Table of Contents
The era of steam locomotives is a remarkable chapter in the history of transportation and engineering. These iconic machines, with their billowing plumes of steam and rhythmic chugging, revolutionized the way people and goods were transported during the 19th and early 20th centuries. In this article, we will explore the fascinating mechanics and engineering principles that powered these classic trains and forever changed the world.
“The era of steam locomotives stands as an indelible testament to the prowess of transportation and engineering during the 19th and early 20th centuries. These iconic machines, with their billowing plumes of steam, rhythmic chugging and awe-inspiring presence, were more than just vehicles; they were the driving force behind a revolution in travel and industry. In this article, we embark on a journey through time to delve into the captivating mechanics and engineering principles that powered these classic trains, forever changing the world and leaving an enduring legacy.
The Birth of Steam Power: The advent of steam power revolutionized transportation. Steam locomotives harnessed the power of pressurized steam to drive massive, rolling engines. This innovative concept laid the foundation for a new era of mobility and laid the tracks for the modern railway system.
Machinery in Motion: Understanding the mechanics of steam locomotives is akin to unlocking the secrets of a mechanical marvel. The intricate interplay of pistons, cylinders and steam valves, all orchestrated with precision, allowed these machines to convert heat energy into mechanical motion.
The Iron Horse: The locomotive earned the moniker ‘Iron Horse’ due to its sheer power and durability. These steam giants could haul immense loads over long distances, making them instrumental in the industrialization of nations and the expansion of frontiers.
Engineering Marvels: Steam locomotives were engineering marvels of their time, designed with meticulous attention to detail. Their boilers, fireboxes and smokestacks were carefully crafted to maximize efficiency and power while adhering to the principles of safety.
The Rhythmic Chug: The rhythmic chugging of a steam locomotive, driven by the rotation of massive drive wheels, became synonymous with the romance of train travel. The sound of the engine was both a melody and a heartbeat, echoing across vast landscapes as trains conquered mountains and plains.
Connecting a Nation: Steam locomotives were instrumental in connecting vast regions and unifying nations. They facilitated the movement of people, goods and ideas, catalyzing economic growth, cultural exchange and westward expansion.
The Legacy Lives On: While the era of steam locomotives has largely given way to modern electric and diesel trains, their legacy endures. Historic steam locomotives are lovingly preserved in museums and heritage railways, offering a glimpse into a bygone era of travel.
A Source of Inspiration: The era of steam locomotives continues to inspire engineers, artists and enthusiasts. Their timeless beauty and mechanical ingenuity serve as a wellspring of inspiration for those who appreciate the marriage of art and engineering.
Preserving History: Efforts to preserve and restore steam locomotives highlight the enduring fascination with these machines. Restoration projects breathe new life into vintage locomotives, ensuring that future generations can experience the awe-inspiring sights and sounds of a bygone era.
An Enduring Symbol: Steam locomotives remain an enduring symbol of human achievement. They represent an era when innovation, determination and daring exploration reshaped the world. Their story is a testament to the power of engineering to shape the course of history.
In conclusion, the era of steam locomotives is a captivating chapter in the annals of transportation and engineering. These magnificent machines, with their majestic plumes of steam and rhythmic chugging, continue to capture our imagination and remind us of a time when innovation and ambition knew no bounds. As we delve into the fascinating mechanics of steam locomotives, we pay homage to the pioneers and engineers whose visionary work forever changed the world, leaving an indelible mark on the tapestry of human history.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: How Steam Locomotives Really Work – P. W. B. Semmens; A. J. …
The Birth of Steam Locomotives
The birth of steam locomotives can be traced back to the late 18th century when engineers and inventors sought more efficient ways to transport heavy loads over long distances. The steam engine, pioneered by figures like James Watt and Richard Trevithick, provided the essential foundation for locomotive development. However, it was George Stephenson’s “Rocket” that is often regarded as the first modern steam locomotive, with its innovative design and improved efficiency.
The late 18th century marked a turning point in the history of transportation as engineers and inventors grappled with the need for more efficient methods of moving heavy loads across long distances. This period of innovation and experimentation laid the groundwork for the eventual emergence of the steam locomotive as a transformative force.
James Watt and Richard Trevithick, two pioneering figures in the development of steam technology, played pivotal roles in advancing the concept of steam-powered transportation. James Watt’s improvements to the steam engine’s design, particularly his separate condenser, significantly enhanced its efficiency and made it a viable power source for various applications. However, the early steam engines were stationary and not yet applied to locomotion.
Richard Trevithick, a Cornish engineer, can be credited with creating one of the earliest steam-powered vehicles. In 1804, he built the “Puffing Devil,” a high-pressure steam engine mounted on four wheels, which could carry passengers and cargo. While this was a remarkable achievement, it was not yet a true locomotive in the sense that it operated on tracks.
The true breakthrough in steam locomotion came with the work of George Stephenson. His creation, the “Rocket,” marked a significant leap forward in locomotive design and efficiency. The “Rocket,” built in 1829 for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, is often hailed as the world’s first modern steam locomotive.
The “Rocket” introduced several innovative features that set it apart from its predecessors. These innovations included a multi-tubular boiler, exhaust steam used to drive a blast pipe for increased draught and flanged wheels to guide the locomotive along the tracks. Perhaps most importantly, it demonstrated a level of efficiency and speed that made it a practical choice for railway transport. The “Rocket” reached speeds of up to 29 miles per hour during its trial run, a remarkable achievement at the time.
George Stephenson’s “Rocket” not only proved the viability of steam locomotion but also set the standard for subsequent locomotive development. Its design principles became the foundation for the steam locomotives that would dominate railway systems worldwide in the decades to come.
The birth of steam locomotives in the late 18th and early 19th centuries thus marked a pivotal moment in the history of transportation. It represented a shift from reliance on traditional horse-drawn wagons and canals to a new era of rapid, efficient and reliable railway travel. The legacy of these early pioneers and their innovative locomotives endures in the railways that crisscross the globe today, reminding us of the transformative power of human ingenuity and engineering progress.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Bill Withuhn writes the essential steam book – Classic Trains …

Boiler
The boiler is the heart of a steam locomotive. It contains water, which is heated to produce steam. The steam generated in the boiler is under high pressure and serves as the locomotive’s driving force.
The boiler, often referred to as the beating heart of a steam locomotive, plays a central role in the graceful dance of mechanics and physics that propels these majestic machines forward. Within the sturdy confines of the boiler, a remarkable transformation takes place, with water being the protagonist of this steaming drama.
At the core of the boiler’s function lies the fundamental principle of thermodynamics. Water, stored in the boiler’s reservoir, is carefully and precisely heated to the point of transformation. As the heat permeates the water, it undergoes a remarkable change, transitioning from a calm, liquid state to a restless, invisible vapor – steam.
This transition is not just a mere change of phase; it’s the birth of power. The steam, now at high pressure, embodies the locomotive’s life force, eagerly awaiting its chance to escape the confines of the boiler. It surges forth with an incredible force, venting through carefully regulated valves and channels its energy into the locomotive’s pistons.
As the steam enters the cylinders, it encounters an assembly of precisely machined components, including valves, pistons and linkages. Here, the brute force of the steam’s high-pressure state is harnessed, meticulously converted into mechanical motion. The pistons are set into a rhythmic dance, driving the locomotive’s wheels to spin with a hypnotic, circular grace.
The boiler, in its unassuming form, thus serves as the crucible where water is transformed into power and where raw potential becomes motion. The mastery of engineering required to control this transformation is nothing short of remarkable. Every aspect of the boiler’s design and operation, from the choice of materials to the control of temperatures and pressures, is a testament to the ingenuity and precision of locomotive engineers.
Beyond its mechanical function, the boiler encapsulates the essence of steam locomotives – a fusion of science and art, form and function. It represents an era when steam-driven marvels crisscrossed continents, their boilers providing the rhythmic heartbeat that powered the dreams of progress and connectivity.
In every puff of steam, the boiler whispers a tale of innovation and perseverance. It reminds us that in the heart of every machine, there’s a story waiting to be told – a story of water turned to steam and steam turned to power, propelling the iron horses of yesteryears along the tracks of history.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Steam release question – Trains Magazine – Trains News Wire …

Firebox
The firebox is located at the front of the locomotive and houses the fire, usually fueled by coal or wood. The heat generated in the firebox is used to boil water in the boiler and produce steam.
The firebox, often referred to as the heart of a locomotive, holds a pivotal position in the world of steam engines. Positioned at the locomotive’s front, it serves as both the source and catalyst for the locomotive’s power. Here, a fiery inferno blazes to life, fueled by the steady consumption of coal or wood. This humble but essential chamber embodies the raw energy and ingenuity that powered the industrial revolution and transformed transportation.
Within the firebox, the intense heat generated by the combustion of fuel is harnessed with precision. The primary function of this scorching crucible is to ignite and sustain a roaring fire, reaching temperatures high enough to turn water into steam. This process forms the cornerstone of steam locomotion, a technology that reshaped the world by enabling faster, more efficient and long-distance transportation.
The firebox’s radiant heat bathes the boiler, a massive vessel nestled behind it, in an unrelenting warmth. This boiler contains a vast reservoir of water and it is the heat from the firebox that imparts life to this otherwise tranquil liquid. As the flames dance and the fire rages, the water begins its remarkable transformation. Gradually, it heats to a rolling boil, sending clouds of steam billowing forth in a majestic display.
It is this steam that becomes the locomotive’s muscle, the driving force behind its movement. The pressure of the expanding steam is harnessed, channeled and directed with remarkable precision to move the locomotive’s massive wheels. These wheels, in turn, grip the rails with unwavering determination, propelling the locomotive and its cargo along the tracks, be it across vast landscapes, through rugged terrain or into bustling cities.
In essence, the firebox is not just a utilitarian component of a steam locomotive; it embodies the power of human innovation, engineering prowess and sheer determination. It symbolizes the fiery spirit of progress that marked the era when steam locomotives ruled the rails. Beyond its physical presence, the firebox is a timeless reminder of how the marriage of fire and water, of heat and steam, revolutionized transportation, reshaped economies and connected communities in ways that continue to inspire awe and admiration to this day.
You can also read more about this here: How steam locomotives work | Trains Magazine
Cylinders
Steam is directed from the boiler to the cylinders, where it expands and pushes pistons. These pistons are connected to the locomotive’s wheels, converting the steam’s energy into mechanical motion.
The operation of a steam locomotive is a marvel of engineering, where the controlled release and expansion of steam play a central role in propelling these iron giants forward. This process, driven by the principles of thermodynamics, transforms the latent energy within the steam into powerful mechanical motion that drives the locomotive’s wheels. Let’s dive deeper into this fascinating mechanism:
“The heart of a steam locomotive lies in its ability to harness the energy locked within steam and convert it into the mechanical power required to set the wheels in motion. This ingenious process relies on a series of intricate steps that unfold within the locomotive’s cylinders and pistons, showcasing the beauty of engineering and the principles of thermodynamics in action.”
Steam Generation: The journey begins in the locomotive’s boiler, where water is heated to generate steam. This boiler, often fueled by coal or other combustible materials, serves as the vessel that transforms water into high-pressure steam. The release of this steam is the locomotive’s source of power.
Steam Direction: The high-pressure steam generated in the boiler is directed through a series of valves and pipes to reach the locomotive’s cylinders. These cylinders are strategically positioned to harness the force of the steam for maximum efficiency.
Expansion and Pressure: As the high-pressure steam enters the cylinders, it encounters pistons that are free to move within the cylinder. The pressure of the steam forces these pistons to move, initiating the process of expansion. This expansion is a fundamental principle of thermodynamics, where the steam’s energy is converted into mechanical work.
Pushing Pistons: The expanding steam pushes against the pistons, driving them outward within the cylinders. This action represents the conversion of thermal energy from the steam into kinetic energy, which translates to the motion of the pistons.
Connecting Rods: The pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive’s driving wheels through connecting rods. As the pistons move back and forth within the cylinders, they transmit this motion to the connecting rods, which, in turn, act on the locomotive’s wheels.
Wheel Rotation: The motion transmitted by the connecting rods sets the locomotive’s wheels into motion. The turning of the wheels provides the locomotive with the traction necessary to move forward along the tracks.
Power and Forward Movement: The result of this intricate process is the locomotive’s forward movement. The power generated by the expansion of steam within the cylinders propels the locomotive, allowing it to pull heavy loads, traverse challenging terrain and transport passengers or cargo across vast distances.
Regulation and Control: Engineers and locomotive crews play a crucial role in regulating the flow of steam, adjusting the pressure and ensuring the locomotive operates efficiently and safely. The art of steam locomotive operation requires skill and experience to optimize performance.
In conclusion, the operation of a steam locomotive is a captivating dance between physics and engineering, where the transformation of steam’s latent energy into mechanical motion powers these magnificent machines. The rhythmic hiss of steam, the rhythmic movement of pistons and the relentless churning of wheels all combine to create an enduring symbol of industrial innovation and human ingenuity. Each journey of a steam locomotive is a testament to the elegant marriage of science and engineering that continues to captivate enthusiasts and evoke a sense of wonder.
You can also read more about this here: Computerised Steam Locomotive

Valves
Valves control the flow of steam into and out of the cylinders. They determine the direction and power of the locomotive’s movement.
Valves play a pivotal role in the intricate dance of steam locomotion. These mechanical marvels are the conductors of power, orchestrating the ebb and flow of steam with precision. As they control the flow of steam into and out of the cylinders, they are the locomotive’s maestros, directing its path and regulating its might. Without these valves, the locomotive would be mute, unable to embark on its journeys and the railroads would fall silent, bereft of the rhythm of progress. In the hands of skilled engineers, these valves transform steam into locomotive poetry, propelling the wheels of industry and history forward.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Steam release question – Trains Magazine – Trains News Wire …

Tender
The tender is a separate car attached to the locomotive, carrying fuel (coal or wood) and water. It supplies the necessary resources for the locomotive’s operation during long journeys.
The tender, a distinctive companion to the locomotive, plays a vital role in ensuring the seamless operation of steam engines on extended journeys. Serving as a dedicated car permanently affixed to the locomotive, its primary function revolves around the transportation and provision of essential resources: fuel, typically coal or wood and water.
In the era when steam locomotives reigned supreme, the tender was not merely a supplementary car; it was the lifeblood of the locomotive. The supply of coal or wood was indispensable for the generation of steam in the locomotive’s boiler, the source of power that propelled the wheels and drove the train forward. Without a steady source of fuel, the locomotive’s capabilities would come to a grinding halt, making the tender’s role pivotal in sustaining the train’s momentum.
Additionally, the tender also carried a substantial quantity of water. Water, when heated within the locomotive’s boiler, turned into steam, which, in turn, powered the locomotive’s pistons and drive wheels. The tender’s reservoir of water was not just for the locomotive’s immediate consumption but also a strategic reserve for the journey. It enabled the steam engine to cover long distances without frequent stops for refilling, a crucial advantage in the era when rail travel was essential for cross-country transportation.
In essence, the tender was not a mere appendage to the locomotive but a critical component, enabling steam engines to conquer vast distances and connect distant regions. Its role in the grand narrative of railway history is a testament to the innovation and engineering excellence that defined the age of steam locomotion, forever shaping the way we view and appreciate the evolution of rail transport.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Ugears 70058 3D Express Steam Locomotive … – Amazon.com

Operating a Steam Locomotive
The operation of a steam locomotive involves a carefully orchestrated process:
The operation of a steam locomotive involves a carefully orchestrated process, a mesmerizing blend of engineering precision and artistry that has left an indelible mark on the history of transportation. At its core, this process is a symphony of elements working in harmony, showcasing the beauty of 19th and early 20th-century industrial innovation.
First and foremost, the heart of the locomotive is its massive boiler. This vessel, typically crafted from robust steel, serves as the crucible where water is heated to produce the steam that powers the engine. The firing of coal or wood inside the firebox generates the intense heat required to turn this water into high-pressure steam. The rhythmic stoking of the fire by skilled firemen is akin to a dance, a delicate balance that maintains the ideal temperature and pressure for optimal locomotive performance.
Once the steam is generated, it is routed through a complex network of pipes and valves to reach the cylinders. Here, the true magic happens as the expansive force of the steam is harnessed to drive the massive pistons back and forth. This back-and-forth motion is transformed into the iconic chug-chug sound of the locomotive, a symphonic cadence that has echoed through history.
The locomotive’s motion is further translated into the rotation of the driving wheels, a feat achieved through an intricate arrangement of rods and linkages. The synchronized movement of these components ensures that the locomotive’s immense power is efficiently transferred to the tracks, propelling it forward with a sense of purpose.
Fuel and water management is an art in itself. As the locomotive devours coal or wood, skilled engineers monitor the consumption rate, ensuring a steady supply to keep the fire burning brightly. Simultaneously, the water level in the boiler is meticulously maintained to prevent overheating or loss of pressure, a delicate task akin to balancing the locomotive’s vital fluids.
The locomotive engineer, perched high in the cab, is the conductor of this symphony. They masterfully coordinate the throttle, brakes and other controls, guiding the locomotive with an intimate knowledge of its quirks and capabilities. Their keen eyes scan the track ahead, their hands deftly manipulating the levers and valves and their ears attuned to the symphony of sounds that reveal the locomotive’s condition.
Every journey of a steam locomotive is a captivating performance, a testament to the craftsmanship and dedication of those who operate and maintain these magnificent machines. As the locomotive steams along the rails, it not only transports passengers and cargo but also carries with it a sense of nostalgia, a connection to a bygone era when the world was vast and journeys were adventures in themselves.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Train Restoration: Reviving Railroad History

Firing
The locomotive engineer, known as the “fireman,” continuously feeds fuel into the firebox. The intense heat produced by the fire generates steam in the boiler.
The role of the locomotive engineer, often referred to as the “fireman,” is pivotal in the operation of a steam locomotive. Their continuous attention to the firebox is essential for maintaining the locomotive’s power and ensuring a smooth journey along the rails.
Stoking the Fire: The fireman’s primary responsibility is to stoke the fire in the locomotive’s firebox. This involves shoveling coal, wood or other fuel into the fire, maintaining a controlled combustion process. The skill lies not just in adding fuel but in doing so at the right rate to maintain the desired steam pressure. It’s a task that demands both physical strength and precision.
Generating Steam: As the fireman feeds fuel into the firebox, the intense heat generated from the burning fuel serves a crucial purpose. It heats the water in the locomotive’s boiler, turning it into steam. This steam, under high pressure, is the locomotive’s source of power. It’s akin to the beating heart of the locomotive, propelling it forward with each powerful surge of steam.
Pressure Management: The fireman must also monitor and regulate the steam pressure within the boiler. Maintaining the correct pressure is essential for the locomotive’s efficiency and safety. Too much pressure can strain the boiler, while too little can result in reduced power and sluggish performance. The fireman adjusts the fire and fuel input to ensure a stable steam pressure throughout the journey.
Skill and Experience: Becoming a skilled fireman is a journey in itself. It requires an understanding of combustion principles, knowledge of the locomotive’s mechanics and the ability to read the signs within the firebox. An experienced fireman can often tell the condition of the fire and the boiler’s state simply by observing the flames and smoke.
Teamwork: The locomotive engineer and fireman work in tandem, relying on each other’s expertise. The engineer controls the locomotive’s speed and direction, while the fireman supplies the power. Effective communication and coordination between them are vital for a safe and efficient journey.
Heritage and Tradition: The role of the fireman is not just a job; it’s a connection to a rich heritage of railroading. It’s a tradition that harks back to the early days of steam locomotives when these mighty machines first began to crisscross the landscape, connecting cities and shaping nations. Many firemen take pride in preserving this heritage and passing on their skills to future generations.
In essence, the fireman is the unsung hero of the steam locomotive, ensuring that it remains a powerful and reliable workhorse. Their labor-intensive work, fueled by the rhythmic stoking of the fire, keeps the locomotive’s heart beating with steam, propelling it forward on its journey down the rails. The fireman’s dedication and skill are a testament to the enduring legacy of steam-powered rail travel.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: How steam locomotives work | Trains Magazine

Boiling Water
Water from the tender is pumped into the boiler, where it is heated by the fire. As it boils, it turns into high-pressure steam.
The process of generating steam in a locomotive’s boiler from the water in its tender is a fundamental and fascinating aspect of steam-powered transportation. This ingenious mechanism, often seen in steam trains of yesteryears, involves a delicate dance of heat and water.
Water is drawn from the locomotive’s tender, typically a large water reservoir located behind or beside the engine. This water, often sourced from a water tower along the rail route, is essential for creating the steam that powers the locomotive. The water is then pumped into the boiler, a sturdy and fireproof container designed to withstand extremely high pressures.
Inside the boiler, the water encounters the heart of the locomotive’s operation: the fire. This fire can be fueled by coal, wood or oil, depending on the locomotive’s design. The intense heat generated by the fire serves as the catalyst for the transformation of water into steam. As the fire’s flames dance around the boiler’s interior, they transfer their energy to the water, causing it to heat up rapidly.
As the temperature rises, the water begins to boil, undergoing a dramatic transformation into high-pressure steam. This steam is incredibly powerful, as it contains an immense amount of energy stored in its high-temperature, high-pressure state. It’s this potent steam that drives the locomotive’s pistons, ultimately propelling the train forward with tremendous force.
This ingenious process of converting water into steam represents the heart and soul of steam locomotion. It’s a beautiful fusion of engineering and physics, where the controlled application of heat turns a humble substance into a powerhouse of kinetic energy, allowing trains to conquer vast distances and connect communities across the world. The rhythmic hissing of steam, the roar of the fire and the rhythmic chugging of the locomotive are all part of this captivating symphony of transportation history.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: engineering – Is there any reason a society might use electric boilers …

Expansion
The high-pressure steam is directed into the cylinders, where it pushes the pistons, creating reciprocating motion. This motion is transferred to the locomotive’s wheels, propelling it forward.
The operation of a steam locomotive is a fascinating testament to the principles of engineering and physics. As we delve deeper into the mechanics of this marvel of 19th-century technology, we discover the intricate dance of components that powers its forward motion.
At the heart of this mechanical ballet is the high-pressure steam, generated within the locomotive’s boiler. This steam, under tremendous pressure, becomes the energetic force that drives the entire locomotive. It is this force that is harnessed and channeled with precision to set the locomotive in motion.
The first crucial step in this process is directing the high-pressure steam into the cylinders. These cylinders are like the locomotive’s beating heart, where the real magic happens. As the steam enters the cylinders, it encounters the pistons – heavy, metal components that are pivotal to the locomotive’s operation.
When the high-pressure steam makes contact with the pistons, it exerts a force, pushing them with incredible power. This interaction between steam and piston creates a reciprocating motion, a rhythmic back-and-forth movement that is fundamental to the locomotive’s locomotion. This piston-driven motion is the very essence of the locomotive’s ability to generate mechanical work.
But how does this motion translate into forward movement? The answer lies in the connection between the pistons and the locomotive’s wheels. The locomotive’s wheels are linked to the pistons through a system of rods and cranks, akin to the tendons and joints in a human body. This mechanical linkage ensures that the reciprocating motion of the pistons is efficiently transferred to the locomotive’s wheels.
As the pistons move back and forth, they turn the wheels in the process. This turning of the wheels propels the locomotive forward along the tracks. It’s a beautifully orchestrated symphony of physics and engineering, where the raw power of steam is transformed into graceful, controlled locomotion.
This elegant interplay of components and forces not only powers the locomotive but also represents an enduring testament to the ingenuity of the engineers and inventors who brought steam locomotion to life. It’s a reminder that even in today’s era of high-speed trains and advanced technologies, the legacy of steam locomotives continues to captivate our imagination and appreciation for the marvels of mechanical engineering.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Industrial Revolution and Technology
Exhaust
After pushing the pistons, the steam is exhausted from the cylinders into the locomotive’s smokestack. The expelled steam creates the iconic plume of smoke and steam.
After the powerful push of the pistons, a pivotal moment in the locomotive’s operation occurs as the steam is expelled from the cylinders into the towering edifice of the locomotive’s smokestack. This seemingly ordinary act carries profound significance, for it not only propels the locomotive forward but also gives birth to an iconic plume of smoke and steam that has become emblematic of the age of steam locomotion.
As the high-pressure steam escapes the cylinders, it enters the smokestack with a force that is both impressive and mesmerizing. It mingles with the combustion byproducts of the locomotive’s roaring fire, creating a dramatic and ever-changing spectacle. This union of steam and smoke gives rise to a billowing cloud that dances and swirls, casting a veil of mystique around the locomotive as it hurtles down the tracks.
The sight of this ethereal plume has an almost poetic quality. It symbolizes the very essence of the locomotive, a machine that harnesses the raw power of steam to conquer distance and time. It is a reminder of an era when these iron giants ruled the rails, when the world was bridged by iron tracks and locomotives were the embodiment of progress and possibility.
Moreover, this plume serves as a visual testament to the engineering marvel that is the steam locomotive. It is a striking demonstration of the controlled release of energy, an intricate dance of pressure and propulsion that propels tons of metal and cargo across vast landscapes. The plume of steam and smoke is not just a byproduct; it is the locomotive’s signature, a declaration of its prowess and a salute to the ingenuity of its creators.
In a world where the relentless march of technology has transformed transportation, the iconic plume of steam and smoke remains a powerful symbol of a bygone era. It evokes a sense of nostalgia and wonder, reminding us of a time when the locomotive was the ultimate symbol of human achievement and progress. It is a reminder that even in the age of high-speed trains and electric engines, the steam locomotive endures as a beloved icon of our industrial heritage.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: What is Modern Steam? — Coalition for Sustainable Rail

Regulation
The engineer controls the locomotive’s speed and direction by adjusting the throttle and valves. The fireman continues to feed the fire to maintain the required steam pressure.
In the intricate dance of steam locomotion, the engineer and fireman play vital roles, each contributing to the locomotive’s power and efficiency. The engineer, perched in the locomotive’s cab, assumes the mantle of control, orchestrating the locomotive’s speed and direction with a precise hand.
To manipulate the locomotive’s power, the engineer deftly adjusts the throttle and valves. This delicate ballet determines the amount of steam admitted into the cylinders, regulating the locomotive’s speed. With a gentle hand on the throttle, the engineer can coax the locomotive into a slow, steady crawl or command it to surge forward with thundering force. This level of control is not only crucial for safety but also for the efficient operation of the locomotive.
Beside the engineer stands the fireman, a steadfast partner in the locomotive’s journey. The fireman tends to the heart of the locomotive—the roaring fire within the firebox. It is the fireman’s responsibility to feed the fire with a steady supply of coal, wood or other fuel, ensuring that the furnace maintains the required temperature and steam pressure.
Maintaining the right steam pressure is paramount. Too much pressure risks straining the locomotive’s components, while too little can result in sluggish performance. The fireman must strike the perfect balance, shoveling just the right amount of fuel to stoke the flames, all while watching the pressure gauge with a keen eye.
The collaboration between engineer and fireman is akin to a well-practiced duet. They communicate through a symphony of gestures, signals and words, their movements synchronized with the rhythmic chugging of the locomotive. The engineer’s commands are met with the fireman’s swift response, as they work together to harness the raw power of steam.
In this intricate ballet of steam locomotion, the engineer and fireman are not mere operators; they are the guardians of a bygone era’s technology, guiding the locomotive along its tracks with skill and precision. Their partnership is a testament to the human mastery of machinery, where the fusion of knowledge, experience and teamwork propels the locomotive forward on its journey, carrying passengers and cargo to their destinations with an ineffable sense of grace and power.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: How steam locomotives work | Trains Magazine
Legacy and Impact
Steam locomotives played a pivotal role in shaping the industrial revolution, expanding transportation networks and connecting distant regions. They revolutionized travel, trade and commerce, opening up new opportunities for economic growth and cultural exchange. The legacy of steam locomotives lives on in the hearts of train enthusiasts and as a symbol of innovation and progress.
Steam locomotives stand as iconic symbols of the industrial revolution, embodying the transformative power of innovation and engineering prowess. Their impact reverberated across continents, shaping the course of history in profound ways.
In the heart of the industrial revolution, steam locomotives emerged as the driving force behind the expansion of transportation networks. These mighty machines bridged geographical divides, linking remote and previously inaccessible regions. The laying of railroad tracks brought about an unprecedented era of connectivity, fostering the exchange of goods, ideas and cultures. This newfound accessibility not only revolutionized travel but also catalyzed economic growth by facilitating the efficient movement of goods and people.
The sound of the locomotive’s whistle heralded an era of progress, ushering in an age of unprecedented mobility. Steam locomotives made long-distance travel not only possible but also practical, greatly reducing the time required for cross-country journeys. This newfound speed transformed the way people perceived space and time, shrinking the world and bringing distant regions closer together.
Trade flourished as goods could now be transported swiftly and reliably across vast distances. The rise of manufacturing industries found innumerable opportunities for expansion, while farmers could transport their produce to wider markets. As cities and towns sprouted along railway lines, urbanization gained momentum, changing the very fabric of society.
Moreover, steam locomotives carried with them the promise of cultural exchange. People from diverse backgrounds and regions came into contact as they shared journeys aboard these marvels of engineering. This convergence of cultures enriched societies, fostering understanding and broadening horizons.
Though the age of steam locomotives has given way to more modern forms of transportation, their legacy endures. Train enthusiasts and historians continue to preserve and celebrate these magnificent machines, ensuring that their significance is never forgotten. Steam locomotives represent not just a chapter in the history of transportation but a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. They remind us that innovation, once harnessed, has the power to reshape the world and connect distant horizons, leaving an indelible mark on the tapestry of human history.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Union Pacific LEGACY Scale 4-8-8-4 Big Boy #4024
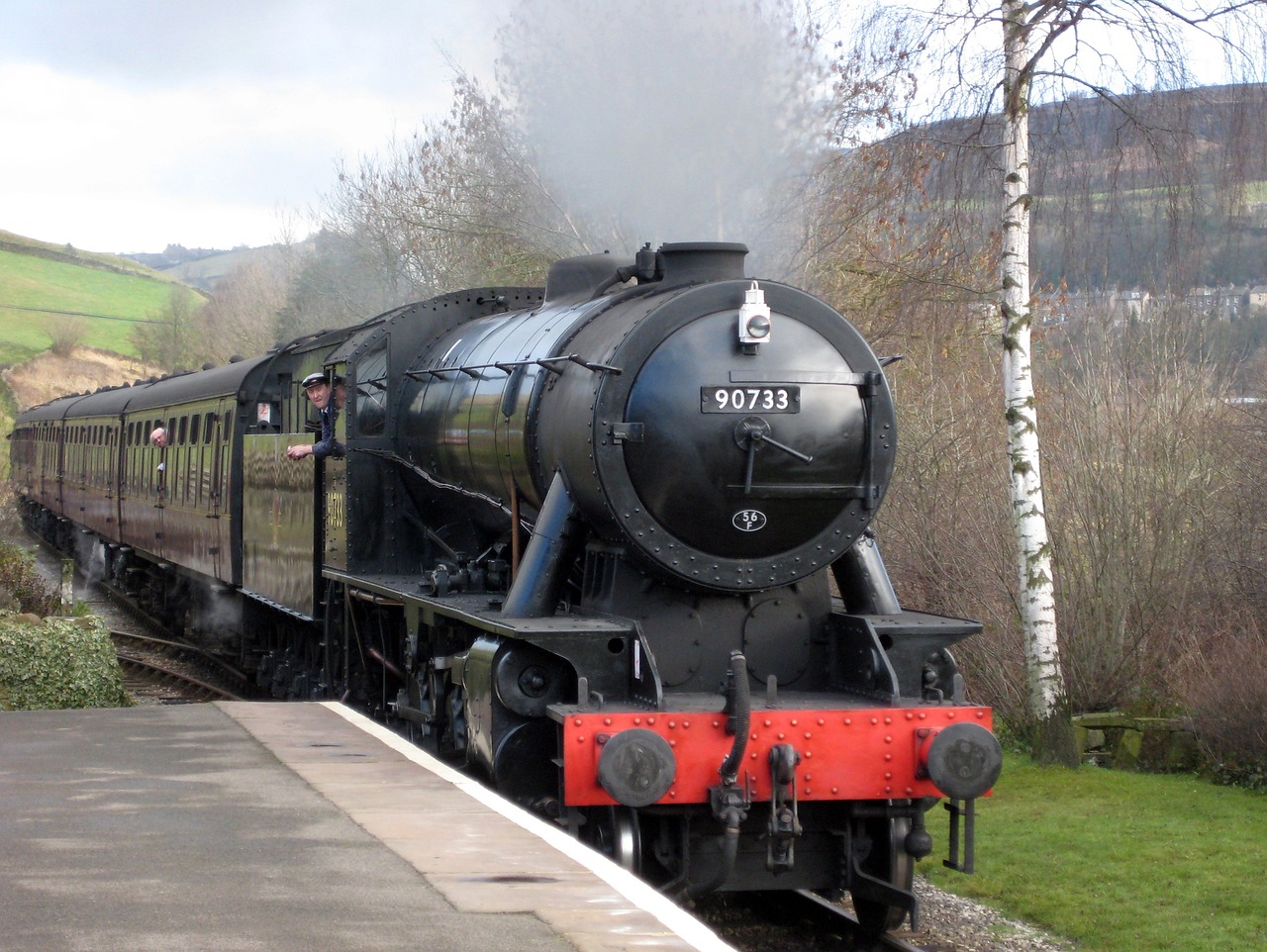

Steam locomotives represent an extraordinary fusion of engineering ingenuity and mechanical artistry. These classic trains, with their complex components and precise coordination, forever changed the world by making travel and trade more accessible and efficient. While steam locomotives have largely been replaced by more modern forms of transportation, their enduring legacy and timeless appeal continue to captivate people around the world, reminding us of an era when the power of steam drove the wheels of progress.
Steam locomotives stand as a testament to human ingenuity and mechanical artistry. These iconic trains, a marvel of their time, brought together intricate engineering and precise coordination in a way that transformed the world in ways previously unimaginable. While they’ve been largely replaced by sleeker, more advanced forms of transportation, the legacy they left behind is both enduring and enchanting.
In an age when the world was still divided by vast distances and treacherous terrain, steam locomotives played a pivotal role in bringing people and goods closer together. They bridged the gap between remote communities and bustling urban centers, facilitating travel and trade on an unprecedented scale. The rhythmic churning of their wheels symbolized progress and innovation, a stark departure from the slower, less reliable modes of transport that preceded them.
Steam locomotives weren’t just machines; they were the heart and soul of an era. The skill and craftsmanship that went into their construction were awe-inspiring. From the massive boiler to the delicate valves and gears, every component was a testament to the dedication of the engineers and workers who built them. The symphony of steam, metal and motion they produced was a mesmerizing dance of power and precision.
Today, as we zip through the landscape in high-speed trains or soar through the skies in airplanes, the allure of steam locomotives endures. Their timeless appeal is a testament to the human fascination with nostalgia and history. People from all walks of life are drawn to steam locomotives, whether as collectors, preservationists or simply enthusiasts. They remind us of a simpler time, when the world was less rushed and the journey was as important as the destination.
Preservation efforts are underway worldwide to keep these majestic machines alive, allowing new generations to experience the magic of steam-powered travel. Museums, heritage railways and dedicated volunteers work tirelessly to restore and maintain these locomotives, ensuring that their stories continue to be told.
In the end, steam locomotives are not just relics of the past; they are ambassadors of an era when the power of steam symbolized progress, connecting distant lands and shaping the world as we know it. Their enduring legacy is a reminder that even in our fast-paced, technologically advanced world, the spirit of innovation and the pursuit of the extraordinary continue to drive us forward.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Henry Ford Biography
More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: How steam locomotives work | Trains Magazine
