Introduction
The advent of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of innovation and disruption across a multitude of industries. Web3 applications, powered by blockchain and decentralized technologies, are reshaping traditional business models, processes, and systems. In this article, we explore how blockchain is transforming various industries, unlocking new possibilities and driving efficiency, transparency, and security.
The impact of blockchain technology on industries cannot be overstated; it’s a catalyst for transformative change. Let’s delve deeper into how this innovation is revolutionizing diverse sectors:
**1. Finance and Banking: The financial sector is witnessing a seismic shift with blockchain at its core. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are challenging traditional banks by offering services like lending, borrowing, and trading with greater accessibility and transparency. Cross-border transactions that used to take days can now be completed within minutes, thanks to blockchain’s borderless nature.
**2. Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains. Companies can track the journey of products from manufacturer to consumer, reducing fraud, ensuring product authenticity, and promoting ethical sourcing. This technology is invaluable for industries like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods.
**3. Healthcare: Patient records, clinical trials, and pharmaceutical supply chains are all benefiting from blockchain’s secure and immutable data storage. Patients have greater control over their health data, and healthcare providers can access accurate patient histories efficiently.
**4. Real Estate: Property transactions often involve cumbersome paperwork and intermediaries. Blockchain simplifies this process by recording property records and transactions on a secure and transparent ledger. Smart contracts can automatically execute transactions when conditions are met, reducing fraud and speeding up property transfers.
**5. Entertainment and Media: Artists and content creators are using blockchain to protect their intellectual property and receive fair compensation for their work. NFTs, representing unique digital assets, are revolutionizing the way we think about digital art, music, and collectibles.
**6. Energy: Blockchain is streamlining energy trading and management by enabling peer-to-peer energy exchanges. Producers can sell excess energy directly to consumers, reducing waste and promoting renewable energy adoption.
**7. Education: Blockchain is verifying academic credentials, eliminating the need for time-consuming verification processes. It ensures that degrees and certificates are tamper-proof and easily accessible for employers.
**8. Government: Blockchain can enhance the transparency and security of government processes, including voting systems, identity verification, and public records. It reduces the risk of fraud and enhances citizen trust in government operations.
**9. Legal: Smart contracts are automating legal agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries in contract execution. This streamlines legal processes, decreases costs, and ensures that agreements are executed as intended.
**10. Transportation: From self-executing insurance policies for autonomous vehicles to secure and transparent shipping logistics, blockchain is optimizing the transportation industry.
**11. Agriculture: Farmers are using blockchain to track the provenance of crops, ensuring food safety and traceability from the field to the table.
**12. Artificial Intelligence: Blockchain is being integrated with AI algorithms to enhance the transparency and fairness of AI decision-making processes.
**13. Social Impact: Blockchain is supporting social impact initiatives by enabling transparent and accountable charitable donations, identity solutions for refugees, and secure land rights for marginalized communities.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is the cornerstone of Web3’s disruptive potential, providing industries with the tools they need to reimagine traditional processes and systems. Its impact extends far beyond finance, reaching into almost every sector, where it enhances efficiency, transparency, and security while unlocking new possibilities for innovation and collaboration. As blockchain continues to evolve, it promises a future where industries operate with greater integrity and inclusivity.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi applications have democratized finance by enabling users to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest on their assets without intermediaries. DeFi protocols, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending platforms, offer financial services to a global audience.
DeFi, short for Decentralized Finance, stands as a groundbreaking and transformative force in the world of finance. It has ushered in a new era where traditional financial intermediaries are challenged, if not replaced, by trustless, blockchain-based protocols. The essence of DeFi lies in its profound ability to democratize finance, empowering individuals from all corners of the globe to access a broad spectrum of financial services without the need for intermediaries.
At the heart of DeFi’s democratization is the removal of barriers that have traditionally restricted access to financial services. Traditional banks and financial institutions have historically imposed geographical, financial, and regulatory limitations, leaving many unbanked or underbanked. DeFi protocols, built on open and permissionless blockchains, extend their services across borders, welcoming anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet.
Borrowing and lending, for instance, become borderless activities in the DeFi realm. Users can lend their digital assets to a global pool, earning interest without the constraints of geographical restrictions or banking hours. Similarly, borrowers can access funds directly from these decentralized lending platforms, often without the need for collateral traditionally demanded by banks.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) exemplify another facet of DeFi’s democratization. They enable users to trade digital assets directly with peers, without the intervention of intermediaries like traditional stock exchanges or brokerage firms. This peer-to-peer trading model affords users greater control over their assets, reduces fees, and minimizes the risk of third-party interference.
Additionally, DeFi’s embrace of blockchain technology and smart contracts ensures transparency and trust. Users can verify transaction histories and explore the underlying code of DeFi protocols, fostering a sense of security and accountability that was previously elusive in traditional finance.
Furthermore, yield farming and liquidity provision have opened up new avenues for individuals to earn income from their crypto assets. Users can provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges or participate in yield farming strategies to generate returns on their holdings. These opportunities democratize the concept of earning passive income from one’s assets, allowing anyone to participate in the DeFi ecosystem.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that DeFi is not without its challenges. The space is characterized by high volatility, smart contract vulnerabilities, and regulatory uncertainties. Users must exercise caution, conduct thorough research, and practice responsible financial management when participating in DeFi activities.
In conclusion, DeFi’s democratization of finance is a testament to the transformative potential of blockchain technology and decentralized systems. By removing geographical barriers, reducing reliance on intermediaries, and promoting financial inclusivity, DeFi is reshaping the landscape of finance and empowering individuals worldwide to take greater control of their financial destinies. As DeFi continues to evolve, it holds the promise of a more equitable, accessible, and user-centric financial future.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey

Cross-Border Payments
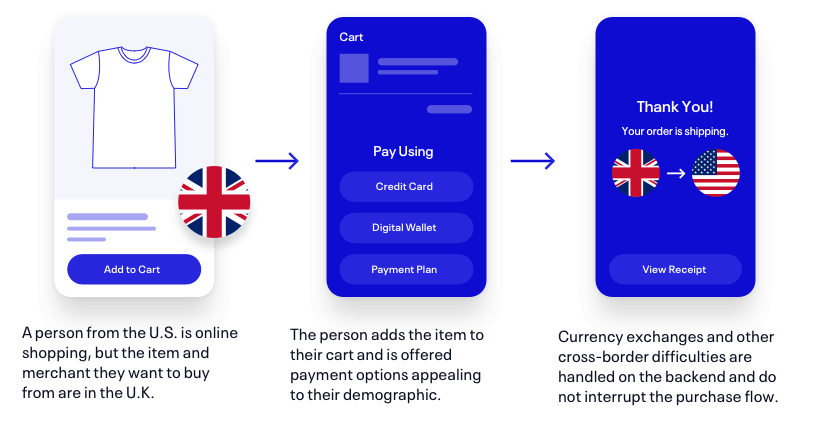
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize cross-border payments, reducing fees and transaction times. Stablecoins, like USDC and USDT, are increasingly used as digital currencies for international transactions.
Blockchain technology stands at the forefront of a financial revolution, promising to transform the landscape of cross-border payments in profound ways. Here’s a deeper look into how blockchain’s potential can be harnessed to revolutionize international transactions:
Reduced Fees and Transaction Times: Traditional cross-border payments are notorious for their inefficiency, high fees, and lengthy processing times. Blockchain technology, powered by cryptocurrencies or stablecoins, offers a streamlined alternative. With blockchain, transactions occur directly between parties on a global network, eliminating the need for multiple intermediaries. This significantly reduces associated fees and accelerates transaction processing, making cross-border payments more cost-effective and efficient.
24/7 Accessibility: Blockchain networks operate 24/7, without the limitations of banking hours or holidays. This round-the-clock accessibility is especially advantageous for international transactions involving different time zones. Users can initiate payments at their convenience, without being constrained by banking schedules, ensuring uninterrupted global trade and financial interactions.
Borderless Nature: Blockchain transcends geographic borders and regulatory jurisdictions. This borderless characteristic facilitates international transactions without the complexities of navigating various banking systems and regulations. Users can send and receive funds across the globe without worrying about currency conversion issues or intermediary banks.
Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security features provide a robust shield against fraud and cyberattacks. Transactions are recorded on a tamper-resistant ledger, ensuring the integrity and transparency of the payment process. This reduces the risk of fraudulent activities often associated with traditional cross-border payments.
Stablecoins for Stability: Stablecoins, such as USDC (USD Coin) and USDT (Tether), have emerged as a bridge between the crypto and traditional financial worlds. These digital currencies are pegged to stable assets like the US dollar, providing price stability while retaining the benefits of blockchain technology. As a result, stablecoins are increasingly adopted for international transactions, offering a reliable store of value and means of exchange.
Financial Inclusion: Blockchain-powered cross-border payments can enhance financial inclusion on a global scale. Individuals in underserved or unbanked regions can access digital wallets and participate in the global economy. This opens up opportunities for businesses and individuals to engage in international trade and remittances, promoting economic growth and reducing financial disparities.
Smart Contracts: Some blockchain platforms, like Ethereum, support smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce predefined conditions when met. Smart contracts can be used to facilitate complex international transactions, ensuring that parties’ obligations are met without relying on intermediaries.
Transparency and Traceability: Blockchain’s transparent ledger records all transaction details. This provides participants with a clear audit trail and enhances transparency in cross-border payments. Users can track the status and history of their transactions in real-time, reducing disputes and ensuring accountability.
In summary, blockchain technology, coupled with stablecoins, is poised to revolutionize cross-border payments by offering reduced fees, faster transaction times, and increased accessibility. This transformative potential has the capacity to reshape global finance, making international transactions more efficient, cost-effective, and inclusive. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, the benefits of this financial revolution will extend to businesses and individuals worldwide.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Enterprise blockchain is transforming business operations and …
Provenance and Traceability
Blockchain allows for end-to-end traceability of products and goods. Supply chain participants can record and verify every step in a product’s journey, enhancing transparency and trust.
The application of blockchain technology in supply chain management goes beyond mere record-keeping; it fundamentally revolutionizes how businesses and consumers perceive and interact with the supply chain. Here’s a deeper exploration of how blockchain enhances transparency and trust in supply chains:
**1. Immutable Records:
Data Integrity: Blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a record is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from network participants. This guarantees the integrity of data, eliminating the risk of fraudulent entries or tampering.
Tamper-Resistant Provenance: Provenance, or the origin of products, can be reliably traced back to their source. This means that consumers can confidently verify the authenticity of products, whether it’s a luxury handbag, organic produce, or a pharmaceutical drug.
**2. Real-Time Visibility:
Streamlined Data Sharing: Supply chain participants, including manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and consumers, can access real-time data from a shared blockchain ledger. This reduces delays, improves decision-making, and enhances coordination across the supply chain.
Reduced Discrepancies: Discrepancies and disputes in supply chain transactions are minimized as all parties have access to a single source of truth. This leads to fewer conflicts and quicker resolutions.
**3. Enhanced Trust and Accountability:
Supplier Accountability: Blockchain incentivizes suppliers to maintain high-quality standards. If a subpar product is detected downstream, the blockchain record can quickly identify the responsible party, encouraging accountability.
Ethical Sourcing: Blockchain can be used to track the ethical sourcing of materials, ensuring compliance with fair trade practices and sustainability standards. Consumers can make informed choices that align with their values.
**4. Smart Contracts for Automation:
Automated Workflows: Smart contracts on blockchain can automate various aspects of the supply chain, such as triggering payments upon delivery confirmation or initiating quality inspections. This reduces manual intervention and streamlines operations.
Efficient Compliance: Smart contracts can enforce compliance with predefined rules and regulations, ensuring that products meet safety and quality standards throughout the supply chain.
**5. Cost Reduction and Efficiency:
Faster Settlements: Blockchain-enabled supply chains streamline payment processes, reducing the time it takes for suppliers to receive payments. This is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Inventory Management: Real-time data on the blockchain helps optimize inventory management, minimizing excess stock and reducing storage costs.
**6. Customer Empowerment:
Consumer Transparency: Consumers can scan QR codes or use mobile apps to access detailed product information, including its journey from creation to the shelf. This empowers them to make informed choices and support products that align with their values.
Product Authentication: Blockchain’s ability to verify product authenticity helps consumers avoid counterfeit goods, boosting trust in brands and ensuring safety.
In essence, blockchain’s impact on supply chains transcends mere traceability; it redefines how stakeholders interact and collaborate within the supply chain ecosystem. By promoting transparency, trust, and accountability, blockchain not only safeguards product quality but also reshapes the entire supply chain landscape, making it more efficient, ethical, and responsive to consumer demands.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) | IBM

Counterfeit Prevention
Blockchain helps prevent counterfeiting by providing immutable records of product authenticity. Consumers can verify the origin and authenticity of products through QR codes or apps.
Blockchain’s role in combating counterfeiting extends well beyond its ability to maintain immutable records. Here’s a deeper look at how this technology is transforming the fight against counterfeit goods:
**1. Immutable Product Provenance: Every step in a product’s journey, from its creation to its final destination, can be recorded on a blockchain. These records are tamper-proof and transparent. Consumers and businesses can trace the entire history of a product, verifying its authenticity and confirming its origin with confidence. This level of transparency is invaluable for high-value items like luxury goods and pharmaceuticals.
**2. Anti-Counterfeiting QR Codes: QR codes on product packaging, when scanned, can reveal detailed information stored on a blockchain. Consumers can verify the product’s authenticity and access information about its production, including dates, locations, and quality control checks. This empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions.
**3. Supply Chain Verification: Blockchain ensures the integrity of supply chains. Companies can use this technology to track the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products. Any irregularities or unauthorized changes in the supply chain are immediately flagged, reducing the risk of counterfeit products entering the market.
**4. Smart Contracts and Digital Twins: Smart contracts, self-executing agreements on the blockchain, can be linked to physical products. These contracts can automatically trigger actions, such as verifying a product’s authenticity before it reaches a consumer. Digital twins—digital replicas of physical products—can also be linked to blockchain records, further enhancing security.
**5. Consumer Empowerment: Blockchain gives consumers a direct means to verify product authenticity. Mobile apps and websites can connect to blockchain databases, providing real-time information about a product’s history and authenticity. Consumers become active participants in the fight against counterfeiting.
**6. Trust and Brand Reputation: Companies that adopt blockchain for product authentication demonstrate their commitment to transparency and quality. This builds trust with consumers, strengthens brand reputation, and can even serve as a competitive advantage in the market.
**7. Customs and Border Control: Blockchain assists customs and border control authorities in verifying the authenticity of imported goods. It streamlines the inspection process by providing a secure and easily accessible record of a product’s journey.
**8. Intellectual Property Protection: Beyond physical products, blockchain protects intellectual property rights by timestamping and storing copyrighted content on an immutable ledger. This helps creators and artists prove ownership and fight against piracy.
**9. Global Collaboration: Blockchain’s transparency and accessibility transcend borders. Global collaboration is essential in the fight against counterfeiting, and blockchain facilitates information sharing and coordination among stakeholders worldwide.
**10. Data-Driven Insights: By analyzing blockchain data, businesses gain insights into supply chain efficiency and consumer preferences. This data-driven approach enables companies to make informed decisions to further enhance product authenticity and customer satisfaction.
In summary, blockchain technology is a formidable weapon in the battle against counterfeit goods. Its ability to provide transparent, immutable records of product authenticity, coupled with consumer empowerment through QR codes and apps, is reshaping industries and ensuring that consumers can trust the products they purchase. As blockchain continues to evolve and gain adoption, it promises to be a critical tool in safeguarding authenticity and integrity in the marketplace.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: How Blockchain and AI are Revolutionizing Industries | by Aman …

Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Blockchain secures electronic health records, granting patients control over their medical data while ensuring its integrity. Patients can securely share their data with healthcare providers.
The intersection of blockchain technology and healthcare heralds a paradigm shift in the management and security of electronic health records (EHRs). In this new landscape, blockchain emerges as a formidable guardian of sensitive medical data, offering patients unprecedented control and confidence in the integrity of their health information.
One of the most salient advantages of employing blockchain in healthcare is the enhanced security it affords to EHRs. Traditional centralized systems have been susceptible to data breaches, exposing patients’ personal health information (PHI) to malicious actors. Blockchain, with its cryptographic underpinnings and decentralized nature, provides a robust defense against such breaches. Patient data is cryptographically sealed within blocks, and each block is linked to the previous one, creating an immutable ledger. This immutability ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without leaving a trace, assuring patients of the integrity of their records.
Furthermore, blockchain empowers patients with unprecedented control over their medical data. Patients are granted private keys that enable them to access and share their EHRs securely. They can choose when, with whom, and for what purpose they share their data, introducing a layer of consent and transparency previously absent in healthcare data management. Patients can confidently provide access to their EHRs to healthcare providers, researchers, or even insurance companies, all while retaining control over their data.
Interoperability is another critical aspect where blockchain shines in healthcare. The healthcare industry has long struggled with the fragmentation of data across disparate systems and providers. Blockchain can act as a common, secure, and standardized platform for storing and sharing EHRs, bridging the gap between different healthcare entities. This facilitates more seamless data exchange, reducing administrative burdens, and ensuring that healthcare providers have access to comprehensive patient information, leading to more informed and timely decision-making.
Moreover, the use of blockchain in healthcare can streamline administrative processes and reduce costs. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions, can automate billing, insurance claims, and other administrative tasks, significantly reducing administrative overhead and the potential for errors.
However, the implementation of blockchain in healthcare also poses challenges. Scalability, privacy concerns, and regulatory compliance are significant considerations. Striking the right balance between data security and accessibility, ensuring data privacy, and navigating the evolving legal and regulatory landscape are ongoing tasks.
In conclusion, blockchain’s integration into healthcare marks a pivotal moment in the industry’s evolution. It offers a secure, transparent, and patient-centric approach to managing electronic health records, giving individuals control over their data and ensuring its integrity. While challenges remain, the potential for blockchain to revolutionize healthcare data management, interoperability, and patient empowerment is undeniable. As the technology continues to mature and healthcare stakeholders collaborate on standards and best practices, the future of healthcare data appears increasingly secure and patient-driven.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Blockchain-Powered Electronic Health Records: Transforming …

Drug Traceability
Blockchain enables the tracking of pharmaceuticals from production to distribution, reducing the risk of counterfeit medications entering the market.
The integration of blockchain technology into the pharmaceutical industry is a monumental step towards ensuring the safety and integrity of medications from their inception to the hands of patients. Let’s delve deeper into how blockchain transforms pharmaceutical supply chains and mitigates the threat of counterfeit drugs:
Immutable Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable ledger records every step of a pharmaceutical product’s journey, from production in the laboratory to distribution through the supply chain. Each transaction is securely timestamped and cryptographically sealed, making it nearly impossible to alter or manipulate. This transparency ensures that all stakeholders can verify the authenticity and provenance of medications with confidence.
Traceability and Accountability: Blockchain’s traceability features enable rapid and precise tracking of pharmaceuticals at every stage. This traceability holds all parties involved in the supply chain accountable for their actions. If a batch of medication is found to be substandard or counterfeit, the blockchain can quickly identify the source, enabling timely interventions to prevent its proliferation.
Anti-Counterfeiting Measures: Counterfeit drugs pose a grave threat to public health, with potentially lethal consequences. Blockchain’s anti-counterfeiting capabilities enable the authentication of pharmaceutical products in real-time. Patients, healthcare providers, and regulators can scan product codes or QR tags to access blockchain-based records and confirm the product’s legitimacy, thereby preventing the consumption of counterfeit or substandard medications.
Enhanced Recall Management: In the unfortunate event of a product recall, blockchain’s efficiency shines. Traditional recall processes can be slow and imprecise, potentially leading to delays in removing unsafe drugs from the market. With blockchain, recalls can be targeted and precise, as the entire history of affected products is readily available. This minimizes disruptions and reduces the risk of further harm to patients.
Supply Chain Efficiency: Blockchain optimizes pharmaceutical supply chain operations. It streamlines documentation, reduces paperwork, and automates compliance with regulatory requirements. This efficiency not only reduces operational costs but also expedites the delivery of life-saving medications to patients, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
Data Privacy and Security: Blockchain ensures the privacy and security of sensitive pharmaceutical data. Patient information, clinical trial results, and proprietary research can be securely stored and shared on blockchain networks with cryptographic safeguards. This protects intellectual property and patient confidentiality, fostering trust in the pharmaceutical ecosystem.
Compliance and Regulatory Oversight: Blockchain facilitates compliance with stringent regulatory standards in the pharmaceutical industry. By maintaining transparent and auditable records, it simplifies the regulatory reporting process and aids in demonstrating compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Good Distribution Practices (GDP), and other industry regulations.
Global Collaboration: The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for global collaboration among pharmaceutical manufacturers, distributors, and regulatory bodies. It promotes interoperability and data sharing while respecting regional and national regulatory nuances. This collaborative approach strengthens the overall pharmaceutical supply chain and enhances its resilience.
In conclusion, blockchain’s impact on the pharmaceutical industry extends far beyond supply chain management. It represents a powerful tool in the ongoing battle against counterfeit drugs, ensuring that patients receive safe and authentic medications. As the pharmaceutical sector continues to embrace blockchain technology, it moves closer to achieving its paramount goal: safeguarding public health and the integrity of medications worldwide.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing Industries and …

Tokenization of Assets
Real estate assets can be tokenized on blockchain, allowing for fractional ownership. This lowers entry barriers for investors and enhances liquidity in the real estate market.
Tokenizing real estate assets on the blockchain marks a significant departure from traditional property ownership and investment practices. It introduces a range of advantages that go beyond fractional ownership and increased liquidity:
**1. Global Accessibility:
Cross-Border Investment: Blockchain tokenization removes geographical barriers, enabling investors from around the world to participate in real estate opportunities without the need for physical proximity or complicated legal processes.
Diverse Portfolios: Investors can easily diversify their portfolios by acquiring tokens representing various real estate assets, spreading risk and maximizing potential returns.
**2. Fractional Ownership Benefits:
Lower Capital Requirements: Fractional ownership means investors can enter the real estate market with smaller capital investments, making it accessible to a broader demographic, including first-time investors.
Liquidity and Dividends: Real estate tokens can be traded on secondary markets, offering liquidity options that traditional real estate investments lack. Additionally, rental income or profits from property sales can be distributed to token holders through smart contracts.
**3. Reduced Intermediaries:
Cost Efficiency: Tokenization minimizes the need for intermediaries like brokers, lawyers, and title companies, reducing transaction costs and administrative overhead.
Speed of Transactions: Real estate transactions conducted through blockchain can be faster and more efficient due to automated processes and reduced paperwork.
**4. Enhanced Transparency:
Immutable Records: Blockchain records every transaction and ownership transfer, creating a transparent and tamper-proof history of the property. This transparency boosts trust among investors and reduces the risk of fraud.
Accessibility of Information: Property details, financial reports, and legal documents can be securely stored on the blockchain, allowing investors to access critical information without reliance on third parties.
**5. Smart Contract Integration:
Automated Governance: Smart contracts can govern token ownership, facilitating decisions related to property management, maintenance, and rental agreements. This automation streamlines decision-making and reduces the potential for disputes.
Leveraging Blockchain Features: Tokenized real estate can take advantage of blockchain’s programmable features to create innovative investment structures, such as automated dividend distributions and governance mechanisms.
**6. Increased Market Efficiency:
Fractional Transactions: Fractional ownership allows for the purchase and sale of small portions of a property. This enables investors to exit their positions more easily and efficiently than selling an entire property.
Market Depth: A larger pool of potential investors can lead to increased market depth and activity, providing more accurate pricing information and reducing the likelihood of market manipulation.
**7. Security and Compliance:
Regulatory Compliance: Tokenized real estate can incorporate regulatory compliance features, ensuring that investors and property owners adhere to legal requirements, such as know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) rules.
Ownership Proofs: Blockchain tokens serve as cryptographic proof of ownership, simplifying the process of verifying property ownership and title history.
In summary, real estate tokenization on the blockchain represents a seismic shift in the way we approach property ownership and investment. It democratizes access to the real estate market, offers newfound liquidity, reduces costs, and enhances transparency. As blockchain technology continues to mature and regulatory frameworks adapt, the tokenization of real estate is poised to become a mainstream investment option, reshaping the real estate industry for the future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The Complete Guide for Asset Tokenization on Blockchain …

Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate property transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries like escrow services and reducing the risk of fraud.
Smart contracts represent a revolutionary leap forward in the world of property transactions and real estate. By harnessing blockchain technology and self-executing code, these digital agreements bring a plethora of benefits to buyers, sellers, and the entire real estate ecosystem.
Efficiency and Speed: Smart contracts operate 24/7, without the constraints of business hours or holidays. This means property transactions can occur at any time, reducing the delays often associated with traditional real estate processes. There’s no need to wait for intermediaries to perform their tasks, and thus, deals can be completed in a matter of minutes rather than weeks.
Cost Reduction: With smart contracts, the need for intermediaries such as real estate agents, escrow services, and even title companies diminishes significantly. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces the associated fees, making property transactions more cost-effective for all parties involved. Moreover, the elimination of physical paperwork and the need for secure storage reduces administrative expenses.
Transparency and Trust: Every step of a property transaction recorded on a blockchain is transparent and immutable. All parties can track and verify the progress of the deal in real-time, eliminating disputes and fostering trust. Property details, ownership history, and legal documents are securely stored and easily accessible, reducing the risk of fraud or disputes over property ownership.
Security: Smart contracts rely on robust cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity of the transaction. Funds and property titles are held securely until predetermined conditions are met, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access. This level of security surpasses traditional paper-based agreements and manual oversight.
Global Accessibility: Smart contracts operate on a decentralized network, which means property transactions are not limited by geographical boundaries. International buyers and sellers can engage in real estate deals with ease, fostering global property markets and opening up new opportunities for investment and diversification.
Fractional Ownership: Smart contracts enable the concept of fractional ownership, where multiple individuals can collectively invest in a property. This opens up real estate investment opportunities to a wider range of people, making it more accessible and affordable.
Automated Compliance: Smart contracts can be programmed to adhere to local, regional, and national regulations automatically. This ensures that property transactions are always in compliance with the law, reducing the risk of legal complications.
Reduced Counterparty Risk: Traditional property transactions often involve counterparty risk, where one party might default on their obligations. Smart contracts mitigate this risk by automatically enforcing the terms of the agreement, releasing funds and property titles only when all conditions are met.
Scalability and Customization: Smart contracts are highly adaptable and can be customized to fit the unique requirements of each property transaction. Whether it’s a residential sale, commercial lease, or even a complex development project, smart contracts can be tailored to suit the specific needs of the parties involved.
In summary, smart contracts are poised to revolutionize property transactions by automating processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, enhancing security and transparency, and ultimately making real estate more accessible and efficient. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to transform the way we buy, sell, and invest in property, ushering in a new era of innovation and opportunity in the real estate industry.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The Ultimate Guide to Web3 – Blockchain Council

NFTs and Digital Ownership
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent ownership of digital assets like art, collectibles, and in-game items. NFTs have created new revenue streams for creators and gamers.
The advent of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has triggered a digital renaissance, fundamentally altering the way we perceive, create, and exchange digital assets. NFTs, as unique, indivisible tokens secured by blockchain technology, have transcended traditional boundaries, giving rise to a profound transformation in various domains, from art and collectibles to gaming and entertainment.
One of the most striking aspects of NFTs is their capacity to confer ownership and provenance to digital assets. In the realm of art, NFTs have unleashed a creative revolution, enabling artists to tokenize their works and authenticate their origin on the blockchain. This digital provenance grants collectors a level of confidence and trust previously reserved for physical art, revolutionizing the art market. Moreover, NFTs have democratized art, allowing emerging artists to gain recognition and monetize their creations without the need for intermediaries or galleries.
Collectibles, too, have found new life in the NFT ecosystem. Whether they are digital trading cards, virtual pets, or digital representations of physical assets, NFT-based collectibles have reinvigorated the concept of ownership and rarity in the digital realm. Collectors can now buy, sell, and trade unique digital items, forming vibrant and decentralized marketplaces around their passions.
The gaming industry, in particular, has witnessed a seismic shift with the advent of NFTs. Gamers can now truly own in-game assets, from skins and weapons to virtual real estate, represented as NFTs. This ownership extends beyond the confines of a single game; players can trade these assets across different gaming universes, creating a metaverse of interconnected digital economies. For gamers, NFTs have unlocked new revenue streams by allowing them to monetize their time and investments in virtual worlds.
Creators, in general, have found in NFTs a novel way to monetize their digital content and creations. Musicians can tokenize their music, authors can tokenize their written works, and even internet memes have been immortalized as NFTs. This enables content creators to receive royalties for their work each time it changes hands in the secondary market, providing ongoing income and recognition for their contributions to the digital landscape.
However, the NFT space is not without its challenges. Issues of environmental sustainability, copyright infringement, and market volatility have emerged as important considerations. The immense energy consumption of some blockchain networks used for NFTs has sparked concerns about their ecological impact. Copyright and intellectual property rights in the digital realm remain complex, with disputes and legal challenges yet to be fully resolved.
In conclusion, NFTs have disrupted traditional notions of ownership, authenticity, and creativity in the digital age. These unique tokens have created new revenue streams for creators and have empowered individuals to take ownership of digital assets. While challenges persist, the transformative potential of NFTs continues to unfold, reshaping industries and opening up unprecedented opportunities for creators and enthusiasts alike in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The Rise Of NFTs: Exploring The Future Of Digital Ownership …
Decentralized Gaming
Blockchain-based games offer players true ownership of in-game assets, allowing them to buy, sell, and trade items across different games.
Blockchain-based games are pioneering a transformative shift in the world of gaming, ushering in an era of true ownership, interoperability, and player-driven economies. Let’s delve deeper into how these games are reshaping the gaming landscape:
Immutable Ownership: In traditional gaming, players invest time and money acquiring in-game assets, such as skins, characters, or items. However, they don’t truly own these assets; they are subject to the rules and limitations set by the game developer. In blockchain-based games, players have immutable ownership of their in-game assets. These assets are represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the blockchain, meaning that players have verifiable and irrevocable ownership rights. This paradigm shift empowers players by granting them control over their digital possessions.
Cross-Game Interoperability: One of the most exciting aspects of blockchain-based games is their ability to facilitate interoperability across different games and platforms. Thanks to standardized protocols like ERC-1155, players can use their NFTs acquired in one game within entirely different gaming universes. For instance, a sword earned in one blockchain RPG can become a weapon in a completely unrelated blockchain strategy game. This interoperability not only adds depth to gameplay but also increases the value of in-game assets.
Player-Driven Economies: Blockchain games introduce player-driven economies, where the in-game assets have real-world value. Players can buy, sell, and trade these assets in decentralized marketplaces, often using cryptocurrencies. This creates opportunities for players to monetize their gaming achievements and earn income by participating in virtual economies. It also fosters player-to-player trading, reducing the need for third-party intermediaries.
Scarcity and Rarity: NFTs in blockchain games introduce the concept of scarcity and rarity to digital assets. Just like physical collectibles or rare trading cards, certain in-game items become highly sought-after due to their limited availability. This scarcity adds a dynamic layer of value and excitement to the gaming experience, as players aim to acquire and trade rare assets.
Player-Centric Game Development: Blockchain games often involve players in the decision-making process through governance tokens or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). This allows players to influence the direction of the game, propose changes, and vote on key decisions. Player feedback and engagement become integral to game development, fostering a sense of community ownership.
Content Creation Opportunities: Blockchain games empower players to become content creators. Players can design and sell custom skins, characters, or levels as NFTs, enabling them to monetize their creativity. This shift from passive consumption to active participation blurs the line between player and developer.
Transparency and Security: Blockchain’s transparency ensures that the scarcity and authenticity of in-game assets are verifiable by anyone. It reduces the risk of counterfeit items or fraudulent transactions. Additionally, blockchain’s cryptographic security protects players from hacks, cheats, and unauthorized modifications.
Ownership Beyond Gaming: Blockchain-based games extend the concept of ownership beyond the gaming world. Players can showcase their NFT collections in virtual galleries, use them in metaverse environments, or even loan them as collateral for financial services in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
In summary, blockchain-based games redefine the gaming experience by granting players true ownership of in-game assets, enabling cross-game interoperability, and fostering player-driven economies. This paradigm shift transforms players from mere consumers into active participants and creators within virtual worlds. As the blockchain gaming ecosystem continues to evolve, its impact on the gaming industry and the broader digital landscape is poised to be nothing short of revolutionary.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: How Web3 Is Transforming The Future Of Business
Energy Trading
Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess renewable energy.
The integration of blockchain technology into the energy sector has the potential to revolutionize how we generate, consume, and trade energy. Peer-to-peer energy trading, made possible by blockchain, offers numerous benefits and opens up exciting possibilities for individuals, businesses, and the environment:
**1. Efficient Resource Utilization:
Optimized Energy Distribution: Peer-to-peer energy trading enables more efficient use of locally generated renewable energy. Excess energy produced by solar panels or wind turbines can be sold directly to nearby consumers, reducing energy waste and grid congestion.
Grid Load Balancing: Blockchain-based systems can dynamically balance energy supply and demand, improving the stability and resilience of the energy grid. This is especially crucial as more renewable energy sources with variable outputs are integrated.
**2. Cost Savings:
Lower Energy Costs: Consumers can access locally generated renewable energy at competitive prices, potentially reducing their energy bills compared to relying solely on centralized utilities.
Avoiding Grid Fees: By trading energy directly with their peers, consumers can circumvent grid fees and other charges imposed by traditional energy providers.
**3. Environmental Impact:
Promoting Renewable Energy: Peer-to-peer energy trading encourages the use of renewable energy sources. It incentivizes individuals and businesses to invest in solar panels, wind turbines, and other clean energy technologies, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: A decentralized energy ecosystem can contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
**4. Empowerment of Producers and Consumers:
Energy Producers: Individuals and businesses that generate excess energy become “prosumers” and can monetize their surplus energy production. This empowers them to take control of their energy generation and distribution.
Consumer Choice: Consumers have the freedom to choose their energy sources, supporting green energy production and promoting sustainability.
**5. Resilience and Reliability:
Grid Independence: Blockchain-based peer-to-peer trading can function independently of the central energy grid. This offers greater resilience in the face of grid failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
Energy Access: Remote or underserved areas can establish microgrids powered by renewable energy sources and engage in energy trading, ensuring access to electricity even in remote locations.
**6. Transparent and Trustworthy Transactions:
Immutable Records: Every energy transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and tamper-proof ledger of all energy trades. This transparency builds trust among participants.
Automated Settlement: Smart contracts on the blockchain automate energy settlements, ensuring that producers are fairly compensated for the energy they provide.
**7. Regulatory Compliance:
- Compliance Frameworks: Blockchain platforms can incorporate regulatory compliance features, ensuring that energy trading adheres to local and national regulations.
**8. Community Building:
- Local Energy Communities: Peer-to-peer energy trading can foster the creation of local energy communities where neighbors collaborate to generate, store, and trade renewable energy. This strengthens community bonds and shared sustainability goals.
**9. Scalability and Future Growth:
Integration of IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) can be integrated with blockchain energy systems to provide real-time data on energy production and consumption, further optimizing energy trading.
Interoperability: Blockchain energy platforms are being designed with interoperability in mind, ensuring compatibility with various energy systems and technologies.
In summary, blockchain-enabled peer-to-peer energy trading is a game-changer in the energy sector. It empowers individuals and businesses to participate actively in the green energy transition, reduces costs, improves grid reliability, and contributes to a more sustainable future. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to reshape the global energy landscape, promoting cleaner and more efficient energy systems.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Accelerating the energy transition with Web3 technologies | Shell …

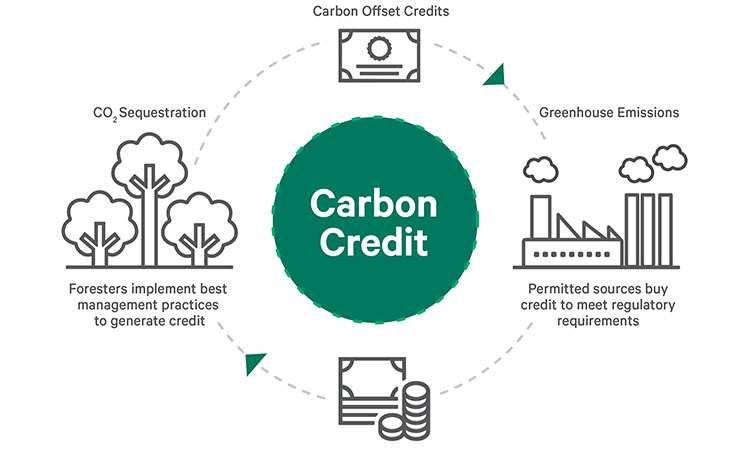
Carbon Credits
Blockchain verifies carbon offset credits, providing transparency and trust in sustainability initiatives.
Blockchain technology has the potential to play a transformative role in the field of carbon offset credits, offering a robust solution to the challenges of verifying and ensuring the legitimacy of sustainability initiatives. Here’s how blockchain enhances transparency and trust in the realm of carbon offset credits:
Immutable Record-Keeping: Blockchain creates a tamper-proof ledger of carbon offset transactions. Each credit issuance, transfer, and retirement is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. This means that once data is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the carbon credit data.
Traceability: Every carbon offset credit can be traced back to its source, such as a renewable energy project or reforestation effort. This traceability allows stakeholders, including individuals, companies, and governments, to verify the origin and authenticity of carbon credits, ensuring that they are genuinely contributing to carbon reduction.
Real-Time Monitoring: IoT (Internet of Things) devices and sensors can be integrated with blockchain to provide real-time data on emissions reductions. This data can be instantly recorded on the blockchain, giving stakeholders immediate access to the performance of sustainability projects and the corresponding carbon credits.
Auditing and Verification: Smart contracts can automate the verification process of carbon offset credits. When predefined conditions are met, such as the reduction of a certain amount of greenhouse gas emissions, the smart contract automatically issues the corresponding carbon credits. This reduces the need for costly and time-consuming third-party audits, making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
Global Accessibility: Blockchain’s decentralized nature allows carbon offset credits to be bought and sold globally, facilitating cross-border transactions. This global marketplace increases the liquidity of carbon credits and encourages wider participation in sustainability initiatives.
Reduced Fraud and Double Spending: Blockchain’s cryptographic security ensures that carbon offset credits cannot be duplicated or fraudulently claimed. This eliminates the risk of double-spending and fraud within the carbon offset market, enhancing the credibility of carbon reduction efforts.
Enhanced Trust: The transparency and security provided by blockchain technology instill trust in consumers, investors, and regulators. They can be confident that the carbon credits they purchase or invest in are legitimate and have a real impact on reducing carbon emissions.
Ecosystem Collaboration: Blockchain networks can facilitate collaboration among various stakeholders in the carbon offset ecosystem, including project developers, certification bodies, and marketplaces. This collaboration streamlines the issuance and trading of carbon credits, making it easier for projects to receive funding and for buyers to invest in sustainable initiatives.
Incentives for Innovation: Blockchain-based carbon offset systems can introduce innovative mechanisms, such as tokenization and decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions, to incentivize sustainable practices. This can create new opportunities for funding and financing sustainability projects.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the carbon offset credit market by bringing transparency, traceability, and trust to sustainability initiatives. As concerns about climate change continue to grow, blockchain’s ability to provide a secure and verifiable infrastructure for carbon credits can drive greater participation in efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey
Credential Verification
Blockchain verifies academic credentials, reducing fraudulent claims on resumes and simplifying the hiring process.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of academic credentials, offering a secure and transparent solution to a longstanding challenge in education and employment. By leveraging blockchain, academic institutions and employers are not only enhancing the integrity of academic records but also streamlining the hiring process.
One of the most significant advantages of using blockchain for verifying academic credentials is the immutability and transparency it brings to the verification process. Academic records, including degrees, certifications, and transcripts, are recorded on the blockchain in a tamper-proof and time-stamped manner. This ensures that once a credential is issued, it cannot be altered or falsified, safeguarding the integrity of the information.
This immutability directly addresses the issue of fraudulent claims on resumes and during the hiring process. With traditional methods of verifying academic credentials, such as contacting universities or checking paper certificates, there is a greater risk of encountering fraudulent documents. Blockchain verification eliminates this risk, providing employers with a high level of confidence in the authenticity of an applicant’s educational background.
Moreover, the transparency of blockchain technology means that anyone with permission can access and verify academic credentials. This accessibility can be a game-changer for both applicants and employers. Applicants have greater control over their credentials, allowing them to share verified academic records with potential employers, educational institutions, or other relevant parties easily. Employers, on the other hand, can efficiently verify the qualifications of candidates during the hiring process, reducing the time and resources spent on manual verification.
The convenience and efficiency offered by blockchain verification can significantly accelerate the hiring process. Employers can quickly and confidently verify the educational backgrounds of candidates, allowing for faster decision-making and onboarding. This is particularly valuable in competitive job markets, where companies strive to attract and retain top talent.
Additionally, the use of blockchain for academic credential verification can have a global impact. It eliminates the need for international candidates to navigate complex and often slow processes for verifying foreign credentials, making it easier for organizations to tap into a diverse and global talent pool.
However, the widespread adoption of blockchain for academic credential verification is still a work in progress. Challenges related to standardization, data privacy, and the integration of existing systems need to be addressed for broader implementation. Furthermore, ensuring that only authorized parties have access to academic records while maintaining individual privacy is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration.
In conclusion, blockchain technology’s role in verifying academic credentials is revolutionizing the way educational records are managed and authenticated. It offers a secure, transparent, and efficient solution to reduce fraudulent claims and simplify the hiring process. As the adoption of blockchain in education and employment continues to grow, it has the potential to enhance the credibility and efficiency of credential verification on a global scale, benefiting both individuals and organizations alike.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What are smart contracts on blockchain? | IBM

Digital Learning
Blockchain enables the creation of digital learning platforms where students can access educational content, certificates, and credentials.
Blockchain technology is catalyzing a groundbreaking evolution in education, offering students, institutions, and employers a new paradigm for learning, credentialing, and verifying educational achievements. Let’s explore how blockchain is transforming the education landscape:
Immutable Academic Records: Blockchain provides an immutable ledger for academic records, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of certificates, diplomas, and transcripts. Students receive digital credentials in the form of blockchain-based certificates or badges that are securely stored and can be easily accessed whenever needed. This eliminates the risk of fraudulent or tampered academic records.
Global Verification: Blockchain-powered digital credentials are accessible globally, allowing students to share their achievements with potential employers or educational institutions worldwide. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that verification can occur seamlessly, without relying on a centralized authority. This streamlines the hiring process for employers and simplifies admission procedures for academic institutions.
Lifelong Learning Portfolios: Students can create comprehensive lifelong learning portfolios on the blockchain. These portfolios include a detailed history of courses, projects, and certifications, providing a holistic view of their skills and knowledge. Such portfolios empower students to showcase their continuous learning journey, enhancing their employability and career progression.
Micro-Credentials and Badges: Blockchain enables the issuance of micro-credentials and digital badges for smaller, specific achievements or skills. These badges are verifiable and can be shared on social media profiles or professional networks, enhancing students’ online presence and credibility.
Self-Sovereign Identity: Blockchain-based education platforms are pioneering the concept of self-sovereign identity for students. This means that students have control over their own identity and personal data. They can choose what information to share, which enhances privacy and security while reducing the risk of data breaches.
Eliminating Degree Mills: The transparency and traceability of blockchain records make it difficult for degree mills or diploma mills to thrive. Employers and institutions can easily verify the authenticity of educational credentials, reducing the risk of hiring individuals with fraudulent qualifications.
Reduced Administrative Burden: Educational institutions benefit from streamlined administrative processes. Blockchain automates the verification of academic records, reducing the administrative burden on registrars and admissions offices. This allows institutions to allocate resources more efficiently.
Access to Global Learning Resources: Blockchain can facilitate global access to educational content and resources. Through decentralized education platforms, students can access courses, textbooks, and learning materials from institutions worldwide, expanding educational opportunities for learners in remote or underserved areas.
Smart Contracts for Learning Agreements: Blockchain’s smart contract capabilities enable the creation of learning agreements and contracts between students, instructors, and institutions. These contracts can automate course enrollment, fee payments, and grading, ensuring transparency and reducing disputes.
Skills-Based Hiring: Employers are increasingly valuing skills over traditional degrees. Blockchain allows students to showcase their skills and competencies, enabling employers to make more informed hiring decisions based on an individual’s abilities rather than their formal qualifications.
In summary, blockchain is revolutionizing education by providing secure, transparent, and globally accessible platforms for learning, credentialing, and verifying educational achievements. This transformative technology is reshaping how students, educational institutions, and employers engage with academic records and lifelong learning, ultimately promoting a more accessible, efficient, and equitable education ecosystem.
You can also read more about this here: What Is the Fourth Industrial Revolution? | Salesforce

Digital Identity
Blockchain provides secure, tamper-proof digital identities for citizens, enabling efficient government services and reducing identity fraud.
Blockchain’s role in digital identity management extends beyond merely providing secure and tamper-proof identities. It revolutionizes the way governments and organizations manage and authenticate identity data, ushering in an era of efficiency, transparency, and security:
**1. Immutable and Secure Identities:
Protection Against Identity Theft: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that once an individual’s identity is recorded, it cannot be altered or manipulated. This protection guards against identity theft and fraud.
Enhanced Data Security: Personal data stored on a blockchain is highly secure, reducing the risk of data breaches that compromise sensitive information.
**2. Efficient Government Services:
Streamlined Access: Citizens can access government services and applications seamlessly with their blockchain-based digital identities, eliminating the need for repetitive document submissions and identity verification.
Reduced Bureaucracy: By eliminating the need for intermediaries and manual document verification, blockchain reduces bureaucratic inefficiencies in government agencies, leading to faster and more cost-effective service delivery.
**3. Data Sovereignty and Privacy:
User-Controlled Data: Citizens have greater control over their personal data and can selectively share it with government agencies or service providers when necessary. This empowers individuals to manage their privacy effectively.
Consent-Based Sharing: Blockchain enables consent-based data sharing, ensuring that individuals have control over who accesses their identity information and for what purpose.
**4. Interoperability and Portability:
Cross-Border Compatibility: Blockchain-based identities can be interoperable across borders, simplifying identity verification for international travel, trade, and immigration.
Portability: Individuals can carry their digital identities across various platforms and services, reducing the need to create and manage multiple identity accounts.
**5. Reduction in Fraud and Cybercrime:
Anti-Fraud Measures: Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it challenging for fraudsters to manipulate or forge identities, lowering the risk of identity-related cybercrimes.
Authentication Confidence: Service providers and organizations can have high confidence in the authenticity of blockchain-based digital identities, reducing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
**6. Immutable Audit Trails:
Auditability: Every access or update to a blockchain-based identity is recorded, creating an immutable audit trail. This is invaluable for forensic investigations, compliance checks, and dispute resolution.
Compliance with Regulations: Blockchain facilitates compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, by providing a transparent record of data usage and consent.
**7. Humanitarian and Inclusive Applications:
Identification for the Unbanked: Blockchain-based identities can provide identification to individuals who lack traditional identification documents, opening access to financial services and humanitarian aid.
Refugee Support: In refugee crises, blockchain identities can help displaced individuals establish their identities, access essential services, and rebuild their lives.
**8. Voting and Civic Engagement:
Secure Voting: Some countries are exploring blockchain-based voting systems to enhance election security, transparency, and accessibility while reducing the risk of voter fraud.
Digital Citizenship: Blockchain enables the concept of “digital citizenship,” allowing individuals to participate in civic processes and access government services online securely.
In conclusion, blockchain-powered digital identities are poised to redefine the landscape of identity management and government services. They enhance security, streamline processes, empower individuals, and reduce fraud. As blockchain technology matures and gains wider adoption, it has the potential to revolutionize the way governments and organizations interact with and verify the identities of their citizens and customers, ultimately leading to a more efficient and secure digital future.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey

Voting
Some countries are exploring blockchain-based voting systems to enhance election transparency and security.
The exploration of blockchain-based voting systems by countries represents a significant step forward in the pursuit of more secure and transparent elections. This innovative approach holds the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct democratic processes and ensures that the integrity of elections is maintained. Here are several ways in which blockchain-based voting systems can enhance election transparency and security:
Immutable Voting Records: Blockchain creates an immutable ledger of all votes cast in an election. Once a vote is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the accuracy and integrity of the voting process, reducing the risk of tampering or fraud.
Transparent Verification: Each voter can verify their vote on the blockchain, allowing them to confirm that their vote was correctly recorded. This transparency builds trust among voters and eliminates concerns about the miscounting or manipulation of votes.
Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic techniques and decentralized nature make it extremely resistant to hacking and unauthorized access. This robust security reduces the vulnerability of voting systems to cyberattacks, safeguarding the electoral process.
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, which means there is no single point of failure. Even if some nodes are compromised, the integrity of the election data remains intact, making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the results.
Accessibility: Blockchain-based voting systems can potentially increase accessibility for voters, including those living abroad, the elderly, and people with disabilities. They can vote securely from the convenience of their own devices, eliminating the need for physical polling locations.
Real-Time Results: With blockchain, election results can be tabulated in real-time as votes are cast. This provides immediate feedback to candidates and voters and reduces the time and resources required for manual counting and result reporting.
Voter Identity Protection: Blockchain can ensure that voter identities are protected. Instead of storing personal information on a central server, only a cryptographic representation of the voter’s identity is recorded on the blockchain, preserving privacy while verifying eligibility.
Reduced Voter Suppression: Blockchain can help reduce instances of voter suppression by providing a secure and accessible voting method. This can empower marginalized communities and ensure that their voices are heard in the electoral process.
Auditable Elections: The transparency of blockchain-based voting systems allows for easy post-election audits. Independent auditors and election officials can verify the results by examining the blockchain, further enhancing trust in the electoral process.
International Elections: Blockchain-based voting can facilitate secure and transparent international elections, such as those for expatriate communities or global organizations. This can improve the representation and participation of people living abroad.
Tamper-Proof Voter Registration: Blockchain can also be used for voter registration to prevent fraudulent registrations and ensure that only eligible voters can participate in elections.
It’s important to note that while blockchain-based voting systems offer numerous advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges, including issues related to voter authentication, scalability, and user-friendly interfaces. Implementing such systems requires careful consideration and collaboration between government bodies, technologists, and cybersecurity experts to address these challenges and ensure the successful integration of blockchain technology into the electoral process.
In summary, the exploration of blockchain-based voting systems represents a promising avenue for enhancing election transparency and security. By leveraging the inherent features of blockchain, countries can reinforce the foundations of democracy and ensure that elections remain a fair and accurate reflection of the will of the people.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: What Is Blockchain Technology? How Does It Work? | Built In

Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain ensures the authenticity and quality of agricultural products by tracking their journey from farms to consumers.
Blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of transparency and trust in the agricultural industry by offering a comprehensive solution to verify the authenticity and quality of products from the farm to the consumer’s table. Through blockchain-based supply chain tracking, agricultural products can be traced with unprecedented accuracy, benefiting not only consumers but also farmers, producers, and regulatory bodies.
At its core, blockchain serves as an immutable ledger that records every step of a product’s journey, from its origin on the farm to its final destination on store shelves or in the hands of consumers. Each transaction and data point is securely logged on the blockchain, creating an unbroken chain of information. This level of transparency empowers consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase, including details about their origin, production methods, and quality.
Farmers and producers are among the primary beneficiaries of blockchain in agriculture. By utilizing blockchain, they can showcase the authenticity and quality of their products, thereby enhancing consumer confidence and trust. This can translate into premium pricing for products that are sustainably and ethically produced, benefiting the bottom line of agricultural businesses.
For consumers, blockchain offers an unprecedented level of transparency and trust in the food supply chain. They can scan a product’s QR code or use a mobile app to access detailed information about its journey, including when and where it was grown, harvested, processed, and distributed. This transparency is particularly important in today’s food-conscious world, where consumers are increasingly concerned about food safety, sustainability, and ethical sourcing.
Blockchain can also play a pivotal role in food safety and traceability. In the event of a foodborne illness outbreak or contamination issue, blockchain technology allows authorities to quickly and accurately trace the source of the problem. This can result in more targeted recalls and improved public health outcomes, reducing the impact of food-related crises.
Furthermore, the benefits of blockchain extend to regulatory bodies and organizations responsible for ensuring food safety and compliance with standards. They can access real-time data on the entire supply chain, facilitating more efficient monitoring and enforcement of regulations. This proactive approach can lead to safer food products and more effective regulatory oversight.
However, the widespread adoption of blockchain in agriculture is not without its challenges. The need for standardization, data privacy, and interoperability among various stakeholders in the supply chain must be addressed. Additionally, smaller farmers and producers may require support and resources to implement blockchain technology effectively.
In conclusion, blockchain’s role in ensuring the authenticity and quality of agricultural products represents a significant advancement in the industry. By offering transparency, trust, and traceability, blockchain benefits consumers, farmers, producers, and regulatory bodies alike. As the adoption of blockchain technology continues to grow, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce, distribute, and consume food, leading to a safer, more transparent, and more sustainable food supply chain.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The Ultimate Guide to Web3 – Blockchain Council

Farm-to-Table Initiatives
Consumers can trace the origin of their food products, promoting sustainability and supporting local farmers.
The utilization of blockchain technology in the food industry marks a significant stride toward transparency, sustainability, and responsible consumerism. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how blockchain enhances food traceability and strengthens support for local farmers while promoting sustainability:
End-to-End Traceability: Blockchain empowers consumers to trace the journey of their food products from farm to fork with unparalleled precision. Each step of the supply chain, from planting and harvesting to processing and distribution, is meticulously recorded on the blockchain ledger. This transparency enables consumers to verify the authenticity and origin of their food, instilling confidence in the products they choose.
Local Farm Promotion: Blockchain’s traceability features are a boon to local farmers and producers. Consumers can easily identify and support products originating from local sources by scanning QR codes or accessing blockchain records. This fosters a stronger connection between consumers and local farmers, bolstering the local economy and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Reducing Food Fraud: Food fraud, such as mislabeling or counterfeit products, is a pervasive issue in the food industry. Blockchain’s tamper-resistant ledger makes it exceedingly difficult for unscrupulous actors to manipulate product information. As a result, consumers can trust that they are purchasing genuine, high-quality products, reducing the risk of food fraud.
Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility: Blockchain enhances supply chain visibility by providing real-time updates on the movement and condition of food products. This transparency is especially vital for perishable goods, as it ensures that products are handled and transported under optimal conditions, reducing food waste and spoilage.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Blockchain technology can incorporate data on sustainable farming and production practices. Consumers can choose products that align with their values, such as organic, fair trade, or eco-friendly options. This promotes sustainability by encouraging responsible consumer choices and rewarding producers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices.
Certifications and Standards: Blockchain facilitates the inclusion of certifications and standards, such as organic or non-GMO labels, in the supply chain records. Consumers can easily verify whether products meet specific criteria, ensuring that they align with their dietary preferences and ethical considerations.
Quality Assurance: Blockchain can record quality assurance data, including lab tests and inspections. This ensures that products meet safety and quality standards, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and health hazards.
Reducing Food Recalls: In the event of a food recall, blockchain expedites the process. The immutable ledger enables rapid identification of affected products and their sources, allowing for targeted recalls. This minimizes waste by only removing contaminated products from the market.
Consumer Empowerment: Blockchain puts consumers in the driver’s seat when it comes to making informed choices about their food purchases. They can access comprehensive information about the nutritional content, allergens, and ethical considerations associated with the products they buy, promoting responsible consumerism.
Global Impact: Blockchain’s impact extends beyond local markets. Consumers can make conscious choices to support sustainable farming practices globally, encouraging responsible agriculture and the preservation of biodiversity.
In conclusion, blockchain’s transformative role in food traceability empowers consumers to make informed, sustainable, and locally supportive choices while holding producers accountable for responsible practices. This technology fosters a stronger connection between consumers, local farmers, and global food systems, ultimately contributing to a more transparent, ethical, and sustainable food industry.
You can also read more about this here: McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook Report 2022

IP Protection
Blockchain offers a secure way to timestamp and protect intellectual property, reducing disputes over ownership and copyright.
The integration of blockchain technology in intellectual property (IP) management offers a comprehensive solution to many of the challenges associated with copyright and ownership disputes. Beyond secure timestamping, blockchain brings a host of benefits to the protection of intellectual property:
**1. Immutable Ownership Records:
Clear Ownership: Blockchain records provide indisputable proof of ownership and the chronological order of creation or publication. This clarity reduces disputes over copyright and authorship.
Protection Against Plagiarism: Artists, writers, and content creators can protect their work against plagiarism by timestamping it on the blockchain. Any attempts to replicate or copy the work can be traced back to the original owner.
**2. Smart Contracts for Licensing:
Automated Licensing Agreements: Smart contracts on the blockchain enable automated royalty payments and licensing agreements. This simplifies the process of granting permissions for the use of intellectual property while ensuring creators are fairly compensated.
Micropayments: Blockchain-based smart contracts can facilitate micropayments for IP usage, allowing creators to monetize their work even in the age of digital sharing.
**3. Global Protection:
International Reach: Blockchain transcends geographical boundaries, making it possible to protect intellectual property globally. Creators can assert their rights and enforce copyright claims worldwide.
Cross-Border Enforcement: In case of infringement, blockchain records can serve as evidence in cross-border legal actions, simplifying the process of seeking remedies in international courts.
**4. Transparency and Accountability:
Public Record: Some blockchains offer public records of IP ownership, providing transparency and accountability in the intellectual property space. This can deter potential infringers.
Data Integrity: Blockchain ensures the integrity of IP records, making it difficult for bad actors to manipulate or falsify ownership information.
**5. Licensing and Monetization:
Secondary Markets: Blockchain can facilitate the creation of secondary markets for IP, allowing creators to sell or license their work to interested parties, including collectors, businesses, or investors.
Fractional Ownership: Fractional ownership of IP assets can be made possible through blockchain, allowing multiple parties to invest in and benefit from the success of a creative work.
**6. Efficient IP Management:
Digital Portfolios: Creators can manage their intellectual property portfolios more efficiently on the blockchain, including registering new works, tracking usage, and managing licensing agreements.
Reduced Administrative Costs: By automating aspects of IP management, blockchain reduces administrative overhead, making it cost-effective for individual artists and small businesses.
**7. IP and NFTs:
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs, often based on blockchain technology, are revolutionizing the way digital art and collectibles are bought and sold. Creators can tokenize their work as NFTs, which represent unique ownership rights and can be traded on blockchain marketplaces.
Provenance and Authentication: NFTs provide proof of authenticity and provenance for digital and physical assets, reducing concerns about counterfeit or unauthorized copies.
In summary, blockchain’s role in protecting intellectual property extends far beyond timestamping; it revolutionizes the entire landscape of IP management. By providing immutable ownership records, facilitating automated licensing, offering global protection, and fostering transparent markets, blockchain empowers creators to assert their rights and fairly monetize their work. As the world continues to digitize and share creative content, blockchain technology stands as a critical tool in safeguarding the rights and livelihoods of artists and creators.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey

Smart Contracts for Legal Agreements
Blockchain-based smart contracts automate legal processes, reducing the need for intermediaries in contract execution.
Blockchain-based smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize the legal industry by automating various legal processes, thereby reducing the reliance on intermediaries and increasing the efficiency, transparency, and security of contract execution. Here are several ways in which blockchain-based smart contracts extend their impact:
Self-Executing Agreements: Smart contracts are self-executing, meaning they automatically enforce the terms and conditions of an agreement when predefined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or escrow services, to oversee and enforce the contract, streamlining the execution process.
Cost Savings: The reduction of intermediaries results in cost savings for all parties involved. Parties can avoid legal fees, administrative costs, and the expenses associated with third-party mediation. This makes contracts more affordable and accessible, particularly for small businesses and individuals.
Accuracy and Precision: Smart contracts operate based on code, which eliminates the possibility of human error in contract execution. This ensures that the contract’s terms are consistently and precisely followed, reducing the risk of disputes arising from misinterpretation or mistakes.
Transparency and Trust: All contract-related data and transactions are recorded on a blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable ledger of activity. Parties can verify the execution of the contract and the fulfillment of its terms in real-time, enhancing trust among stakeholders.
Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security features make it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to tamper with contract data or manipulate the terms. This enhances the security of contracts, reducing the risk of fraud or breaches.
Global Accessibility: Smart contracts can be accessed and executed from anywhere with an internet connection, making them suitable for international transactions. This opens up new opportunities for global trade and collaboration without the need for complex cross-border legal processes.
Automated Compliance: Smart contracts can be programmed to automatically comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements. This ensures that contracts are executed within the bounds of the law, reducing the risk of legal complications.
Conditional Payments: Smart contracts can handle conditional payments, releasing funds only when specified conditions are met. For example, in real estate transactions, funds could be held in escrow until both parties fulfill their obligations, reducing the risk for buyers and sellers.
Streamlined Dispute Resolution: While smart contracts aim to prevent disputes through automated execution, they can also include dispute resolution mechanisms within the contract code. This can expedite the resolution process by providing a clear framework for dispute handling.
Customizability: Smart contracts can be tailored to fit a wide range of agreements, from simple sales contracts to complex multi-party agreements. This adaptability makes them suitable for various industries and use cases.
Integration with Oracles: Smart contracts can be connected to external data sources through oracles, allowing them to react to real-world events and updates. For example, insurance contracts can automatically process claims based on external weather data.
Compliance and Auditing: The transparency of blockchain allows for easy auditing and regulatory compliance. Regulators can access the blockchain to ensure that businesses are adhering to relevant laws and regulations.
In conclusion, blockchain-based smart contracts offer a promising avenue for automating legal processes, reducing the need for intermediaries, and improving the efficiency and reliability of contract execution. As this technology continues to evolve, it is likely to disrupt traditional legal practices, making legal agreements more accessible and efficient for individuals, businesses, and organizations around the world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Which Industries Can Benefit From Smart Contracts? – Harris …

Conclusion
The impact of blockchain and Web3 applications extends far beyond these industries, reaching sectors like art, insurance, aviation, and more. As blockchain technology continues to mature and gain widespread adoption, it has the potential to reshape our economy and society, ushering in an era of greater transparency, efficiency, and empowerment for individuals and businesses alike.
The transformative power of blockchain technology and Web3 applications transcends traditional boundaries, leaving an indelible mark on a myriad of sectors across the global landscape. Beyond finance and supply chain, industries as diverse as art, insurance, aviation, and many others are experiencing the profound effects of this digital revolution. As blockchain technology continues to mature and enjoys increasing adoption, its potential to reshape not only specific sectors but our entire economy and society becomes increasingly evident, promising a future characterized by greater transparency, efficiency, and empowerment for individuals and businesses alike.
In the realm of art, blockchain has sparked a creative renaissance by providing artists with the means to tokenize their works as non-fungible tokens (NFTs). This innovative approach to provenance and ownership authentication has democratized the art world, enabling artists to reach a global audience without the traditional gatekeepers. Additionally, NFTs have opened up new revenue streams for artists by allowing them to earn royalties with each subsequent sale of their digital creations.
Insurance is another sector undergoing a profound transformation. Blockchain’s ability to create tamper-proof, transparent records has made it a valuable tool for verifying insurance claims and streamlining the claims process. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements that automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, have the potential to automate insurance payouts, reducing administrative overhead and expediting the resolution of claims.
In aviation, blockchain technology is improving the efficiency of supply chain management and maintenance tracking. Airlines and manufacturers can securely store and share maintenance records, part histories, and other critical data on a blockchain, ensuring that aircraft are maintained to the highest standards and that spare parts are genuine and compliant with safety regulations.
The applications of blockchain are virtually limitless, touching areas such as real estate, healthcare, and energy management. In real estate, blockchain can facilitate property transactions, reduce fraud, and increase transparency in property records. In healthcare, it offers a secure and transparent means of managing electronic health records, ensuring data integrity and patient privacy. In energy management, blockchain can enable peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess energy in a decentralized and transparent manner.
As blockchain technology continues to mature and gain widespread acceptance, its potential to drive economic and societal change becomes increasingly apparent. It holds the promise of reducing fraud, enhancing transparency, improving efficiency, and empowering individuals and businesses to have greater control over their assets and data. While challenges and regulatory considerations remain, the overarching trajectory of blockchain is one of progress, innovation, and transformation across a wide spectrum of industries, ultimately shaping a future that is more inclusive, equitable, and digitally empowered.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here 5 Ways Blockchain Web3 is Revolutionizing the Decentralized Industry
More links
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: How Web3 And Decentralization Are Transforming The Real Estate …
