Table of Contents
Moving Beyond the Basics
Safety has always been a paramount concern in the world of railroads. As a critical mode of transportation for both passengers and freight, the rail industry has continuously strived to enhance safety standards. In recent years, significant advancements in railroad engineering and design have led to safer rail systems, reduced accidents and a more secure future for rail travel. This article explores the innovative technologies and strategies that are shaping the future of railroad safety.
Safety has always been a paramount concern in the world of railroads and for good reason. Railroads are an integral part of global transportation, serving as the backbone for the movement of goods and people. Over the years, the rail industry has remained committed to improving safety standards to ensure the well-being of passengers, workers and the communities through which trains pass. In recent years, there has been a notable acceleration in the pace of innovation in railroad engineering and design, resulting in safer rail systems, reduced accidents and a more secure future for rail travel. This article delves into the multifaceted realm of railroad safety, examining the remarkable strides made in technology and strategies that are reshaping the landscape.
Advanced Risk Assessment and Planning
Modern railroads have embraced sophisticated risk assessment tools and planning techniques. These systems use historical data, weather forecasts and real-time information to anticipate potential hazards. They allow rail operators to make proactive decisions, such as rerouting trains or adjusting schedules to avoid adverse conditions or high-risk areas.
Predictive Maintenance
Maintenance is a critical aspect of railroad safety. Advances in predictive maintenance techniques leverage sensors and data analytics to monitor the condition of tracks, rolling stock and infrastructure. By detecting issues before they become critical, railroads can schedule maintenance more efficiently, reducing the risk of accidents caused by equipment failures.
Education and Training
Ensuring that railroad workers are well-trained and educated on safety protocols is a top priority. Training programs now incorporate virtual reality simulations, allowing workers to practice emergency scenarios in a controlled environment. This hands-on training enhances their ability to respond swiftly and effectively in real-life situations.
Community Engagement
Railroads are increasingly engaging with the communities they serve to raise awareness about safety. Educational initiatives, public outreach and collaboration with local authorities help reduce the risk of accidents involving pedestrians and vehicles at rail crossings. The goal is to create a culture of safety that extends beyond the rail industry itself.
Environmental Considerations
Safety isn’t just about preventing accidents; it also involves mitigating environmental impacts. Railroads are adopting eco-friendly practices, such as the use of cleaner locomotives and the implementation of spill containment measures for hazardous cargo. These initiatives safeguard the environment and prevent potential disasters.
Cross-Industry Collaboration
Railroad safety is a shared responsibility. The rail industry collaborates closely with regulators, technology providers and other stakeholders to develop and implement safety standards. This collaborative approach ensures that the best practices and innovations from various sectors are applied to railroad safety.
In conclusion, safety in the world of railroads is a dynamic, evolving field that has made significant strides in recent years. The combination of advanced technology, predictive maintenance, robust training, community engagement, environmental considerations and cross-industry collaboration is creating a safer and more secure future for rail travel. As the rail industry continues to adapt and innovate, it reaffirms its commitment to ensuring that railroads remain a safe and reliable mode of transportation for generations to come.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: South Coast Rail | Projects | MBTA

Positive Train Control (PTC)
The Digital GuardianOne of the most notable advancements in railroad safety is the implementation of Positive Train Control systems. PTC is a GPS-based technology that continuously monitors and controls train movements. It can automatically apply brakes to prevent collisions, overspeed incidents and unauthorized access to tracks. PTC is a game-changer for safety, reducing the risk of human error and enhancing the overall safety of rail operations.
The Digital Guardian: Transforming Railroad Safety
In an age characterized by technological innovation, the railroad industry has embraced cutting-edge solutions to enhance safety and mitigate risks. Among these advancements, one of the most remarkable is the implementation of Positive Train Control (PTC) systems. PTC represents a seismic shift in how railroads approach safety, leveraging GPS-based technology and digital prowess to create a vigilant and responsive digital guardian over rail operations.
At its core, PTC serves as a relentless sentinel, continuously monitoring and controlling train movements with unparalleled precision. This real-time surveillance capability revolutionizes the way railroads manage their operations, significantly reducing the potential for accidents caused by human error or unexpected circumstances.
One of the primary functions of PTC is collision prevention. By instantaneously assessing the position and speed of trains on the network, PTC can calculate potential collision scenarios. In the event that two trains approach each other on the same track or if a train encounters an obstacle, PTC has the capability to automatically apply the brakes, bringing the train to a safe stop. This rapid response is a game-changer in the realm of safety, as it dramatically reduces the risk of catastrophic accidents caused by inattentiveness, miscommunication or unforeseen circumstances.
Overspeed incidents, another significant safety concern, are also effectively addressed by PTC. The system continuously monitors a train’s speed and location, cross-referencing it with predetermined safety parameters. Should a train exceed the allowable speed limit for a specific section of track, PTC can initiate automatic braking, preventing the train from endangering itself or others. This feature not only enhances safety but also optimizes fuel efficiency, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Unauthorized access to railway tracks is a persistent safety challenge. Trespassing incidents and attempts to gain unauthorized access to the rail network can lead to tragic consequences. PTC acts as a digital gatekeeper, closely monitoring track access points and alerting authorities to any breaches in real-time. By creating a virtual barrier that deters unauthorized intrusions, PTC enhances the security of railway operations, safeguarding both passengers and personnel.
The implementation of PTC is not merely a technological milestone; it is a testament to the railroad industry’s unwavering commitment to safety. By harnessing the power of digital technology, PTC transforms railroads into safer and more efficient transportation networks. It addresses longstanding safety challenges, mitigates risks and instills a sense of confidence in passengers, regulators and the industry as a whole.
As we look ahead, the digital revolution in railroad safety continues to evolve. With the integration of machine learning, artificial intelligence and predictive analytics, PTC systems are becoming even more sophisticated and responsive. This ongoing innovation ensures that the digital guardian of railroad safety remains vigilant, adaptive and dedicated to preserving human lives and the integrity of rail operations. In an era where technology increasingly shapes our world, the digital guardian of railroads stands as a beacon of progress and a symbol of unwavering commitment to safety.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Positive Train Control (PTC) | FRA
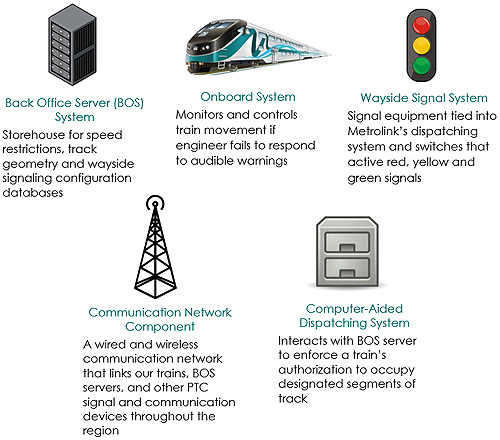
Delving Deeper
Advanced Signaling SystemsModern signaling systems have evolved significantly. Traditional signal lights have been replaced with state-of-the-art digital signaling systems that offer real-time data transmission and precise control. These systems can detect obstacles on the tracks, such as debris or vehicles and communicate instantly with train operators to prevent accidents.
The advent of advanced signaling systems represents a pivotal leap forward in the realm of rail safety and efficiency. While traditional signal lights served their purpose admirably, the emergence of state-of-the-art digital signaling systems has ushered in a new era of precision and responsiveness in rail operations.
At the heart of these modern signaling systems lies the marvel of digital technology. Unlike their mechanical predecessors, digital systems are equipped with real-time data transmission capabilities, allowing for seamless communication between different components of the rail network. This instantaneous flow of information empowers rail operators with a level of control and situational awareness that was previously unimaginable.
One of the most remarkable features of these digital systems is their ability to detect potential obstacles on the tracks with a remarkable degree of accuracy. Sensors strategically placed along the rail corridors continuously monitor the rails, identifying any anomalies or obstructions that may pose a risk to train safety. Whether it’s a fallen tree branch, a piece of debris or even a vehicle that has inadvertently strayed onto the tracks, these advanced systems can swiftly detect and assess the situation.
The real-time communication capabilities of these systems are nothing short of revolutionary. When an obstacle is detected, the system springs into action, sending instant alerts to train operators. This rapid exchange of information enables operators to take proactive measures to avert accidents. Trains can be brought to a halt or redirected to alternative tracks, ensuring the safety of passengers and crew.
Beyond the critical role they play in safety, digital signaling systems also enhance operational efficiency. They enable trains to maintain precise schedules by optimizing speed and routing based on real-time conditions. This not only reduces delays but also contributes to fuel efficiency, lower emissions and overall cost savings.
As we embrace these advanced signaling systems, we witness a harmonious synergy between human expertise and technological innovation. The vigilance and experience of train operators are now bolstered by the precision and responsiveness of digital systems. Together, they create a formidable partnership that enhances both the safety and efficiency of rail travel.
In an era where rapid technological advancements are reshaping the world, the evolution of signaling systems serves as a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in the rail industry. These systems are not just the future of rail; they are a shining example of how innovation can transform an industry, making it safer, more efficient and better equipped to meet the evolving needs of a changing world.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Leaders or followers? Developments in commercial vehicle …

Added Perspective
Collision Avoidance TechnologiesCollision avoidance technologies have come a long way. Radar, lidar and sensor-based systems can detect obstacles in a train’s path and trigger automatic braking or route changes to avoid collisions. These systems provide an additional layer of safety, especially in adverse weather conditions or low-visibility scenarios.
Collision Avoidance Technologies:
The evolution of collision avoidance technologies represents a remarkable leap in enhancing the safety and efficiency of rail transportation. As we delve deeper into this innovation, it becomes evident that these systems are not just limited to preventing collisions but also hold the potential to revolutionize various aspects of railway operations:
Precision and Efficiency: Beyond their primary function of collision avoidance, these technologies are adept at optimizing railway operations. They enable precise control over speed, ensuring that trains maintain optimal distances and follow schedules with minimal deviations. This not only improves safety but also enhances the efficiency and punctuality of rail services.
Weather Resilience: Adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain, snow or fog, can pose significant challenges for rail travel. Collision avoidance technologies are equipped to perform consistently in these conditions, mitigating the impact of inclement weather on rail operations. By providing real-time data and automated responses, these systems bolster railway resilience during storms or low-visibility scenarios.
Reduced Human Error: Human factors have historically played a role in train accidents. Collision avoidance technologies serve as a safeguard against human error, complementing the skills and vigilance of train operators. This reduction in the potential for human-induced accidents significantly contributes to passenger and crew safety.
Enhanced Capacity: The integration of these systems can lead to increased railway capacity. By ensuring that trains can safely operate closer together, railways can transport more passengers and goods while maintaining safety standards. This enhancement in capacity supports economic growth and sustainability.
Predictive Maintenance: Sensor-based technologies can monitor the condition of rail tracks and rolling stock in real time. By detecting wear and tear early, they enable predictive maintenance, preventing breakdowns and minimizing service disruptions. This proactive approach translates into cost savings and improved reliability.
Data-Driven Insights: The wealth of data collected by these systems offers valuable insights for railway operators. Analyzing this data can lead to better decision-making, route optimization and infrastructure planning. It also facilitates continuous improvement in safety protocols and system performance.
Integration with IoT: The internet of things (IoT) is increasingly being integrated into rail networks, allowing for seamless communication between trains, tracks and control centers. This interconnectedness enables a more comprehensive and responsive approach to collision avoidance, as well as improved management of rail assets.
Global Standardization: As collision avoidance technologies become more prevalent, there is a growing push for global standardization. This ensures compatibility and interoperability across different railway systems, fostering safer and more efficient cross-border rail travel.
In conclusion, collision avoidance technologies have evolved into a pivotal component of modern rail systems, far surpassing their initial purpose. They not only prevent accidents but also bolster efficiency, resilience and data-driven decision-making in the railway industry. As these technologies continue to advance, the future of rail transportation promises to be safer, more efficient and increasingly interconnected with the broader landscape of smart transportation.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Rail: Getting On Track for Decarbonization | FRA

Further Insights
Improved Track DesignThe design and maintenance of railroad tracks have also seen significant improvements. Advances in materials and track geometry have led to tracks that are more durable, stable and resistant to wear and tear. These enhancements reduce the likelihood of derailments and ensure a smoother and safer ride.
The evolution of railroad track design and maintenance represents a pivotal chapter in the ongoing quest for safer and more efficient rail transportation. The tracks themselves are the silent heroes of the rail network, bearing the weight of heavy trains and facilitating the seamless flow of goods and passengers. As technology and engineering have advanced, so too has our ability to enhance the performance and longevity of these vital arteries of transportation.
One of the key advancements lies in the materials used in track construction. Modern tracks often incorporate high-strength steel, concrete and composite materials that are exceptionally durable and resistant to the wear and tear caused by the passage of trains. These materials have dramatically extended the lifespan of tracks, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing disruptions to rail services.
Beyond the choice of materials, innovations in track geometry have been transformative. Precision engineering and computer-aided design have allowed for tracks to be laid with an unprecedented degree of accuracy. This precise alignment not only enhances stability but also contributes to the reduction of friction and wear on wheels and tracks. Consequently, trains can operate more smoothly, quietly and efficiently, while the risk of derailments is significantly mitigated.
Maintenance practices have also seen remarkable improvements. Regular inspections using advanced technologies like ultrasonic testing and track geometry cars enable operators to detect issues before they escalate. This proactive approach to maintenance ensures that minor defects are addressed promptly, preventing them from evolving into major safety concerns.
The net result of these advancements is a rail network that is not only safer but also more environmentally friendly. Reduced wear and tear translate to less frequent replacement of track components, which in turn reduces resource consumption and waste. Moreover, the smoother ride afforded by modern track design decreases energy consumption, making rail transportation an even more sustainable mode of travel.
In conclusion, the improvements in track design and maintenance represent a silent revolution in the world of rail transportation. These advancements have not only bolstered safety but have also made rail travel more reliable, efficient and environmentally responsible. As the rail industry continues to innovate and invest in track infrastructure, it ensures that the tracks of the future will be even more durable, stable and capable of supporting the ever-growing demands of the modern world.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: The rail sector’s changing maintenance game

Clarification
Enhanced Passenger SafetyPassenger safety has received special attention in recent years. Modern passenger train carriages are equipped with advanced safety features such as crumple zones, reinforced structures and improved seating arrangements to protect passengers in the event of an accident. Moreover, emergency evacuation procedures and systems have been refined to ensure swift and efficient responses.
Enhancing passenger safety in modern rail travel is a top priority and the relentless pursuit of safer journeys has led to remarkable advancements in the design and technology of passenger train carriages.
One of the most significant strides in this regard is the incorporation of crumple zones and reinforced structures in train carriages. These engineering marvels are akin to protective shields for passengers. Crumple zones are strategically designed sections of the train that deform upon impact, absorbing and dissipating the energy generated during a collision. This ingenious design helps to minimize the force transferred to passengers, reducing the risk of injury in the event of an accident. Reinforced structures further bolster the train’s integrity, maintaining passenger compartments’ structural integrity even under significant external forces.
Seat design and arrangements have also evolved to enhance passenger safety and comfort. Seats are meticulously engineered to withstand sudden deceleration forces, reducing the risk of occupant injury. Moreover, innovative seat designs aim to minimize the risk of passenger ejection during a collision, keeping travelers securely in their seats.
In addition to the physical safety features, emergency evacuation procedures and systems have undergone substantial refinements. Train operators and crews are trained rigorously to ensure swift and efficient responses in the event of emergencies. Evacuation routes are well-marked and easily accessible and train carriages are equipped with emergency communication systems to facilitate rapid coordination with rescue teams.
Furthermore, the integration of digital technology plays a pivotal role in passenger safety. Modern trains are equipped with advanced sensors and communication systems that continuously monitor various parameters, from track conditions to potential obstacles. In the event of a hazard or obstruction on the tracks, these systems can trigger automatic emergency braking, mitigating the risk of accidents.
It’s important to note that passenger safety isn’t just a concern within the confines of the train itself; it extends to the stations and platforms as well. Railway stations are designed with safety in mind, featuring barriers, warning systems and clear signage to keep passengers safe while boarding and disembarking.
In conclusion, the commitment to passenger safety in modern rail travel is reflected in a comprehensive approach that encompasses engineering, technology and procedural enhancements. From crumple zones and reinforced structures to refined seating arrangements and improved evacuation procedures, every aspect of rail travel is meticulously designed to protect passengers. As technology continues to advance, rail travel will undoubtedly become even safer, ensuring that passengers can embark on their journeys with confidence in their well-being.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: California High-Speed Rail 2023 Project Update Report

Moving Beyond the Basics
Driver Assistance SystemsFor railroads that have human operators, advanced driver assistance systems are making a significant impact. These systems provide operators with real-time information, alerting them to potential hazards, speed limits and track conditions. This technology acts as a safety net, helping operators make informed decisions and avoid accidents.
Driver Assistance Systems are ushering in a transformative era for railroads that rely on human operators. These cutting-edge systems are revolutionizing safety protocols and operational efficiency, with profound implications for the entire industry.
1. Real-Time Insights: Driver Assistance Systems leverage state-of-the-art sensors, cameras and monitoring technologies to provide operators with a comprehensive view of their surroundings. This real-time data encompasses crucial information such as track conditions, weather updates and speed limits. Armed with these insights, operators can make informed decisions that prioritize safety and efficiency.
2. Hazard Detection and Prevention: Perhaps the most vital aspect of these systems is their ability to detect and prevent potential hazards. They serve as vigilant sentinels, constantly scanning the tracks for obstacles, obstructions or irregularities. When a danger is identified, the system promptly alerts the operator, giving them precious seconds to react and mitigate risks.
3. Enhanced Safety: Driver Assistance Systems are not intended to replace human operators but rather to enhance their capabilities. By acting as an additional layer of safety, these systems contribute to a reduction in accidents and near misses. This increased safety benefits both crew members and passengers, instilling confidence in the reliability of rail travel.
4. Efficiency and Precision: Beyond safety, these systems also enhance the operational efficiency of railroads. They enable operators to maintain optimal speeds, adhere to schedules and minimize fuel consumption. This results in a more punctual, cost-effective and environmentally friendly rail service.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making: The data collected by Driver Assistance Systems is a treasure trove of insights that can be harnessed for continuous improvement. Railroads can analyze this data to refine their operations, identify trends and proactively address maintenance issues, ultimately leading to higher levels of service quality and reliability.
6. Adaptability and Scalability: These systems are designed to adapt to various rail environments and can be scaled to accommodate different types of rolling stock and infrastructure. Whether operating in urban transit networks or long-distance freight routes, Driver Assistance Systems can be tailored to suit the specific needs of each railroad.
In summary, Driver Assistance Systems represent a paradigm shift in railroad operations. They empower human operators with a wealth of real-time information and threat detection capabilities, creating a safer and more efficient rail travel experience. As the technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of railroads, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of modern transportation while upholding the highest standards of safety and reliability.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: FACT SHEET: The American Jobs Plan | The White House

Providing More Context
The safety landscape of railroads has undergone a remarkable transformation, thanks to the relentless pursuit of innovation in engineering and design. As the industry continues to invest in cutting-edge technologies and practices, the future of rail travel looks brighter and safer than ever before. With advancements like Positive Train Control, advanced signaling systems, collision avoidance technologies, improved track design, enhanced passenger safety measures and driver assistance systems, railroads are poised to set new benchmarks in safety standards. These advancements not only protect the lives of passengers and rail workers but also promote the sustainability and efficiency of rail transportation, ensuring that safety remains a top priority on the rails.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Improving Intersections for Pedestrians and Bicyclists: Informational …

More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: South Coast Rail | Projects | MBTA
