Introduction
Web3, the next evolutionary stage of the internet, promises a decentralized and user-centric digital landscape. It champions principles of privacy and security as core tenets, aiming to provide individuals with greater control over their data and online interactions. However, as this groundbreaking technology evolves, it raises both hopes and concerns regarding privacy and security. In this article, we will delve into the benefits and concerns associated with privacy and security in the Web3 era.
Web3, the natural evolution of the internet, emerges as a beacon of promise in our digital journey, with its sights set on creating a decentralized and user-centric digital realm. Rooted in principles of privacy and security, Web3 envisions a future where individuals wield unprecedented control over their data and online experiences. Yet, as this groundbreaking technology unfolds, it sparks a complex tapestry of hope and apprehension, revolving around the pivotal issues of privacy and security. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore the profound benefits and pressing concerns that accompany the advent of privacy and security in the Web3 era.
At the heart of Web3’s allure is its commitment to bolstering user privacy. Unlike the Web 2.0 landscape, where tech giants have amassed colossal reservoirs of user data, Web3 promotes a paradigm where individuals own and control their data. This fundamental shift not only safeguards personal information from indiscriminate data mining but also grants users the autonomy to decide how, when, and with whom their data is shared. In a Web3 world, the days of opaque data practices and pervasive surveillance are poised to give way to a more transparent, consent-driven model of data management.
Security, another cornerstone of Web3, underpins the promise of a resilient and tamper-proof digital landscape. By harnessing the cryptographic power of blockchain technology, Web3 ensures that data and transactions are protected from malicious actors and manipulation. Decentralized networks, characterized by their redundancy and resilience, fortify the infrastructure against single points of failure and cyberattacks. Moreover, smart contracts, which automate and enforce agreements, mitigate the risk of fraud and manipulation, further enhancing the overall security landscape.
However, the path to the Web3 utopia is not without its shadows. Privacy concerns arise in tandem with the proliferation of blockchain networks. While individuals gain greater control over their data, the transparency inherent in blockchain also means that certain data, once recorded, cannot be erased. This immutability raises concerns about personal information being permanently exposed on a public ledger.
Moreover, the surge in Web3 applications and platforms brings forth new security challenges. While the technology offers robust security features, it also introduces novel attack vectors that malicious actors may exploit. As the ecosystem evolves, cybersecurity threats will inevitably evolve alongside it, demanding continuous vigilance and innovation to safeguard digital assets and interactions.
In conclusion, Web3 embodies the promise of a decentralized, user-centric digital frontier, championing privacy and security as its foundational pillars. It aspires to empower individuals with unprecedented control over their data and interactions, ushering in an era where transparency and consent govern the digital realm. Yet, in its pursuit of progress, Web3 confronts the dual-edged sword of privacy and security concerns. As we navigate this transformative landscape, we must strike a delicate balance, harnessing the benefits while addressing the challenges, to ensure that the Web3 era truly delivers on its promise of a more private, secure, and user-centric internet.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and …
Web3 places users in the driver’s seat when it comes to their data. It empowers individuals to have complete control over their personal information, deciding how, when, and with whom it is shared.
Web3 heralds a transformative shift in how individuals interact with their own data, empowering them with unprecedented control and sovereignty over their digital identities. This newfound control transcends the traditional model where centralized entities held sway over users’ personal information. In the Web3 paradigm, individuals become the architects of their digital lives, dictating the terms of data usage with precision.
One of the cornerstones of Web3 is the concept of self-sovereign identity. It empowers users to manage their personal information autonomously, granting or revoking access to specific data elements as they see fit. For instance, when interacting with a service or platform, users can selectively share only the data required for that transaction while keeping the rest of their information securely private. This granular control over data sharing not only enhances privacy but also reduces the risk of personal information being exploited or mishandled.
Furthermore, Web3 technologies like decentralized identity (DID) and verifiable credentials enable individuals to cryptographically prove their identity without divulging unnecessary details. This means that when, for instance, proving one’s age for accessing age-restricted content, users can do so without disclosing their birthdate, ensuring that their privacy remains intact.
The concept of data monetization also undergoes a profound transformation in Web3. Rather than having their data commodified and profited upon by centralized platforms, individuals can now choose whether, when, and how to share their data in exchange for value. This shifts the balance of power in the data economy, enabling users to be compensated for the use of their personal information, should they opt to share it. Web3 introduces innovative models where individuals are rewarded for participating in data marketplaces, advertising, or other data-driven activities, creating a more equitable and user-centric digital landscape.
Moreover, the decentralized nature of Web3 ensures that personal data is not stored in centralized silos that are vulnerable to breaches and unauthorized access. Instead, data is often distributed across a network of nodes, and access is controlled through cryptographic keys. This architecture significantly reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches and enhances the security of individuals’ information.
In essence, Web3’s user-centric approach to data places individuals firmly in control of their digital identities. It empowers them to dictate the terms of engagement, reclaiming ownership of their personal information, and demanding transparency and fairness from the digital ecosystem. As Web3 continues to evolve, the idea of data sovereignty and user empowerment will remain central, reshaping the way we interact with technology and ensuring that the digital world aligns more closely with our values and desires.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook Report 2022

With blockchain and cryptographic technologies as its foundation, Web3 offers robust data protection mechanisms. Users can trust that their data is secure and tamper-proof.
The foundation of Web3, built upon blockchain and cryptographic technologies, provides a fortress-like shield against data breaches and tampering. This robust data protection ecosystem instills a newfound sense of trust and confidence in users:
Immutable Data Records: At the core of Web3’s data security is the immutability of blockchain. Once data is recorded, it becomes a permanent part of the blockchain’s history. This means that past records cannot be altered, deleted, or manipulated by any single entity. Every transaction and data entry is timestamped and cryptographically linked to the preceding one, forming an unbroken chain of verifiable information.
Cryptography as the Guardian: Cryptographic techniques in Web3 act as the guardians of data. Information is encrypted, ensuring that only authorized parties possess the keys to decrypt and access it. This encryption extends to communication as well, safeguarding messages, transactions, and sensitive interactions from prying eyes. Even in the event of data breaches, encrypted data remains unreadable and unusable without the decryption keys.
Decentralized Data Control: In Web3, data control is decentralized, with users holding the keys to their own digital kingdoms. This means that individuals can determine who gets access to their data and under what conditions. Rather than relying on centralized platforms, users can interact directly with decentralized applications (DApps) while maintaining control over their personal information.
Tamper-Proof Transactions: Smart contracts, a hallmark of Web3, execute transactions with the precision of a digital notary. These self-executing agreements ensure that predefined conditions are met before executing an action. This tamper-proof functionality eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of fraudulent or erroneous transactions.
User Trust and Confidence: Web3’s data protection mechanisms inspire trust and confidence among users. They know that their data is stored securely on a blockchain, resistant to unauthorized alterations. This trust encourages individuals to embrace digital interactions, engage with decentralized services, and participate in the emerging Web3 ecosystem.
Challenges and Ongoing Innovation: While the data protection foundation of Web3 is robust, it is not without its challenges. Scalability, privacy in public blockchains, and user education are areas that require ongoing innovation and development. As Web3 evolves, so too will its data protection mechanisms, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of digital security.
In conclusion, Web3’s data protection mechanisms, grounded in blockchain and cryptographic technologies, usher in a new era of trust and security in the digital realm. The immutable, encrypted, and decentralized nature of Web3’s data ecosystem empowers users with greater control over their personal information and fosters a climate of trust that underpins the revolutionary changes taking place in the digital world. As Web3 continues to evolve, it will likely set even higher standards for data protection and privacy, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the digital age.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and …

Web3 introduces the concept of selective, permissioned access to data. Users can grant or revoke access to their data as they see fit, ensuring that only trusted parties can view it.
Web3’s emphasis on selective, permissioned access to data represents a significant departure from the Web2 model, where user data often resides in centralized silos controlled by tech giants. This shift empowers individuals with greater control over their personal information and introduces a host of benefits:
Enhanced Data Privacy: Web3 prioritizes user privacy by allowing individuals to determine who can access their data. This control minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized sharing of personal information.
Data Monetization: Users can choose to share their data with trusted parties in exchange for fair compensation, disrupting the traditional model where tech companies profit from user data without adequately compensating individuals.
Reduced Data Harvesting: In Web3, data is not collected and stored by centralized entities without user consent. This reduces the prevalence of pervasive data harvesting practices and promotes a more ethical approach to data usage.
Customized Experiences: By granting selective access to data, users can receive more personalized and relevant online experiences. This ensures that the information shared is used to improve user experiences rather than exploit them.
Data Portability: Web3 facilitates the seamless transfer of data between applications and services, enabling users to maintain control and ownership of their data even as they switch between platforms.
Trust and Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain technology ensures that data access permissions are recorded on an immutable ledger. Users can easily verify who has access to their data, promoting trust in the system.
Reduced Centralization: By shifting control over data from centralized platforms to individuals, Web3 reduces the concentration of power in the hands of a few tech giants, promoting a more decentralized and equitable internet.
Innovative Data Use Cases: The ability to selectively share data opens the door to innovative use cases in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management. Users can securely share health records, financial data, and other sensitive information with authorized parties.
Data Security: The use of blockchain and cryptographic techniques enhances the security of data access. Unauthorized access attempts are more challenging due to the decentralized and tamper-proof nature of the technology.
Challenges and Education: Despite its potential, Web3’s approach to data access requires user education and awareness. Users must understand how to manage data permissions effectively and responsibly.
Regulatory Considerations: Regulatory frameworks for data management in a Web3 environment are still evolving. The industry will need to collaborate with regulators to ensure compliance with data protection and privacy laws.
In conclusion, Web3’s emphasis on user-controlled, permissioned data access heralds a new era of data sovereignty and privacy. By putting individuals in charge of their data, Web3 strives to create a more ethical and equitable digital landscape, where users can enjoy the benefits of technology without compromising their privacy and security. As this paradigm shift continues to evolve, it has the potential to redefine the way data is managed, shared, and valued in the digital age.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What are smart contracts on blockchain? | IBM

Web3 promotes decentralized identity solutions, allowing users to own and manage their digital identities securely. This eliminates the need for central authorities to verify identity, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Web3’s commitment to decentralization extends beyond data management and privacy—it encompasses the very essence of our digital identities. In this new era, Web3 champions decentralized identity solutions, heralding a paradigm shift where users take full ownership and control of their digital personas in a profoundly secure and empowering way.
In a traditional online landscape, verifying one’s identity often involves relying on central authorities, such as government agencies, financial institutions, or tech giants. These entities accumulate vast troves of personal data, wielding immense power over individuals’ online identities. However, this centralized model has proven susceptible to data breaches and misuse, as evidenced by numerous high-profile incidents.
Web3 disrupts this status quo by decentralizing identity management. Here, users become the masters of their digital identities, managing them through secure, blockchain-based protocols. This transformative approach eliminates the need for intermediaries or central authorities to verify identity, fundamentally altering the dynamics of online identification.
One of the key advantages of decentralized identity is the heightened security it offers. In a Web3 context, personal data is not stored in a single, vulnerable database susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access. Instead, it is fragmented, cryptographically secured, and distributed across a decentralized network. This dramatically reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches that can expose sensitive information en masse.
Furthermore, decentralized identity solutions grant individuals granular control over the information they share and with whom they share it. This permission-based approach to data sharing ensures that users only disclose relevant details when necessary, enhancing privacy and minimizing exposure to unnecessary data collection. Users can selectively reveal attributes such as age, address, or proof of qualifications, all without compromising their entire identity.
The applications of decentralized identity extend far beyond traditional online services. They have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and education. Imagine a world where financial transactions can be conducted securely without revealing one’s full identity, or where patients can grant access to specific medical records for diagnosis and treatment, all while retaining control over their health data.
However, like any revolutionary technology, decentralized identity faces its own set of challenges. Interoperability, standards, and widespread adoption are hurdles that must be overcome to ensure seamless integration into our digital lives. Additionally, user education and awareness are essential to empower individuals to manage their identities effectively in this new paradigm.
In conclusion, Web3’s promotion of decentralized identity solutions represents a monumental shift in the way we think about and manage our online personas. By returning control to the hands of users and leveraging blockchain technology, Web3 not only enhances security but also unlocks a world of possibilities for more private, secure, and self-determined digital interactions. As we navigate this transformative landscape, decentralized identity promises to be a cornerstone of a more empowered and privacy-conscious digital future.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Web3: A comprehensive review on background, technologies …
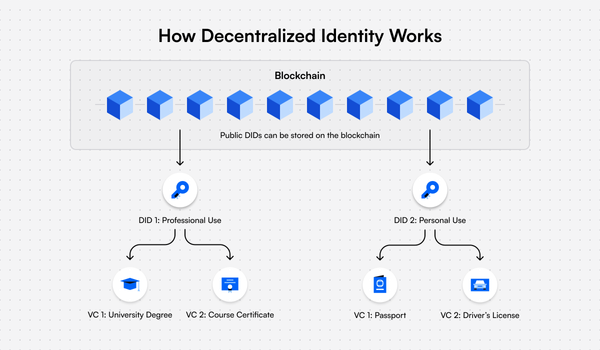
Web3 relies on blockchain technology, known for its immutability. This means that once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus, providing a high level of security.
The immutability of blockchain technology, a foundational pillar of Web3, ushers in a new era of data security and trustworthiness that stands in stark contrast to the mutable nature of traditional databases and centralized systems.
In Web3, blockchain’s immutability is a game-changer for data integrity. When information is recorded on a blockchain, it is cryptographically sealed into an unchangeable and tamper-proof ledger. This means that once a transaction, record, or piece of data is added to the blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of the historical record, indelibly etched in the digital annals. This permanence is crucial for building trust among users and stakeholders because it ensures that data cannot be altered, manipulated, or deleted without the consensus of the network.
The security afforded by blockchain’s immutability is particularly vital in scenarios where data integrity is paramount. For instance, in supply chain management, the provenance of products and goods can be traced with absolute certainty, eliminating the risk of counterfeit goods entering the market. Similarly, in healthcare, patient records and medical histories can be securely stored on a blockchain, safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized changes or breaches.
Moreover, the immutability of blockchain technology is a powerful tool for reducing disputes and fraud. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is easily verifiable by all parties involved. This transparency and auditability significantly reduce the likelihood of disagreements or fraudulent activities, as there is a single, immutable source of truth that all participants can reference.
The concept of smart contracts, prevalent in Web3, further leverages the immutability of blockchain. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions. Once deployed on a blockchain, they autonomously execute actions when specified conditions are met. This automation, combined with the immutability of the underlying blockchain, ensures that smart contracts operate exactly as programmed, free from human error or tampering. This makes them particularly useful in a wide range of applications, from financial services to supply chain management.
However, it’s essential to recognize that while blockchain technology’s immutability is a tremendous asset for data security, it also presents unique challenges. For example, if erroneous data is recorded on a blockchain, correcting it can be a complex and contentious process. Additionally, the right to be forgotten, a fundamental principle of data protection, may clash with blockchain’s immutability, as personal data cannot be easily erased.
In conclusion, Web3’s reliance on blockchain technology and its immutability brings a new level of data security and trust to the digital world. This immutability ensures that once data is recorded on a blockchain, it remains unaltered and tamper-proof, enhancing transparency, reducing disputes, and providing a strong foundation for secure digital interactions across a multitude of sectors and applications.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is Blockchain Technology? – IBM Blockchain | IBM

Smart contracts, self-executing agreements on the blockchain, enable trustless transactions. They eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce the risk of fraud or disputes.
Smart contracts, often regarded as the crown jewels of Web3 technology, represent a seismic shift in how transactions and agreements are executed in the digital realm. Their profound impact extends far beyond trustless transactions and touches upon several critical aspects of decentralized ecosystems:
1. Trustless Efficiency: Smart contracts are the epitome of trustless efficiency. They are self-executing and self-enforcing, which means that once the conditions encoded within the contract are met, the contract automatically executes without the need for intermediaries or manual intervention. This trustlessness ensures that transactions occur as intended, eliminating the risk of fraud or manipulation.
2. Disintermediation: The elimination of intermediaries is one of the most revolutionary aspects of smart contracts. Traditional financial systems, legal processes, and supply chain operations often involve multiple intermediaries, each adding complexity and cost to transactions. Smart contracts cut through this bureaucratic red tape, reducing costs, streamlining processes, and making transactions more efficient.
3. Reduced Risk of Disputes: Smart contracts are unambiguous and deterministic. The terms and conditions of the contract are written in code, leaving no room for interpretation or disputes. This clarity reduces the risk of disagreements between parties and minimizes the need for costly litigation or arbitration.
4. Cost Savings: By removing intermediaries and automating processes, smart contracts deliver significant cost savings. Whether it’s in the financial sector with automated lending and borrowing, in supply chains with automated tracking and payments, or in legal agreements with self-executing contracts, the cost-efficiency gains are substantial.
5. Enhanced Transparency: Smart contracts operate on public or private blockchains, and their execution is recorded on the blockchain for all parties to see. This transparency ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same information, reducing the chances of disputes arising from information asymmetry.
6. Global Accessibility: Smart contracts are not bound by geographic limitations. Anyone with an internet connection and the requisite cryptocurrency tokens can participate in transactions powered by smart contracts. This global accessibility democratizes access to financial services and other transactional opportunities.
7. Programmable Money: Smart contracts extend beyond simple financial transactions. They enable programmable money, where funds can be automatically allocated, invested, or redistributed based on predefined rules. This programmability opens up a world of possibilities for automated financial strategies, crowdfunding, and more.
8. Challenges and Evolution: While smart contracts offer immense potential, they also face challenges such as security vulnerabilities, scalability concerns, and regulatory compliance. Continuous development, audits, and innovation are essential to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of smart contracts.
In summary, smart contracts represent the pinnacle of automation, efficiency, and trustlessness in Web3. Their role extends well beyond transactional efficiency, transforming how agreements are made and executed across industries. As Web3 matures, smart contracts are poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in reshaping traditional business models and processes, leading to a more transparent, efficient, and inclusive digital economy.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Asymmetric Key …

Web3 employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and communication. This ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from malicious actors.
Web3’s commitment to security goes beyond just encrypting data; it leverages advanced cryptographic techniques to establish a robust foundation for securing data and communication across the decentralized web. This approach offers a multitude of advantages that fortify the digital landscape:
End-to-End Encryption: Web3 platforms often employ end-to-end encryption, which ensures that data is encrypted on the sender’s side and only decrypted on the recipient’s side. Even service providers cannot access the unencrypted data, enhancing user privacy.
Data Integrity: Cryptographic hashing techniques are used to verify the integrity of data. This means that any tampering with the data during transmission or storage can be detected, ensuring the authenticity of information.
Immutable Records: Blockchain technology, a cornerstone of Web3, provides an immutable ledger for recording transactions and data. Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered, providing a permanent and tamper-proof record.
Secure Multi-Party Computation: Web3 leverages secure multi-party computation (MPC) to enable parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. This is particularly useful in situations where multiple parties need to collaborate without revealing sensitive data.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Zero-knowledge proofs allow one party to prove to another party that they possess certain information without revealing that information itself. This technique is valuable for authentication and authorization without exposing unnecessary details.
Identity Management: Web3 solutions often incorporate decentralized identity management systems that allow users to have full control over their digital identities while maintaining privacy and security.
Smart Contracts and Privacy: Privacy-focused blockchains and protocols enable confidential smart contracts, ensuring that sensitive contract details remain private while still being executed on a public blockchain.
Secure Communication: In Web3, secure communication channels are established using cryptographic protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) and end-to-end encryption. This ensures that data transmitted between users and applications is protected from interception.
Protection Against Quantum Threats: Web3 is actively exploring post-quantum cryptography techniques to prepare for the potential future threat posed by quantum computers, which could compromise current encryption methods.
Trust and Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain technology allows users to verify the security measures in place. The cryptographic keys and algorithms used are open for inspection, fostering trust in the system’s security.
Challenges in Key Management: While cryptography enhances security, managing cryptographic keys is critical. Web3 platforms are actively addressing key management challenges to ensure that users can securely manage their keys.
Continuous Advancements: Web3’s commitment to security involves ongoing research and development of cutting-edge cryptographic techniques to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, Web3’s utilization of advanced cryptographic techniques represents a pivotal advancement in data and communication security. It underpins the vision of a more secure, private, and trustworthy digital ecosystem where individuals have greater control over their data while remaining protected from malicious actors. As Web3 technologies continue to mature, they have the potential to reshape the digital landscape, making it more resilient and secure in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Asymmetric Key …

Decentralized applications (DApps) on Web3 are less susceptible to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks because they are distributed across multiple nodes rather than hosted on centralized servers.
The decentralized applications (DApps) that thrive within the Web3 ecosystem bring not only innovation and autonomy but also robust security features that set them apart from their centralized counterparts. One of the standout advantages is their resilience against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, which have plagued centralized systems for years.
In a traditional, centralized infrastructure, DDoS attacks target a single point of failure—the central server. Attackers flood the server with an overwhelming volume of requests, effectively rendering it unable to respond to legitimate user requests. The consequences of such attacks can be catastrophic, leading to downtime, data breaches, and financial losses.
Web3’s DApps, on the other hand, are distributed across a network of nodes, each running a copy of the application or contributing to its functionality. This decentralized architecture fundamentally alters the DDoS landscape. Instead of targeting a single server, attackers would need to simultaneously overwhelm a multitude of nodes distributed across the network.
The distributed nature of DApps introduces several layers of defense against DDoS attacks:
Redundancy: DApps are designed to function even if some nodes in the network go offline. This redundancy means that an attack on one node may disrupt that specific node, but it won’t cripple the entire application. Users can continue to interact with the DApp through other available nodes.
Geographic Distribution: DApp nodes are often located in different geographic regions. This geographical diversity complicates DDoS attacks, as attackers would need to coordinate attacks across multiple locations, each with its unique infrastructure and security measures.
Consensus Mechanisms: Many DApps operate on blockchain networks, which employ consensus mechanisms like proof of work (PoW) or proof of stake (PoS). These mechanisms require participants (nodes) to perform work or stake assets to validate transactions. This deters malicious actors from easily launching DDoS attacks, as they would need to control a significant portion of the network’s resources.
Scaling Solutions: DApps often incorporate scaling solutions like sharding or layer 2 solutions to enhance performance and throughput. These scaling solutions can distribute the workload and mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks by reducing the concentration of activity on a single chain or node.
While DApps demonstrate resilience against DDoS attacks, it’s important to note that they are not entirely immune. Determined attackers may still attempt to disrupt DApps by targeting vulnerable nodes or employing new tactics. However, the distributed nature of Web3 and DApps significantly raises the bar for would-be attackers, making successful DDoS attacks less frequent and less impactful.
In conclusion, DApps within the Web3 ecosystem present a formidable defense against DDoS attacks due to their decentralized, distributed nature. This resilience not only enhances the availability and reliability of these applications but also bolsters the security of the broader Web3 ecosystem. As Web3 continues to evolve, it promises to set new standards for security and resilience in the digital world, paving the way for a more robust and reliable internet.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: What is Anycast? | How does Anycast work? | Cloudflare

While Web3 grants users greater control, it also places more responsibility on them. Users must safeguard their private keys and make informed decisions about data sharing.
The empowerment that Web3 offers users comes hand in hand with increased responsibility—a paradigm shift that places individuals firmly in control of their digital lives. As users gain greater autonomy over their data and digital assets, they must proactively take steps to protect their interests and make informed choices in the digital realm.
One of the primary responsibilities in Web3 is the safeguarding of private keys. Private keys are the cryptographic keys that grant access to one’s digital assets and identity on the blockchain. With this power, users become their own custodians, responsible for securing these keys against loss, theft, or compromise. This critical shift in ownership places the onus on individuals to adopt robust security practices. Hardware wallets, strong passwords, and secure backup procedures become essential tools for protecting digital wealth and personal information.
Furthermore, Web3 demands a heightened awareness of data sharing and privacy. While users gain control over how and when they share their data, they must also navigate the complexities of consent, permissions, and trust. This responsibility extends to understanding how their data is used, who has access to it, and the implications of sharing it with various services and platforms. In Web3, users are not passive subjects but active participants in shaping their digital footprint, requiring a more sophisticated understanding of digital literacy and data ethics.
The decentralized and open nature of Web3 also calls for users to exercise due diligence when engaging with decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Unlike traditional centralized applications, dApps often operate in a trustless environment, relying on code and algorithms rather than intermediaries. While this introduces efficiency and transparency, it also exposes users to the risks of vulnerabilities or bugs in smart contracts. Users must be cautious when interacting with new dApps, conduct audits, and ensure they understand the potential risks before participating.
Web3’s responsibility-driven model extends to the realm of financial management. In a decentralized financial ecosystem, users are their own financial custodians. They must manage their assets, participate in governance decisions, and be vigilant against scams and fraudulent schemes. This requires a level of financial literacy and awareness that goes beyond traditional banking, as well as the ability to evaluate risks and rewards in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Despite the increased responsibilities, Web3 offers tools and resources to empower users in fulfilling these roles. Decentralized identity solutions, secure wallets, and educational resources are all part of the Web3 toolkit that helps users navigate this new paradigm. Additionally, Web3 communities often place a strong emphasis on knowledge sharing, peer support, and collaboration, fostering a culture of collective responsibility.
In conclusion, Web3’s shift towards user empowerment is accompanied by a parallel increase in individual responsibility. Users must proactively safeguard their private keys, make informed decisions about data sharing, and exercise caution in their interactions with decentralized applications and financial systems. While this new model may seem demanding, it ultimately leads to a more equitable, secure, and user-centric digital ecosystem where individuals have agency and control over their digital destinies.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Top metaverse cybersecurity challenges: How to address them …

The decentralized nature of Web3 complicates regulatory oversight. Striking a balance between privacy, security, and compliance with existing laws is a challenge.
The decentralized nature of Web3, while offering unparalleled advantages in terms of privacy and security, presents a complex landscape for regulatory oversight. This complexity arises from the unique features and architecture of Web3, and striking a balance between the core principles of Web3, regulatory compliance, and security is indeed a formidable challenge.
1. Regulatory Adaptation: Traditional regulatory frameworks were designed for centralized systems and intermediaries. The decentralized nature of Web3 challenges these frameworks, as it often lacks central authorities or intermediaries to hold accountable. Regulators are faced with the task of adapting existing regulations or crafting new ones that can effectively govern decentralized ecosystems.
2. Data Privacy and Ownership: Web3 empowers individuals to have full control over their data, including personal and financial information. While this enhances privacy, it also makes data less accessible for regulatory purposes, such as combating financial crimes or ensuring consumer protection. Striking a balance between data privacy and regulatory requirements is a delicate task.
3. Cross-Border Complexity: Web3 operates on a global scale, transcending national borders. Regulatory challenges multiply when transactions and activities involve multiple jurisdictions. Coordinating international regulations to address cross-border issues becomes paramount.
4. Anonymity and Pseudonymity: Many Web3 users operate under pseudonyms or anonymously, which can hinder efforts to verify identities for regulatory purposes, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements. Regulators must devise mechanisms that uphold privacy while still enabling the necessary level of identity verification.
5. Smart Contracts and Legal Recognition: Legal systems are designed to interpret and enforce human-readable contracts. Smart contracts, being self-executing and code-based, challenge the legal system’s ability to interpret and enforce them. Achieving legal recognition and enforceability for smart contracts while ensuring fairness and compliance is a novel challenge.
6. Regulatory Arbitrage: The decentralized nature of Web3 can lead to regulatory arbitrage, where entities seek out jurisdictions with lenient or favorable regulations. Regulators need to address these incentives for entities to “forum shop” for more accommodating regulatory environments.
7. Technological Innovation Outpacing Regulation: The rapid pace of technological innovation in Web3 often outpaces the ability of regulators to keep up. New DeFi protocols, token offerings, and emerging use cases constantly challenge regulatory frameworks. Regulators need to adopt a flexible and adaptive approach to address emerging technologies and practices.
8. Collaborative Solutions: Achieving a balance between privacy, security, and regulatory compliance requires collaboration among stakeholders. This includes regulators, blockchain developers, industry participants, and privacy advocates. An open dialogue and cooperative efforts can lead to more effective regulatory solutions.
In conclusion, the decentralized nature of Web3 introduces a myriad of challenges for regulatory oversight. Striking a balance between the core principles of Web3, such as privacy and security, and regulatory compliance is a complex and ongoing endeavor. As Web3 continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks will need to evolve in tandem, embracing innovative approaches that maintain trust, protect users, and foster responsible innovation in the decentralized digital landscape. Finding this equilibrium is essential for the continued growth and adoption of Web3 technologies.
You can also read more about this here: The ethics of artificial intelligence: Issues and initiatives

Ensuring both privacy and scalability in Web3 can be a delicate balance. As the technology evolves, maintaining privacy features without sacrificing performance is a significant challenge.
Balancing privacy and scalability in the context of Web3 is a complex and dynamic challenge that requires continuous innovation and careful consideration of trade-offs. Striking the right equilibrium between these two critical aspects is essential to ensure the long-term success and adoption of Web3 technologies:
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Web3 leverages advanced cryptographic techniques, such as zero-knowledge proofs, ring signatures, and homomorphic encryption, to enhance privacy without compromising scalability. These techniques enable confidential transactions and data sharing while maintaining efficient network performance.
Layer-2 Solutions: Layer-2 solutions, built on top of blockchain networks, aim to improve scalability without sacrificing privacy. Techniques like state channels and sidechains allow many transactions to be processed off-chain, reducing congestion and latency while preserving the privacy of on-chain data.
Sharding: Sharding is a scalability technique that divides blockchain networks into smaller, interconnected parts or “shards.” Each shard processes a portion of transactions, improving overall network throughput. Ensuring that data privacy is maintained across shards remains a challenge.
Blockchain Interoperability: Web3 projects are working on interoperability solutions to connect different blockchains and networks. This not only enhances scalability but also enables privacy features to be preserved across interconnected ecosystems.
Privacy by Default: Some Web3 platforms prioritize privacy by default, ensuring that user data remains confidential without requiring additional configurations. This approach simplifies privacy for users while maintaining a scalable architecture.
Trade-offs and Customization: Web3 acknowledges that there are trade-offs between privacy and scalability. Users and organizations may need to customize their solutions based on their specific requirements, finding the right balance for their use cases.
Layered Architecture: Some Web3 platforms adopt a layered architecture, separating the core blockchain layer from application-specific layers. This separation allows for greater flexibility in implementing privacy solutions while optimizing scalability at each layer.
Research and Development: Web3’s commitment to privacy and scalability involves ongoing research and development efforts. Innovations in consensus algorithms, data compression techniques, and state management are continuously explored to enhance both aspects.
User Education: Educating users about the implications of privacy and scalability choices is essential. Users should understand the trade-offs and be empowered to make informed decisions regarding their data and interactions in the Web3 ecosystem.
Regulatory Considerations: Balancing privacy with regulatory compliance is a complex challenge. Web3 projects must work with regulators to develop frameworks that accommodate privacy-preserving technologies while addressing concerns related to illegal activities.
In summary, ensuring both privacy and scalability in Web3 is an intricate dance that requires careful coordination of technological advancements, user preferences, and regulatory considerations. As the technology matures, innovative solutions and a better understanding of the nuanced trade-offs between these two pillars will pave the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and private digital future. Successfully striking this balance will be pivotal in realizing the full potential of Web3 and its transformative impact on various industries and sectors.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: The Power of Web 3: Benefits, Challenges, and Opportunities

New security threats specific to Web3 may emerge as the technology gains prominence. Vigilance and adaptive security measures will be crucial.
As Web3 continues its ascent into the mainstream, it’s important to recognize that along with its immense potential come unique and evolving security challenges. This dynamic digital landscape is not immune to the emergence of new security threats, some of which may be unprecedented. To navigate this brave new world of technology effectively, vigilance and adaptive security measures will be absolutely crucial.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts, a cornerstone of Web3, are not immune to coding errors or vulnerabilities. Flaws in smart contracts can be exploited, leading to financial losses and other adverse consequences. Continuous auditing and testing of smart contracts, along with the development of more secure coding practices, will be essential to mitigate this risk.
DeFi Risks: The rapid growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) in Web3 has introduced novel security challenges. From flash loan attacks to vulnerabilities in decentralized exchanges (DEXs), DeFi platforms are prime targets for malicious actors. Comprehensive security audits, robust risk management strategies, and decentralized insurance solutions are necessary to protect users and their assets.
Oracles and Data Manipulation: Web3 applications often rely on external data sources known as oracles to make decisions. Manipulation of these oracles can lead to fraudulent activities, like price manipulation in decentralized markets. Implementing secure oracle solutions and mechanisms to verify data integrity is critical.
Phishing and Social Engineering: Malicious actors may employ sophisticated phishing and social engineering tactics to deceive users and gain access to their private keys or credentials. User education and awareness campaigns, coupled with secure identity management solutions, can help combat these threats.
Governance Attacks: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are at the heart of Web3’s governance structure. Attackers may attempt to manipulate DAO voting processes or decisions. Robust governance mechanisms, multi-signature wallets, and well-defined dispute resolution processes are essential safeguards.
Interoperability Challenges: As Web3 incorporates various blockchains and protocols, interoperability becomes a security concern. Vulnerabilities in one blockchain can potentially affect connected systems. Ensuring secure cross-chain interactions and fostering cooperation between different blockchain communities will be key.
Legal and Regulatory Risks: The evolving legal and regulatory landscape surrounding Web3 can present compliance risks for projects and users. Staying informed about changing regulations and implementing compliance measures is essential to avoid legal pitfalls.
Scalability and Network Congestion: As Web3 networks grow, they may face scalability issues and network congestion, which can create opportunities for attacks like front-running. Implementing solutions to enhance network scalability and prevent congestion-related vulnerabilities will be crucial.
In this ever-evolving Web3 landscape, security must be a top priority. Organizations, developers, and users alike must remain vigilant, actively seeking out and addressing security threats as they emerge. This proactive approach, coupled with ongoing education and collaboration within the Web3 community, will be the cornerstone of a secure and resilient digital future. As the saying goes, “Trust, but verify.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: FACT SHEET: White House Releases First-Ever Comprehensive …

Conclusion
Web3 holds immense promise for advancing privacy and security on the internet. Its focus on user control, data protection, and cryptographic security represents a significant leap forward. However, addressing the associated concerns, such as user responsibility and regulatory compliance, will be essential for realizing the full potential of Web3 while maintaining a safe and secure digital environment. As Web3 continues to evolve, striking the right balance between innovation and safeguarding individual rights will be an ongoing endeavor, shaping the future of privacy and security in the digital age.
Web3 represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of the internet, with the potential to usher in a new era of privacy and security. Its core principles of user empowerment, data protection, and cryptographic security offer a compelling vision for a safer and more private digital landscape. However, navigating the challenges and considerations associated with this transformation is critical to ensuring that Web3 reaches its full potential while maintaining a secure and responsible environment.
One of the central promises of Web3 is putting users in the driver’s seat when it comes to their data. This not only safeguards personal information but also minimizes the risk of massive data breaches and unauthorized access. By giving individuals control over what they share and with whom, Web3 significantly reduces the attack surface for malicious actors seeking to exploit centralized data repositories.
Furthermore, the cryptographic security measures inherent in Web3, such as the use of public and private keys, provide robust protection against data tampering and unauthorized access. These mechanisms ensure that data remains confidential and unaltered, bolstering trust among users and fostering a heightened sense of digital security.
However, the transformative potential of Web3 also presents a set of challenges. User responsibility is paramount, as individuals must adapt to new security practices and actively protect their digital assets and identities. This responsibility entails secure key management, privacy-aware data sharing, and a broader understanding of digital literacy and cybersecurity. Educational efforts and user-friendly tools will play a crucial role in helping users meet these newfound obligations.
Another challenge lies in regulatory compliance. As Web3 continues to disrupt traditional models of governance and data handling, it may clash with existing legal frameworks and regulatory expectations. Striking a balance between innovation and compliance is vital to ensure that Web3 projects and technologies can operate within the boundaries of the law while pushing the envelope of what is possible in the digital realm.
Moreover, concerns related to identity verification, fraud prevention, and dispute resolution in a decentralized environment need to be addressed. Innovations like decentralized identity systems and smart contracts are emerging to provide solutions, but their widespread adoption and standardization are ongoing endeavors.
As Web3 continues to evolve, it will be essential to maintain a collaborative and multi-stakeholder approach. This includes active engagement from technology developers, policymakers, industry leaders, and civil society to collectively address the challenges and opportunities that Web3 presents. It’s a delicate balancing act, one that involves harnessing the potential of decentralized technologies while safeguarding individual rights and societal interests.
In conclusion, Web3 offers a promising vision of enhanced privacy and security on the internet. Its user-centric approach and cryptographic underpinnings have the potential to revolutionize digital interactions. However, realizing this vision requires addressing associated concerns such as user responsibility, regulatory compliance, and identity management. The ongoing collaboration of various stakeholders will be key in shaping a future where Web3 can thrive, offering both innovation and robust safeguards for individuals in the digital age.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Impact of digital surge during Covid-19 pandemic: A viewpoint on …
More links
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here The Power of Web 3: Benefits, Challenges, and Opportunities
