The internet has undergone a significant transformation since its inception. We’ve moved from Web 1.0, a static and information-centric web, to Web 2.0, characterized by user-generated content and social interactions. Now, we stand on the brink of another evolution
Web3. This new paradigm promises a fundamental shift in how we interact with the digital world, emphasizing ownership, decentralization, and user empowerment. At the heart of Web3 are concepts like NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), digital assets, and digital identity, which collectively form the foundation of the Ownership Economy.
Web3 represents a remarkable evolution of the digital landscape, offering a profound transformation in our online experiences and how we relate to digital assets. This shift is underpinned by core principles like NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), digital assets, and digital identity, collectively building what is often referred to as the Ownership Economy. Let’s delve deeper into the significance and implications of these concepts within Web3:
NFTs Redefining Ownership: NFTs have emerged as the poster child of Web3, enabling individuals to truly own unique digital assets. Whether it’s digital art, collectibles, or virtual real estate, NFTs use blockchain technology to certify the authenticity and provenance of digital items. This has opened up exciting possibilities for creators, allowing them to sell their work directly to a global audience, while buyers enjoy clear ownership rights and the potential for appreciation.
Digital Assets as Investments: Web3 introduces the idea of digital assets as valuable investments. People can now acquire and trade digital assets with the expectation of future value appreciation. This has created new markets and opportunities for investors to diversify their portfolios, with the potential for significant returns.
Decentralization Empowering Users: Unlike the centralized models of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, Web3 champions decentralization. Blockchain technology and decentralized applications (dApps) empower users by giving them control over their data and digital interactions. This shift represents a significant departure from the data-harvesting business models of traditional platforms, where users often surrender their privacy and control.
User-Centric Digital Identity: In the Web3 era, individuals have greater control over their digital identities. Blockchain-based identity solutions provide secure and portable identity verification, allowing users to manage their personal information and decide who has access to it. This enhances privacy, reduces the risk of identity theft, and promotes user autonomy.
Tokenization of Everything: Web3 expands the concept of ownership to virtually anything that can be tokenized. Beyond art and collectibles, we’re seeing the tokenization of real estate, intellectual property, and even social influence. This democratizes access to traditionally exclusive markets and assets, making them more inclusive and accessible.
New Business Models: Web3 introduces novel business models based on decentralized networks, such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). These entities are governed by smart contracts and enable collective decision-making and resource allocation, potentially disrupting traditional corporate structures.
The Creator Economy: Web3 fosters the growth of the Creator Economy, where content creators, influencers, and artists can interact directly with their audiences, monetize their work, and retain a larger share of the revenue. This economic model rewards creators for their contributions and creativity.
Open Innovation and Collaboration: Decentralized platforms and protocols encourage open innovation and collaboration. Developers can build on existing blockchain networks, leading to the rapid development of new applications, services, and solutions without being beholden to a single entity’s rules.
Globalization of Opportunities: Web3 has a borderless nature, allowing individuals from around the world to participate in the Ownership Economy. This global reach expands opportunities and creates a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
In conclusion, Web3 represents a paradigm shift that prioritizes ownership, decentralization, and user empowerment in the digital realm. Concepts like NFTs, digital assets, and digital identity are at the heart of this transformation, reshaping how we interact with the digital world and offering new avenues for creativity, investment, and collaboration. As Web3 continues to evolve, it holds the potential to redefine not only how we view the digital landscape but also how we engage with it on a personal and professional level.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE THE NEXT DIGITAL FRONTIER?

NFTs: Redefining Digital Ownership
NFTs have taken the world by storm, showcasing the potential for digital ownership in Web3. NFTs are unique digital tokens that represent ownership of a specific item or piece of content. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and interchangeable, NFTs are non-fungible, meaning each one is distinct and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis.
NFTs have been primarily associated with digital art, collectibles, and entertainment. Artists, musicians, and creators can tokenize their work as NFTs, allowing them to sell and monetize digital assets in ways previously impossible. This newfound digital ownership extends to various domains, including virtual real estate, in-game assets, and even domain names. NFTs provide indisputable proof of ownership and provenance, making them a powerful tool in the Ownership Economy.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Your Ultimate Guide To: NFTs In Web3 Ecosystem: Role And Future …
Digital Assets and Tokenization
Beyond NFTs, Web3 introduces the concept of digital assets and tokenization. Digital assets encompass a wide range of virtual and real-world items, from real estate and stocks to in-game items and intellectual property. These assets can be tokenized, meaning they are represented as blockchain-based tokens. Tokenization unlocks several benefits:
The concept of digital assets and tokenization within the Web3 framework ushers in a new era of possibilities that extend far beyond the realm of NFTs. Here, we delve into the broader landscape of digital assets and their tokenization, shedding light on the manifold advantages they offer:
Fractional Ownership: Tokenization enables the fractional ownership of traditionally illiquid assets like real estate or high-value art. Investors can now purchase fractions of these assets, allowing for diversification and broader access to investment opportunities that were once reserved for the privileged few.
Liquidity and Accessibility: Tokenization enhances the liquidity of assets. With assets represented as blockchain tokens, they can be easily bought, sold, and traded on digital asset exchanges, creating a more accessible and dynamic marketplace. This increased liquidity benefits both asset owners and investors.
Global Reach: Blockchain operates on a global scale, making tokenized assets accessible to a worldwide audience. Investors from different countries can participate in the ownership and trading of assets without geographical constraints, expanding the pool of potential buyers and sellers.
Transparency and Security: Blockchain’s transparent and tamper-resistant nature ensures that the ownership and transaction history of tokenized assets are verifiable by all stakeholders. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, and disputes, fostering trust in the asset’s provenance.
Efficient Settlement: Traditional asset transfers often involve intermediaries and lengthy settlement periods. Tokenized assets can be transferred almost instantly, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing settlement times to minutes or even seconds.
Automated Compliance: Smart contracts, a hallmark of blockchain technology, can automate compliance with regulatory requirements. This ensures that tokenized assets adhere to relevant laws and regulations, providing peace of mind to asset owners and investors.
Inclusivity: Tokenization democratizes access to asset ownership. It allows individuals to invest in assets that were previously beyond their reach. This inclusivity empowers a broader range of people to participate in investment opportunities and wealth-building.
Enhanced Traceability: The blockchain ledger provides an immutable record of asset ownership and transfer history. This traceability is invaluable for auditing, proving ownership, and maintaining an accurate historical record of asset transactions.
Reduced Costs: Tokenization streamlines the issuance and management of assets, reducing administrative and operational costs. This cost efficiency benefits both issuers and investors, making asset ownership more economically viable.
New Business Models: Tokenization has the potential to foster innovative business models. Companies can tokenize assets like loyalty points, patents, or digital content, creating new revenue streams and engagement opportunities with their customers.
Environmental Impact: Some blockchains are exploring more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like proof of stake (PoS), reducing the environmental impact associated with tokenization and asset management.
In summary, the broader scope of digital assets and tokenization within the Web3 ecosystem ushers in a transformative era of finance, investment, and ownership. From increased accessibility and liquidity to enhanced transparency and security, these innovations have the potential to reshape the way we interact with and invest in a wide array of assets, unlocking opportunities for individuals and businesses alike.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey

Fractional Ownership
Investors can purchase fractions of high-value assets, such as real estate or art, making these markets accessible to a broader range of participants.
The concept of tokenizing high-value assets, like real estate or art, opens up a world of possibilities in the Ownership Economy. Beyond making these markets accessible to a broader range of participants, it introduces several noteworthy implications:
1. Fractional Ownership Democratizes Investment:
Reduced Financial Barriers: Fractional ownership allows individuals with limited capital to invest in assets that were traditionally out of reach. This democratization of investment opportunities fosters financial inclusion and wealth distribution.
Diversification: Fractional ownership enables investors to diversify their portfolios across various asset classes. Instead of allocating substantial funds to a single property or artwork, they can spread their investments across multiple assets, reducing risk.
2. Increased Liquidity in Illiquid Markets:
Unlocking Value: Illiquid assets like real estate often tie up capital for extended periods. Tokenization brings liquidity to these markets by allowing owners to sell fractions of their assets, unlocking the value trapped in illiquid holdings.
Efficient Trading: Blockchain-based markets for fractionalized assets facilitate seamless trading and transactions, reducing the time and effort required for buying or selling high-value assets.
3. Enhanced Accessibility for Global Investors:
Global Reach: Digital tokenization transcends geographical boundaries, making it possible for investors from around the world to participate in markets traditionally tied to specific regions.
Borderless Investments: Investors can diversify their portfolios across international real estate markets, art collections, or other assets without the need for complex cross-border transactions.
4. New Investment Models and Opportunities:
Real Estate Crowdfunding: Fractional ownership paves the way for real estate crowdfunding platforms, where multiple investors collectively own and profit from properties. This model expands the range of investment opportunities in the real estate sector.
Art Market Evolution: Tokenization of artwork enables artists to gain direct support from a global audience. Art lovers can invest in their favorite artists’ work and benefit from any future appreciation in value.
5. Regulatory Considerations and Challenges:
Legal Frameworks: The tokenization of assets introduces regulatory complexities that vary by jurisdiction. Governments and regulatory bodies are actively developing frameworks to ensure investor protection and market integrity.
Security and Compliance: Ensuring the security of tokenized assets and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations is paramount to maintain market trust.
6. Potential for Secondary Markets:
- Secondary Trading Platforms: As tokenized assets become more prevalent, we can expect the emergence of secondary trading platforms where investors can buy and sell these asset-backed tokens. This further enhances liquidity and market accessibility.
In summary, fractional ownership through asset tokenization is reshaping investment landscapes by making high-value assets accessible to a broader and more diverse group of investors. It brings liquidity to traditionally illiquid markets, increases opportunities for diversification, and introduces innovative investment models. However, it also presents regulatory and security challenges that must be addressed as the Ownership Economy continues to evolve.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Building Psychological Attachment — Not Just Ownership — Into …

Liquidity
Blockchain-powered markets allow assets to be bought, sold, and traded more efficiently, enhancing liquidity and reducing barriers to entry.
Blockchain-powered markets represent a groundbreaking evolution in the world of finance and asset trading. These markets leverage blockchain technology to revolutionize the way assets are bought, sold, and traded, resulting in increased efficiency, liquidity, and accessibility while significantly reducing barriers to entry. Let’s explore how this transformation unfolds:
24/7 Accessibility: Blockchain-powered markets operate around the clock, 24/7, without the limitations of traditional trading hours or geographical boundaries. This constant availability means that investors can engage in asset trading at their convenience, making financial markets more inclusive and accommodating to a global audience.
Immediate Settlement: Blockchain transactions settle in near real-time, eliminating the need for lengthy clearing and settlement processes that can take days in traditional markets. This instant settlement accelerates the pace of trading and reduces counterparty risk, as there is minimal exposure to market fluctuations.
Fractional Ownership: Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets, allowing them to be divided into smaller, more affordable units. This fractional ownership concept makes high-value assets like real estate, art, and even stocks accessible to a broader range of investors who may not have the capital to buy whole assets.
Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain’s transparent and immutable ledger ensures that all trading activities are recorded and can be audited by anyone. This transparency builds trust among market participants, as they can independently verify trade history and asset ownership, reducing the risk of fraud.
Reduced Intermediaries: Blockchain eliminates many intermediaries traditionally involved in asset trading, such as brokers, custodians, and clearinghouses. This streamlines the trading process, reduces fees, and minimizes the complexity associated with multi-party transactions.
Global Market Access: Blockchain-powered markets are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This global reach means that investors can access a wide range of assets from various markets worldwide, diversifying their portfolios and taking advantage of investment opportunities that were previously out of reach.
Democratized Finance: By lowering the barriers to entry, blockchain-powered markets democratize finance. Individuals who were previously excluded from traditional financial systems can now participate in asset trading, wealth creation, and investment opportunities, promoting financial inclusion.
Security and Ownership Rights: Blockchain’s cryptographic security ensures the integrity of ownership records and asset transfers. Owners have full control of their digital assets, reducing the risk of asset seizure or unauthorized access.
Innovation in Asset Classes: Blockchain’s flexibility enables the creation of entirely new asset classes, such as utility tokens, security tokens, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These innovative assets introduce unique investment opportunities and redefine traditional notions of value.
Automated Smart Contracts: Smart contracts on blockchain networks can automate various aspects of trading, including dividend payments, voting rights, and compliance with regulatory requirements. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries and enhances operational efficiency.
Enhanced Liquidity: Liquidity in blockchain-powered markets is often higher due to the ease of trading and fractional ownership. This liquidity benefits both buyers and sellers by reducing the time and effort required to find willing counterparties.
Resilience to Centralized Failures: Blockchain’s decentralized architecture reduces the risk of system failures or disruptions that can affect centralized exchanges. This resilience enhances the stability of blockchain-powered markets.
In summary, blockchain-powered markets are ushering in a new era of asset trading that emphasizes accessibility, efficiency, and transparency. These markets are tearing down traditional barriers to entry, opening up opportunities for a more diverse and global pool of investors, and fostering innovation in the financial industry. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we can expect further enhancements in asset trading and the continued growth of decentralized financial ecosystems.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Web3, metaverse, the next internet | Deloitte Insights

Global Accessibility
Digital assets can be accessed and traded globally, transcending geographical restrictions and enabling cross-border investments and transactions.
The advent of digital assets has ushered in a new era of global financial accessibility and inclusivity, effectively dismantling the geographical barriers that have traditionally constrained investments and transactions. In this borderless digital landscape, individuals and businesses can harness the full potential of their financial resources, enabling cross-border investments and transactions with unparalleled ease and efficiency.
One of the standout advantages of digital assets is their accessibility to a global audience. Unlike traditional financial instruments that often require intermediaries, digital assets can be accessed and managed directly by anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet. This democratization of access ensures that individuals in regions with limited financial infrastructure can participate in the global economy and diversify their investments.
Cross-border investments have never been more straightforward. Investors can seamlessly allocate their capital across different asset classes, such as cryptocurrencies, stocks, bonds, and real estate, without being encumbered by currency conversions, foreign exchange fees, or complex regulatory processes. Digital asset platforms provide a unified marketplace where a diverse range of assets can be bought and sold, offering unprecedented opportunities for diversification and risk management.
Furthermore, digital assets facilitate cross-border transactions with remarkable efficiency. Traditional international money transfers through banks and financial institutions can be marred by delays, high fees, and uncertainties related to currency conversion rates. Digital assets, on the other hand, enable near-instantaneous cross-border transactions with significantly reduced fees. This not only benefits individuals sending remittances to their families abroad but also empowers businesses engaged in international trade by streamlining payment processes and reducing operational costs.
The global reach of digital assets extends to fundraising as well. Through initial coin offerings (ICOs), security token offerings (STOs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, businesses can attract investment capital from a global pool of investors without the constraints of geographical borders. This democratized approach to fundraising has the potential to level the playing field for startups and entrepreneurs, unlocking opportunities that were previously out of reach.
However, it’s important to note that the global nature of digital assets also presents regulatory challenges. Different countries have varying approaches to the taxation, classification, and regulation of digital assets, which can create complexities for users and businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. Additionally, the borderless nature of digital assets can attract illicit activities, necessitating the development of robust compliance and security measures.
In conclusion, digital assets have redefined the possibilities of cross-border investments and transactions, liberating financial markets from geographical constraints. By offering accessibility, efficiency, and global reach, digital assets empower individuals and businesses to participate in a truly interconnected global economy. As regulatory frameworks evolve and industry standards mature, the potential for digital assets to continue reshaping the financial landscape on a global scale remains substantial, promising a future marked by increased financial inclusion and opportunity.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: opportunities-in-the-metaverse.pdf

Digital Identity and Control
In the Ownership Economy, digital identity takes on new significance. Individuals have true ownership and control over their digital identities, including personal data and online presence. Blockchain technology enables secure, user-controlled digital identities, fostering trust and privacy in the digital realm.
The emergence of the Ownership Economy underscores the paramount importance of digital identity in the modern age. It not only redefines ownership but also revolutionizes how individuals manage and safeguard their digital personas. Let’s delve deeper into this pivotal concept:
Self-Sovereign Identity: In the Ownership Economy, individuals exercise self-sovereign identity, which means they have full authority over their personal data and digital presence. Blockchain technology, with its cryptographic security and decentralized architecture, empowers users to control access to their identity information. This shift places individuals in the driver’s seat, allowing them to decide who can access their data and under what circumstances.
Enhanced Privacy: The Ownership Economy prioritizes privacy as a fundamental right. Blockchain-based digital identity systems are designed to protect user data from unauthorized access and misuse. Users can selectively share specific pieces of information without revealing their entire identity, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
User-Centric Identity Verification: Traditional identity verification methods often involve sharing excessive personal information with various service providers, raising concerns about data aggregation and surveillance. With blockchain-based digital identity, users can undergo identity verification once and then reuse that verified identity across multiple platforms and services. This streamlined process minimizes data exposure and simplifies interactions with online services.
Trust and Reputation Building: Blockchain enables the creation of verifiable digital reputations. Users can accumulate trustworthiness scores based on their behavior and interactions within the digital realm. This reputation can be shared with others, facilitating trust in online transactions, peer-to-peer interactions, and decentralized marketplaces.
Interoperability and Portability: Blockchain-based digital identities are designed to be interoperable and portable. Users can carry their digital identities across various online services, applications, and platforms. This interoperability enhances user convenience and reduces reliance on centralized identity providers.
Reduced Identity Fraud: The decentralized and tamper-resistant nature of blockchain makes it exceedingly challenging for cybercriminals to impersonate individuals or manipulate identity records. This heightened security contributes to a significant reduction in identity fraud and related cybercrimes.
Global Accessibility: Blockchain digital identities are accessible on a global scale, transcending geographical boundaries. This accessibility is especially valuable for individuals in regions with limited access to traditional identification methods, facilitating their participation in the digital economy.
Identity Ownership Economy: The Ownership Economy extends beyond digital identity to include the ownership of other digital assets, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) representing personal achievements, experiences, and credentials. This expanded ownership reinforces the value of individual identity in the digital landscape.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: As blockchain-based digital identities gain prominence, legal and regulatory frameworks are evolving to protect individuals and ensure compliance with data protection laws. These frameworks provide clarity and legal support for users seeking to assert their digital identity rights.
Empowering User-Centric Services: The Ownership Economy encourages the development of user-centric services that prioritize individual preferences and needs. Businesses and service providers can tailor their offerings based on users’ self-sovereign identities and preferences, fostering a more personalized and respectful digital environment.
In conclusion, the Ownership Economy redefines digital identity as a cornerstone of trust, privacy, and individual empowerment. With blockchain technology at its core, individuals can take charge of their digital identities, reclaiming control over their personal data and online presence. This paradigm shift not only enhances security and privacy but also paves the way for a more inclusive and user-centric digital landscape.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Web3 – Decentralization, Disruption and Digital Assets | EY – US

Data Privacy
Users decide how their data is used and shared, providing a solution to the ongoing concerns about data privacy and surveillance.
The user-centric control over data in the context of Web3 and digital identity represents a significant leap forward in addressing the pressing concerns about data privacy and surveillance:
1. Personalized Data Permissions:
Granular Control: Users have the ability to set precise permissions for their data, determining what information can be accessed, by whom, and for what purposes. This granular control ensures that only necessary data is shared, minimizing the risk of misuse.
Dynamic Settings: Users can adjust their data sharing preferences in real-time, adapting to changing circumstances or preferences. This dynamic control ensures that data remains in the user’s hands.
2. Consent-Based Data Sharing:
Informed Consent: Web3 emphasizes informed consent, ensuring that users are fully aware of how their data will be used before granting permission. This shifts the balance of power away from data collectors and toward individuals.
Revocable Permissions: Users retain the right to revoke data permissions at any time. If they feel that their data is being misused or they no longer wish to share it, they can instantly withdraw access.
3. Enhanced Privacy Protection:
Reduced Data Silos: With user-controlled data, there’s less need for centralized data silos that store vast amounts of personal information. This, in turn, reduces the attractiveness of these silos as targets for cyberattacks.
Minimized Data Exposure: Users only expose the data necessary for a specific transaction or interaction, reducing the potential impact of data breaches or leaks.
4. Trust and Transparency:
Blockchain Audibility: Transactions involving user data on blockchain networks are transparent and auditable. This transparency builds trust among users, knowing that their data isn’t being manipulated or misused behind closed doors.
Immutable Records: The immutability of blockchain ensures that user data history is preserved accurately, making it easier to trace any unauthorized access or changes.
5. Data Monetization and Compensation:
User Data as an Asset: In the Ownership Economy, users may have the opportunity to monetize their data by granting access to businesses or researchers. This model allows individuals to benefit from the value their data generates.
Fair Compensation: Users can negotiate fair compensation for the use of their data. This shift toward more equitable data exchange challenges the conventional model where data is harvested without compensation.
6. Decentralized Identity Verification:
Eliminating Central Authorities: Decentralized identity systems reduce reliance on centralized authorities for identity verification, enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of identity theft or data breaches.
Self-Sovereign Identity: Individuals gain self-sovereign control over their identities, reducing the need to share excessive personal information with third parties for verification purposes.
7. Challenges and Considerations:
Interoperability: To ensure widespread adoption, interoperability standards must be established to enable seamless data sharing across various platforms and services.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies must adapt to the evolving data privacy landscape and establish clear guidelines for user-controlled data management.
Security: User-controlled data systems must prioritize robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access or data loss.
In conclusion, the power of user-controlled data in Web3 and the Ownership Economy empowers individuals to protect their data privacy and regain control over their digital identities. This paradigm shift towards consent-based data sharing and decentralized identity management offers a promising solution to the ongoing challenges of data privacy and surveillance in the digital age.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Web3, metaverse, the next internet | Deloitte Insights
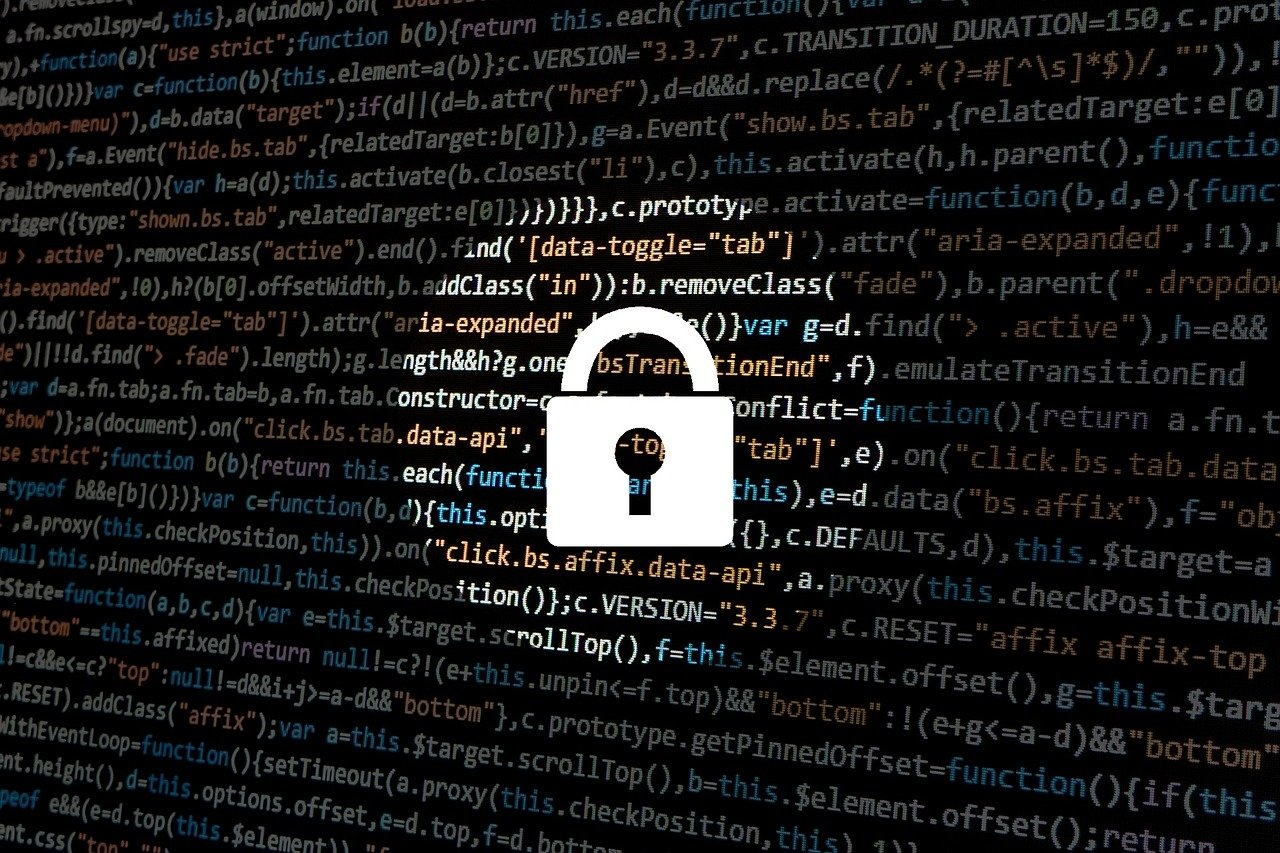

Self-Sovereign Identity
Web3 promotes the concept of self-sovereign identity, where individuals manage and verify their identities without relying on centralized authorities.
Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how we perceive and manage our online identities, ushering in the era of self-sovereign identity. In this paradigm, individuals have unprecedented control over their personal information and digital presence, without being beholden to centralized authorities or platforms. Here’s how Web3 continues to shape and empower self-sovereign identity:
Personal Data Ownership: Web3 empowers individuals to take ownership of their personal data. Instead of ceding control to centralized platforms that monetize user data, individuals have the autonomy to decide who can access their information and under what terms. This shifts the power dynamic from corporations to users.
Blockchain-Based Identity: Blockchain technology serves as the cornerstone of self-sovereign identity. It provides a secure and tamper-proof ledger for identity-related transactions and information, enhancing the trustworthiness and integrity of identity management.
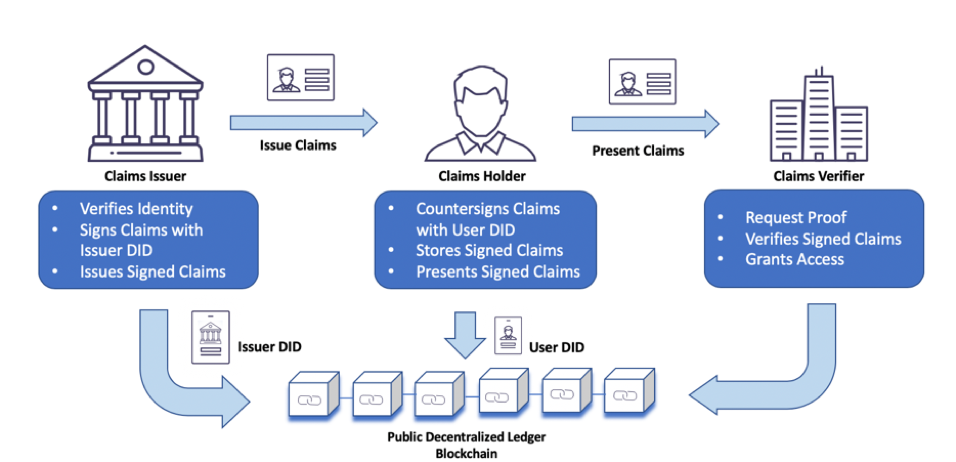
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): DIDs are a critical component of self-sovereign identity. They are unique identifiers anchored on a blockchain, allowing individuals to prove their identity without relying on third-party intermediaries. DIDs can be used across various services and platforms, enhancing interoperability.
Verifiable Credentials: Web3 introduces the concept of verifiable credentials, which are cryptographic attestations of personal information or attributes. Individuals can share these credentials selectively, providing proof of identity or qualifications without revealing unnecessary details.
Privacy by Design: Self-sovereign identity solutions are designed with privacy in mind. They minimize the exposure of personal data by only sharing the necessary information, reducing the risk of identity theft or misuse.
User-Centric Authentication: Web3 enables user-centric authentication methods, such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication, giving individuals the flexibility to choose the most secure and convenient way to prove their identity.
Cross-Platform Portability: Self-sovereign identity is not tied to a single platform or service. Users can carry their digital identities with them across different applications and services, making it easier to navigate the digital landscape seamlessly.
Interoperability: Web3 promotes interoperability among identity solutions. This means that different self-sovereign identity systems can work together, creating a cohesive and comprehensive digital identity ecosystem.
Reduced Identity Fraud: The cryptographic security of self-sovereign identity solutions makes it significantly more challenging for malicious actors to impersonate individuals or forge credentials, reducing identity fraud.
Global Accessibility: Web3’s borderless nature allows individuals to access and manage their identities from anywhere in the world. This is especially valuable for people in regions with limited access to traditional identity services.
Inclusivity: Self-sovereign identity empowers marginalized and underserved populations who may lack traditional forms of identification. It can help grant access to financial services, education, healthcare, and more.
Revocation and Control: Individuals have the power to revoke access to their personal information or credentials at any time. This control ensures that they are not tied to a single identity provider or service.
In conclusion, Web3’s promotion of self-sovereign identity is a paradigm shift with profound implications for how we manage and protect our digital identities. It empowers individuals with greater control, privacy, and security over their online presence, reducing the influence of centralized authorities and creating a more equitable and user-centric digital world. As Web3 continues to evolve, self-sovereign identity solutions are likely to become even more sophisticated and integrated into various aspects of our digital lives.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: How to take back our identities in a Web3 world | Fortune Crypto
Secure Authentication
Decentralized identity systems offer robust authentication methods that reduce the risk of identity theft and online fraud.
Decentralized identity systems represent a significant leap forward in the realm of online security and personal data protection. These systems harness the power of blockchain and distributed ledger technology to create a new paradigm of robust authentication methods, effectively mitigating the risks associated with identity theft and online fraud.
One of the standout advantages of decentralized identity systems is the enhancement of security through self-sovereign identity. In traditional online authentication methods, individuals are often required to divulge sensitive personal information to various service providers. This exposes them to the ever-present threat of data breaches, where a single breach at one service provider can lead to cascading consequences, including identity theft. Decentralized identity systems, however, adhere to the principle of self-sovereign identity, ensuring that individuals have control over their own identity data. Instead of sharing personal information, users provide cryptographic proofs that they are who they claim to be, without revealing unnecessary details. This significantly reduces the surface area for potential data breaches and identity theft.
Blockchain’s immutable ledger plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of decentralized identity systems. All identity-related transactions, such as the creation of digital credentials and their verification, are recorded on the blockchain. This ledger is tamper-proof, meaning that once information is entered, it cannot be altered or deleted without leaving a trace. This feature enhances the trustworthiness of identity data, as individuals and service providers can verify the authenticity and history of digital credentials with confidence.
Decentralized identity systems also introduce the concept of selective disclosure. Instead of presenting a complete identity profile to every service provider, users can selectively disclose only the specific information necessary for a particular transaction or interaction. For example, when verifying their age for an online purchase, users can share their age without revealing their full birthdate or other unnecessary details. This minimizes the amount of personal information exposed, reducing the risk of misuse and online fraud.
Moreover, decentralized identity systems are inherently resistant to single points of failure and hacking. Traditional centralized identity providers are prime targets for cyberattacks, as compromising a central authority can yield access to a vast trove of user data. In contrast, decentralized identity systems distribute identity data across a network of nodes, making it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to compromise the entire system.
However, the adoption and standardization of decentralized identity systems remain ongoing challenges. Achieving widespread acceptance and integration with existing digital ecosystems and regulatory frameworks is a complex task that requires collaboration among various stakeholders.
In conclusion, decentralized identity systems represent a significant advancement in online security and identity protection. By adhering to the principles of self-sovereign identity, utilizing blockchain’s immutable ledger, and enabling selective disclosure, these systems offer robust authentication methods that substantially reduce the risk of identity theft and online fraud. While challenges remain, the potential for decentralized identity systems to enhance personal data security and privacy is undeniable, promising a future where individuals have greater control and confidence in their digital identities.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: opportunities-in-the-metaverse.pdf

The Transition to Web3 and the Ownership Economy
The transition to Web3 and the Ownership Economy is still in its early stages, but its potential impact is profound. As individuals gain more control over their digital lives and assets, we can anticipate significant shifts in various industries, including finance, art, entertainment, and governance. Innovations such as decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain-based governance, and tokenized communities are already beginning to reshape the digital landscape.
However, this transformation also brings challenges, including regulatory considerations, cybersecurity concerns, and the need for widespread blockchain adoption. As Web3 continues to evolve, it is crucial to strike a balance between innovation, security, and regulatory compliance.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Potential of Web3 | McKinsey

Conclusion
In conclusion, Web3 and the Ownership Economy represent a paradigm shift in how we perceive and interact with the digital world. NFTs, digital assets, and user-controlled digital identities empower individuals and redefine the concept of ownership in the digital age. While challenges lie ahead, the potential for a more decentralized, user-centric, and inclusive digital future is within reach as we navigate the exciting possibilities of Web3.
In conclusion, Web3 and the Ownership Economy mark a profound and transformative shift in our digital landscape, redefining the very essence of ownership and control. The concepts of NFTs, digital assets, and user-controlled digital identities are catalysts for a more decentralized, user-centric, and inclusive digital future. However, as we embrace these exciting possibilities, it’s crucial to acknowledge and address the challenges and considerations that accompany this paradigm shift:
1. Regulatory Evolution: The regulatory environment surrounding Web3 is still evolving. Striking the right balance between innovation and protection will be an ongoing challenge. Regulatory bodies must adapt to the changing landscape while ensuring users’ rights and interests are safeguarded.
2. Security and Trust: The security of blockchain systems, user-controlled digital identities, and the integrity of digital assets are paramount. Building and maintaining trust in these technologies is essential for widespread adoption.
3. Interoperability: As the Web3 ecosystem expands, ensuring that different platforms, applications, and blockchain networks can seamlessly interact is vital. Interoperability standards will play a critical role in connecting the various components of the Ownership Economy.
4. Education and Accessibility: Web3 introduces complex concepts and technologies. Bridging the knowledge gap and ensuring accessibility for all users, regardless of their technical background, will be essential for the successful transition to this new paradigm.
5. Ethical Data Use: While user-controlled data promises greater privacy and control, it also places responsibility on users to make informed decisions about their data. Promoting ethical data practices and informed consent is crucial.
6. Scalability: As Web3 gains traction, scalability will be a key concern. Ensuring that blockchain networks can handle increased user activity and transaction volumes is vital for a seamless user experience.
7. Inclusivity: The Ownership Economy should not exacerbate existing inequalities. Efforts must be made to ensure that Web3 technologies are inclusive and accessible to individuals from all backgrounds.
Despite these challenges, the potential for a more equitable, transparent, and user-driven digital future is undeniable. Web3 and the Ownership Economy empower individuals with newfound control over their digital lives, data, and assets. It presents a vision where the internet serves as a tool for liberation, innovation, and empowerment, returning the agency to the users who form its backbone.
As we navigate this exciting frontier, it’s crucial to remain vigilant, adaptable, and collaborative. With the right balance of innovation and responsibility, Web3 and the Ownership Economy can shape a digital era that truly belongs to its users, ushering in a new age of ownership and agency in the digital age.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: NFT Digital Identity: Empowering Identity Ownership
More links
You can also read more about this here: Web3, metaverse, the next internet | Deloitte Insights
