems exemplify the industry’s commitment to sustainability, health, and cleaner air. As technology advances, we can anticipate even more sophisticated and efficient solutions to continually reduce the footprint of automotive emissions, contributing to a healthier planet for current and future generations.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Civil Cases and Settlements by Statute | Enforcement | US EPA
Among the most recognized elements of emissions control systems, catalytic converters contain precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which serve as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions. These reactions transform harmful pollutants like CO, HC, and NOx into less harmful substances, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and nitrogen.
“Catalytic converters, one of the most iconic components within emissions control systems, have a remarkable role in shaping our environmental stewardship efforts. These unassuming devices, housing precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, act as silent heroes in our ongoing battle against air pollution.
Within the confines of a catalytic converter, a symphony of chemical reactions unfolds. These reactions are orchestrated by the catalytic properties of these noble metals. They work in concert to convert a cocktail of harmful pollutants – carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) – into far more benign substances. The alchemical transformation that occurs within this metallic chamber yields primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and nitrogen.
This transformative process represents the embodiment of responsible engineering, as it not only mitigates the harmful impact of vehicle emissions on air quality but also contributes to a collective effort to combat climate change. By rendering the pollutants less harmful and capturing their latent energy, catalytic converters align with our commitment to cleaner, more sustainable transportation.
Despite their silent operation, catalytic converters serve as beacons of environmental responsibility, embodying the progress we’ve made and the path forward toward a greener automotive future. As we embrace increasingly stringent emissions standards and a growing eco-consciousness, these remarkable devices continue to play a vital role in reducing our automotive carbon footprint and protecting the planet we call home.”
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The Volkswagen emissions scandal explained – The Guardian
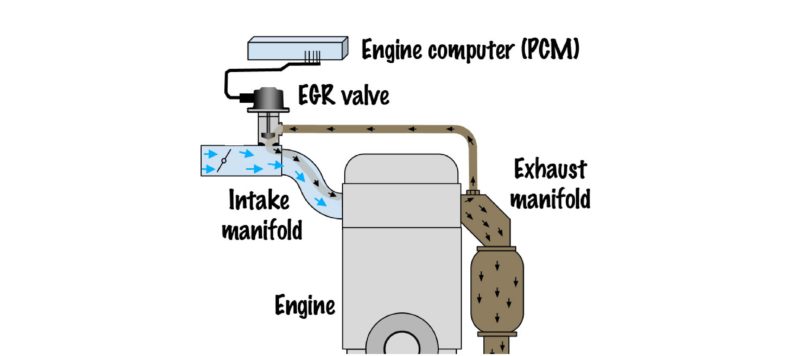
EGR systems redirect a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold. By diluting the air-fuel mixture with inert exhaust gases, EGR reduces the production of NOx during combustion.
EGR systems, or Exhaust Gas Recirculation systems, stand as a testament to the automotive industry’s commitment to reducing harmful emissions and enhancing engine efficiency. These systems operate as a strategic ally in the ongoing battle against one of the most notorious culprits of air pollution: nitrogen oxides (NOx).
The core principle of EGR is simple yet profound. It involves redirecting a portion of exhaust gases – the byproduct of combustion – back into the engine’s intake manifold. This seemingly counterintuitive maneuver has far-reaching benefits that extend well beyond the surface.
When these exhaust gases re-enter the combustion chamber, they introduce an ingenious form of moderation. By their very nature, exhaust gases are inert, lacking the oxygen necessary for combustion. As they mix with the incoming air-fuel mixture, they effectively “dilute” it, reducing the concentration of oxygen available for combustion. This, in turn, lowers the peak combustion temperature.
Why is this temperature reduction significant? It all boils down to the formation of NOx. At high combustion temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen in the air combine to form nitrogen oxides, a group of compounds notorious for their detrimental impact on air quality and human health. By reducing the combustion temperature through EGR, the formation of NOx is significantly curtailed.
EGR systems are not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather finely tuned mechanisms. They adapt their operation based on a multitude of factors, including engine load, speed, and temperature, ensuring that the right amount of exhaust gases is reintroduced to maintain the delicate balance between emissions reduction and engine performance.
Moreover, EGR systems don’t merely function as a compliance tool to meet emissions standards; they embody the automotive industry’s commitment to sustainability. They exemplify how innovation can contribute to cleaner, more efficient internal combustion engines while extending their relevance during the transition to cleaner technologies.
In summary, EGR systems are like the conductor of an orchestra, orchestrating a symphony of efficiency and environmental responsibility within the engine. They are a testament to the industry’s dedication to reducing emissions and fostering a cleaner, more sustainable future, one exhaust gas at a time.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Tampering and Aftermarket Defeat Devices | Clean Air Northeast
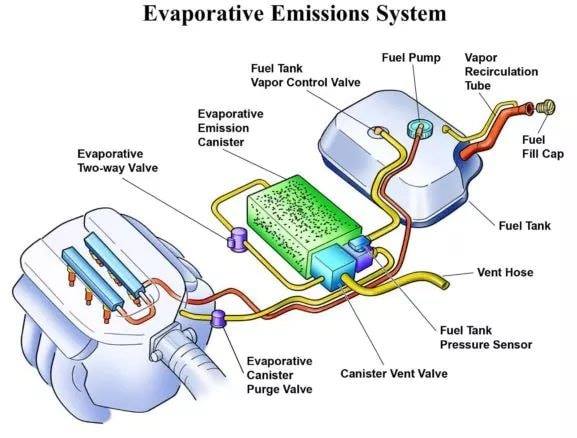
This component prevents the release of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. Systems like charcoal canisters absorb and store fuel vapors until they can be safely burned in the engine.
This critical component plays a pivotal role in modern vehicles, not only safeguarding the environment but also contributing to improved fuel efficiency and overall engine performance. Its primary purpose is to prevent the release of gasoline vapors, which can be harmful to the atmosphere and wasteful of a valuable resource.
At the heart of this system are charcoal canisters, ingenious devices designed to efficiently capture and store fuel vapors. When your vehicle is not in operation or when the engine isn’t actively combusting these vapors, they are channeled into the charcoal canister. Here, the activated charcoal, known for its exceptional adsorption capabilities, goes to work.
The charcoal within the canister acts like a sponge, absorbing and retaining the gasoline vapors until they can be safely reintroduced into the engine’s combustion process. This ensures that no harmful emissions escape into the atmosphere, mitigating the environmental impact of driving.
Moreover, the benefits extend beyond environmental protection. By utilizing the captured fuel vapors as part of the combustion cycle, the vehicle enhances fuel efficiency. This means that more of the fuel you purchase is utilized to power your vehicle, reducing both your fuel expenses and the overall carbon footprint of your daily commute.
In recent years, innovations in this technology have made the EVAP system even more efficient and reliable. Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated sensors and monitoring systems that can detect even the smallest leaks or malfunctions in the system, ensuring that it continues to perform its crucial role effectively.
In summary, the EVAP system with its charcoal canisters is a prime example of how automotive engineering strives for a harmonious balance between environmental responsibility and vehicle efficiency. By preventing the release of harmful gasoline vapors into the atmosphere and harnessing their energy for propulsion, it exemplifies the industry’s commitment to cleaner, more sustainable transportation.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Control of Air Pollution from New Motor Vehicles Heavy Duty Engine …
While emissions control systems are highly effective, they can’t entirely eliminate all pollutants. This is where aftertreatment technologies come into play, particularly in diesel engines and vehicles with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. Aftertreatment further reduces NOx emissions, using a chemical reduction process to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water vapor.
Emissions control systems have undoubtedly made remarkable progress in curbing the release of harmful pollutants from internal combustion engines. However, the quest for purer air and reduced environmental impact doesn’t end with these systems alone. This is where aftertreatment technologies emerge as a crucial second line of defense, especially in the context of diesel engines and vehicles equipped with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
While emissions control systems are highly effective at capturing and reducing various pollutants, they still can’t entirely eliminate certain compounds, most notably nitrogen oxides (NOx). NOx emissions are a notorious contributor to air pollution, and addressing them effectively requires a specialized approach.
Aftertreatment systems, which are an integral part of many modern diesel engines and SCR-equipped vehicles, step in to tackle this challenge head-on. These systems are designed to take the environmental responsibility a step further by further reducing NOx emissions through a chemical reduction process. The heart of this process lies in the application of a reducing agent, most commonly ammonia (NH3), in the presence of a catalyst.
This chemical alchemy takes place within the aftertreatment system, where NOx molecules encounter the reducing agent. Through a series of precisely controlled reactions, the NOx compounds are transformed into entirely benign substances – nitrogen (N2) and water vapor (H2O). These end products are harmless and, in fact, naturally occurring components of the Earth’s atmosphere.
The significance of aftertreatment technologies extends beyond mere compliance with emission regulations. They are instrumental in improving air quality, particularly in densely populated urban areas where vehicular emissions are a major contributor to smog and health issues. By implementing aftertreatment systems, diesel engines have undergone a remarkable transformation, shedding their historical reputation for high emissions and contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Furthermore, the influence of aftertreatment technologies is not confined to diesel engines alone. Many modern gasoline-powered vehicles also incorporate advanced catalytic converters and aftertreatment systems to effectively curb NOx emissions and enhance overall environmental performance.
As stringent emission standards continue to evolve, aftertreatment technologies remain at the forefront of environmental efforts. They exemplify human innovation and dedication to mitigating the impact of internal combustion engines on the environment. In an era of growing environmental consciousness, aftertreatment technologies serve as a testament to our commitment to cleaner air and a healthier planet for generations to come.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Control of Air Pollution from New Motor Vehicles Heavy Duty Engine …

The automotive industry is characterized by a spirit of innovation in emissions control. Lean-burn engines, direct injection, and advanced exhaust gas sensors enable more precise control of emissions, enhancing engine efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
The automotive industry has long been defined by its relentless spirit of innovation, especially when it comes to emissions control. As environmental concerns intensify and regulatory standards become increasingly stringent, engineers and manufacturers have risen to the challenge by developing cutting-edge technologies to address emissions-related issues.
One noteworthy innovation that has transformed the landscape of emissions control is the advent of lean-burn engines. These engines have been meticulously designed to operate with a higher air-to-fuel ratio than conventional engines. By doing so, they can achieve more efficient combustion, which not only boosts fuel efficiency but also reduces the emission of harmful pollutants. Lean-burn engines are pivotal in meeting emission standards while simultaneously minimizing the environmental footprint of vehicles.
Direct injection technology represents another milestone in emissions control. This precision-engineered system allows fuel to be injected directly into the combustion chamber, facilitating a more controlled and efficient combustion process. The result is not only enhanced engine efficiency but also a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions, aligning perfectly with the industry’s commitment to sustainability.
One cannot understate the importance of advanced exhaust gas sensors in the emissions control landscape. These sophisticated sensors play a critical role by continuously monitoring the composition of exhaust gases in real-time. The data they provide is used by the engine management system to make instantaneous adjustments, optimizing the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing for minimal emissions. This level of precision control ensures that vehicles not only comply with stringent emission regulations but also maintain engine efficiency and performance.
In summary, the automotive industry’s dedication to emissions control is a testament to its forward-thinking approach and commitment to environmental responsibility. The development of lean-burn engines, direct injection systems, and advanced exhaust gas sensors represents a collective effort to achieve cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions. As the industry continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking innovations that will further enhance emissions control, reducing the environmental impact of vehicles while delivering efficient and powerful performance. This ongoing commitment to innovation will undoubtedly shape the future of automotive emissions control.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Civil Cases and Settlements | Enforcement | US EPA

Emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies play a pivotal role in mitigating the environmental impact of transportation and industry. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contribute to cleaner air in urban areas, and protect public health.
Emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are the unsung heroes of environmental preservation, acting as transformative forces in mitigating the colossal environmental impact of both transportation and industrial activities. Their multifaceted contributions extend far beyond the reduction of harmful emissions; they are instrumental in fostering a holistic, sustainable, and healthier world for present and future generations.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
One of the most compelling facets of emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies is their role in curtailing greenhouse gas emissions. The reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other potent greenhouse gases is pivotal in the battle against climate change. While these technologies primarily target local pollutants, their global impact is undeniable. By curbing CO2 emissions from internal combustion engines and industrial processes, they play a critical part in helping the world meet its carbon reduction goals and slow down the relentless pace of global warming.
Enhancing Urban Air Quality:
The significance of emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies becomes particularly pronounced in urban areas, where the intersection of traffic congestion and industrial activity often leads to compromised air quality. Harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can accumulate, resulting in smog formation and posing grave health risks to urban populations. These technologies are formidable tools in the arsenal to combat urban air pollution. By reducing NOx emissions and trapping particulate matter, they contribute to cleaner and healthier urban environments.
Protecting Public Health:
Perhaps their most immediate and tangible impact is on public health. Harmful emissions from vehicles and industrial facilities have been linked to a wide array of health issues, including respiratory ailments, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature death. By reducing the release of pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and NOx, emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies serve as protectors of public health, shielding individuals, especially those in vulnerable communities, from the detrimental effects of polluted air.
A Global Shift Toward Sustainability:
In an era where environmental responsibility is not merely a choice but a global imperative, the continuous development and integration of emissions control technologies have become pivotal. Governments, industries, and individuals are increasingly recognizing the urgent need to embrace sustainability and reduce their environmental footprint. These technologies are at the forefront of this global shift, guiding the transformation of transportation and industrial practices toward cleaner and more sustainable alternatives.
The Path Forward:
As the world navigates a complex landscape of environmental challenges, emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies will continue to evolve. Innovations in materials, sensors, and energy-efficient designs will further enhance their effectiveness. Simultaneously, the shift toward electrification, alternative fuels, and sustainable practices will play complementary roles in reducing emissions across various industries.
Conclusion:
Emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are the guardians of a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable world. Their ongoing evolution and integration into our daily lives are not just commendable; they are indispensable. In a world where environmental concerns are paramount, these technologies stand as steadfast sentinels, ensuring that our quest for progress does not come at the cost of the environment and public health. As we tread toward a brighter and more sustainable future, they remain our unwavering allies, steadfastly committed to preserving the delicate balance of our planet and securing a legacy of responsible stewardship for generations to come.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Civil Cases and Settlements | Enforcement | US EPA
Challenges remain in achieving even cleaner emissions while optimizing engine efficiency. As the world shifts toward sustainability, emissions control will continue to evolve, with innovations in materials, sensors, and energy-efficient designs.
The journey toward achieving ever cleaner emissions while simultaneously optimizing engine efficiency is akin to walking a tightrope, requiring a deft balance between environmental responsibility and technological innovation. These dual objectives are not mere aspirations; they represent an urgent necessity as the world pivots decisively towards sustainability.
One of the foremost challenges in this pursuit is the delicate equilibrium between reducing emissions and enhancing engine efficiency. The engineering conundrum lies in finding ways to minimize pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) without compromising the power and performance that engines deliver. It’s akin to crafting a masterpiece, where every brushstroke must be precise to achieve the desired harmony.
The landscape of emissions control is far from static. It is a dynamic realm where continuous innovation is the norm. Engineers are exploring new frontiers in materials, delving into advanced catalysts and filtration materials that can further refine the purification of exhaust gases. Cutting-edge sensors, capable of real-time monitoring and adjustments, are emerging as crucial tools in this endeavor. These sensors enable engines to adapt on the fly, optimizing their performance while keeping emissions in check.
Energy-efficient designs are also at the forefront of this revolution. Hybrid powertrains, electrification, and more efficient combustion processes are just a few examples of how engineers are reimagining the very core of engine technology. These innovations hold the potential to not only minimize emissions but also reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, which is a significant step towards a greener and more sustainable future.
As we move forward in this era of heightened environmental awareness, emissions control systems will continue to evolve and adapt. They are not just technological advancements; they represent a commitment to a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable planet. The challenges may be complex, but they are met with unyielding determination, as we collectively strive to create a world where responsible engineering and environmental consciousness go hand in hand, paving the way for a brighter, cleaner future.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Volkswagen emissions scandal explained – The Guardian

Conclusion
Emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are the unsung heroes in the drive for cleaner air and a more sustainable future. Their continuous development and integration into engine design are pivotal in mitigating the adverse environmental effects of transportation and industry. As the world strives for a greener and healthier planet, these technologies will remain at the forefront of the battle against air pollution and climate change, ensuring that future generations breathe cleaner air and enjoy a more sustainable world.
Emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are indeed the often-overlooked champions in the relentless pursuit of cleaner air and a more sustainable future. Their role extends far beyond mere compliance with regulations; they are essential components of our commitment to environmental well-being.
The continuous development and seamless integration of these technologies into engine design are pivotal in our collective effort to mitigate the adverse environmental effects of transportation and industrial activities. As these systems evolve, they become more sophisticated, efficient, and capable of reducing harmful emissions to unprecedented levels.
In an era where climate change and air pollution are urgent global concerns, emissions control systems and aftertreatment technologies are the vanguards of change. They represent our unwavering dedication to curbing the emission of greenhouse gases and pollutants, leading us toward a future where clean air and a sustainable environment are the norm.
As the world strives for a greener and healthier planet, these technologies will remain steadfastly at the forefront of the battle against air pollution and climate change. They will continue to advance, innovate, and adapt to emerging challenges, ensuring that future generations inherit a world where breathing clean air is not a luxury but a birthright. These unsung heroes are instrumental in shaping a more sustainable, vibrant, and flourishing world for all.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: The Volkswagen emissions scandal explained – The Guardian
More links
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Civil Cases and Settlements by Statute | Enforcement | US EPA
