Introduction
The concept of a “smart home” has transitioned from science fiction into reality, thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT technology has revolutionized the way we interact with our living spaces, making them more convenient, efficient, and secure. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the profound impact of IoT on smart homes, covering everything from the basics to advanced applications and future trends.
The integration of IoT technology into smart homes has fundamentally transformed the way we perceive and interact with our living spaces. IoT devices, sensors, and connectivity solutions have become the building blocks of modern smart homes, offering a wide range of benefits that extend beyond mere convenience.
One of the most significant impacts of IoT on smart homes is the enhanced level of automation and control. Homeowners can now remotely manage various aspects of their homes, from adjusting the thermostat to controlling lighting, security cameras, and even kitchen appliances, all through a smartphone or voice-activated assistant. This not only simplifies daily routines but also contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings.
IoT has also greatly improved the safety and security of smart homes. Smart security systems, equipped with motion sensors, doorbell cameras, and smart locks, provide homeowners with real-time alerts and the ability to monitor their properties from anywhere. These advancements in security technology offer peace of mind and help reduce the risk of break-ins or accidents.
Moreover, IoT-driven smart homes contribute to environmental sustainability. By optimizing energy consumption through intelligent HVAC systems and lighting controls, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and lower utility bills. In addition, IoT-enabled water management systems can detect leaks and minimize water wastage.
The healthcare sector has also seen the impact of IoT in smart homes, especially in the context of elderly care. IoT devices such as wearable health monitors, fall detection sensors, and medication reminders enable older adults to maintain their independence while providing caregivers with valuable insights into their well-being.
As the IoT ecosystem continues to evolve, smart homes are poised to become even more integrated and seamless. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms will enable devices to adapt to homeowners’ preferences and anticipate their needs. For example, AI-powered smart thermostats can learn from occupants’ temperature preferences and adjust settings accordingly.
Voice-activated assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant have also become central to smart homes, offering intuitive and natural ways to control IoT devices and access information. These assistants are continually expanding their capabilities, making them indispensable for homeowners.
In the realm of entertainment, IoT has transformed how we experience multimedia content. Smart speakers, connected TVs, and streaming devices have made it easier than ever to access a vast array of digital media, from music and movies to live sports and news.
However, with the growing integration of IoT devices into smart homes, privacy and security concerns have come to the forefront. Protecting personal data and ensuring the security of IoT networks is of paramount importance. Manufacturers and users alike must take measures to safeguard against potential vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
In conclusion, the impact of IoT on smart homes is far-reaching, enhancing convenience, safety, sustainability, and entertainment. As IoT technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative solutions that further integrate and optimize our living spaces, ultimately providing homeowners with a higher quality of life and greater peace of mind.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …
Understanding IoT and Its Role in Smart Homes
IoT, in essence, is a network of interconnected devices that can communicate and share data with each other over the internet. These devices can range from everyday household items like thermostats and light bulbs to more complex systems like security cameras and voice assistants. In the context of smart homes, IoT plays a central role by enabling devices to connect, collect, and share data for various purposes.
“At the heart of IoT is the concept of interconnected devices capable of sharing data across the internet. These devices encompass a wide spectrum, from commonplace household gadgets like thermostats and light fixtures to intricate systems such as security cameras and voice-activated assistants. In the realm of smart homes, IoT serves as the linchpin, facilitating device connectivity and data exchange, thereby ushering in a new era of convenience, efficiency, and automation.”

Key Components of IoT in Smart Homes
To comprehend the impact of IoT on smart homes, it’s essential to understand the key components involved:
To fully grasp the profound impact of the Internet of Things (IoT) on smart homes, one must delve into the intricate web of key components that form the foundation of this transformative technology landscape. These components not only define the functionality of smart homes but also herald a new era of convenience, efficiency, and connectivity in our daily lives. Let’s explore these vital elements:
1. Sensors and Devices: At the heart of every smart home are an array of sensors and devices that serve as the eyes, ears, and hands of the system. These include motion detectors, temperature sensors, cameras, smart locks, thermostats, and many more. These components collect real-time data from the environment, enabling smart systems to make informed decisions and respond to various triggers.
2. Connectivity: The seamless exchange of data among devices and systems is made possible through connectivity technologies. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and cellular networks are some of the prominent connectivity options. The choice of connectivity technology influences the range, reliability, and compatibility of smart devices within a home.
3. Data Processing: The collected data undergoes intricate processing to extract meaningful insights and trigger actions. Edge computing, cloud computing, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) play pivotal roles in analyzing and interpreting the data. These technologies enable smart homes to adapt, learn, and optimize their operations based on user preferences and changing conditions.
4. Control Interfaces: Control interfaces provide homeowners with the means to interact with their smart systems. These interfaces range from smartphone apps and voice-activated assistants (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant) to dedicated control panels and even gesture-based controls. They empower users to manage and customize their smart home ecosystem effortlessly.
5. Actuators and Automation: Actuators are the responsive agents that carry out commands issued by the smart home system or the homeowner. They include smart locks that secure doors, smart thermostats that adjust temperatures, and smart lights that illuminate rooms. Automation routines and scripts enable these actuators to function autonomously, enhancing comfort and security.
6. Integration Platforms: Smart homes often consist of a mix of devices from various manufacturers. Integration platforms and protocols like Apple HomeKit, Google Home, and Samsung SmartThings unify these disparate devices under a single umbrella, allowing seamless communication and centralized control.
7. Security Measures: As the digital realm expands into our homes, robust security measures are crucial. Encryption, authentication, and security certificates safeguard data privacy and protect against unauthorized access. Ensuring the security of IoT devices and networks is paramount to prevent cyber threats.
8. Energy Management: Smart homes contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability. Energy management systems monitor energy consumption and optimize usage patterns. Smart thermostats, lighting controls, and power outlets enable homeowners to reduce energy waste and lower utility bills.
9. User Data and Privacy: The collection of user data in smart homes raises important ethical and privacy concerns. Transparent data policies, consent mechanisms, and data encryption are essential for safeguarding user privacy while deriving value from collected data.
10. Ecosystem Expansion: The world of smart homes is dynamic and ever-expanding. Compatibility with emerging technologies and the ability to integrate new devices are vital considerations for homeowners looking to future-proof their smart home ecosystems.
In summary, the impact of IoT on smart homes is deeply rooted in these key components. These elements work in harmony to create an ecosystem where homes become more intelligent, responsive, and tailored to the needs and preferences of their occupants. Understanding these components is not only essential for comprehending the present state of smart homes but also for envisioning the boundless possibilities they hold for the future of living.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Smart Home: Definition, How They Work, Pros and Cons
Sensors and Actuators
These are the “sensory organs” of smart homes. Sensors collect data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, or motion. Actuators, on the other hand, are responsible for carrying out actions based on the data received, like adjusting the thermostat or locking the doors.
In the realm of smart homes, the synergy between sensors and actuators is akin to a dynamic dance. Sensors continuously monitor and interpret the surroundings, while actuators execute precise actions in response. This harmonious partnership fuels the intelligence behind automation, ensuring your home adapts seamlessly to your needs and preferences.
You can also read more about this here: What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …

Connectivity
IoT devices rely on wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or Bluetooth to communicate with each other and with a central hub, often referred to as a smart home controller.
The foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT) in smart homes lies in its ability to connect a multitude of devices seamlessly and efficiently. These devices rely on various wireless communication technologies to establish a network within the home, allowing them to communicate with each other and with a central hub, often referred to as a smart home controller.
Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is perhaps the most familiar and widely used wireless technology in smart homes. It offers robust and high-speed connectivity, making it ideal for devices that require a substantial amount of data transfer, such as streaming media players, smart TVs, and security cameras. Wi-Fi enables users to control these devices remotely through smartphones or voice assistants. However, Wi-Fi’s power consumption can be relatively high, which may not be suitable for battery-operated IoT devices.
Zigbee: Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate wireless communication protocol designed specifically for IoT applications. It excels in creating mesh networks, where each device acts as a node that can relay messages to other nodes. Zigbee’s energy efficiency makes it well-suited for battery-powered sensors and smart home devices like door/window sensors, motion detectors, and smart lighting systems. It operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band and boasts strong security features, making it a popular choice for smart home ecosystems.
Bluetooth: Bluetooth, particularly Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), is another wireless technology prevalent in smart homes. It’s known for its energy efficiency, making it suitable for devices like smart locks, wearables, and Bluetooth speakers. One advantage of Bluetooth is its compatibility with smartphones, allowing users to easily connect and control devices using their mobile devices. However, the range of Bluetooth is generally shorter than Wi-Fi and Zigbee, limiting its use in larger homes.
Z-Wave: Z-Wave is a wireless protocol designed explicitly for home automation and IoT applications. Like Zigbee, Z-Wave excels in creating mesh networks, providing reliable and efficient communication between devices. It operates on the sub-1 GHz frequency band, which typically offers better range and penetration through walls compared to 2.4 GHz technologies like Wi-Fi. Z-Wave devices are known for their interoperability, making it possible for products from different manufacturers to work seamlessly within the same smart home ecosystem.
Thread: Thread is an emerging wireless protocol that is gaining traction in the smart home space. It’s built on the 6LoWPAN standard and operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Thread offers robust security and low-power operation, making it suitable for a wide range of IoT devices. It’s backed by major tech companies and promotes interoperability between devices, fostering a more open ecosystem.
These wireless technologies serve as the backbone of IoT connectivity in smart homes, each with its own set of advantages and use cases. The choice of technology often depends on factors such as the device’s power requirements, range, data throughput, and compatibility with other devices in the ecosystem. As IoT continues to evolve, we can expect to see further innovations in wireless communication technologies that enhance the capabilities of smart homes even more.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: What is a Smart Home? Everything You Need to Know|Definition …
Smart Home Controller
This hub serves as the central command center for all IoT devices in the home. It allows users to monitor, control, and automate various aspects of their living space.
“The IoT hub acts as the nerve center, orchestrating the symphony of interconnected devices within a smart home. It empowers users with the ability to effortlessly oversee, manage, and even automate a myriad of functions throughout their living environment. This technological nucleus not only simplifies daily tasks but also enhances convenience and efficiency, all at the tip of one’s fingers.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Implementing Smart Voice Control in Appliances: A Comprehensive …
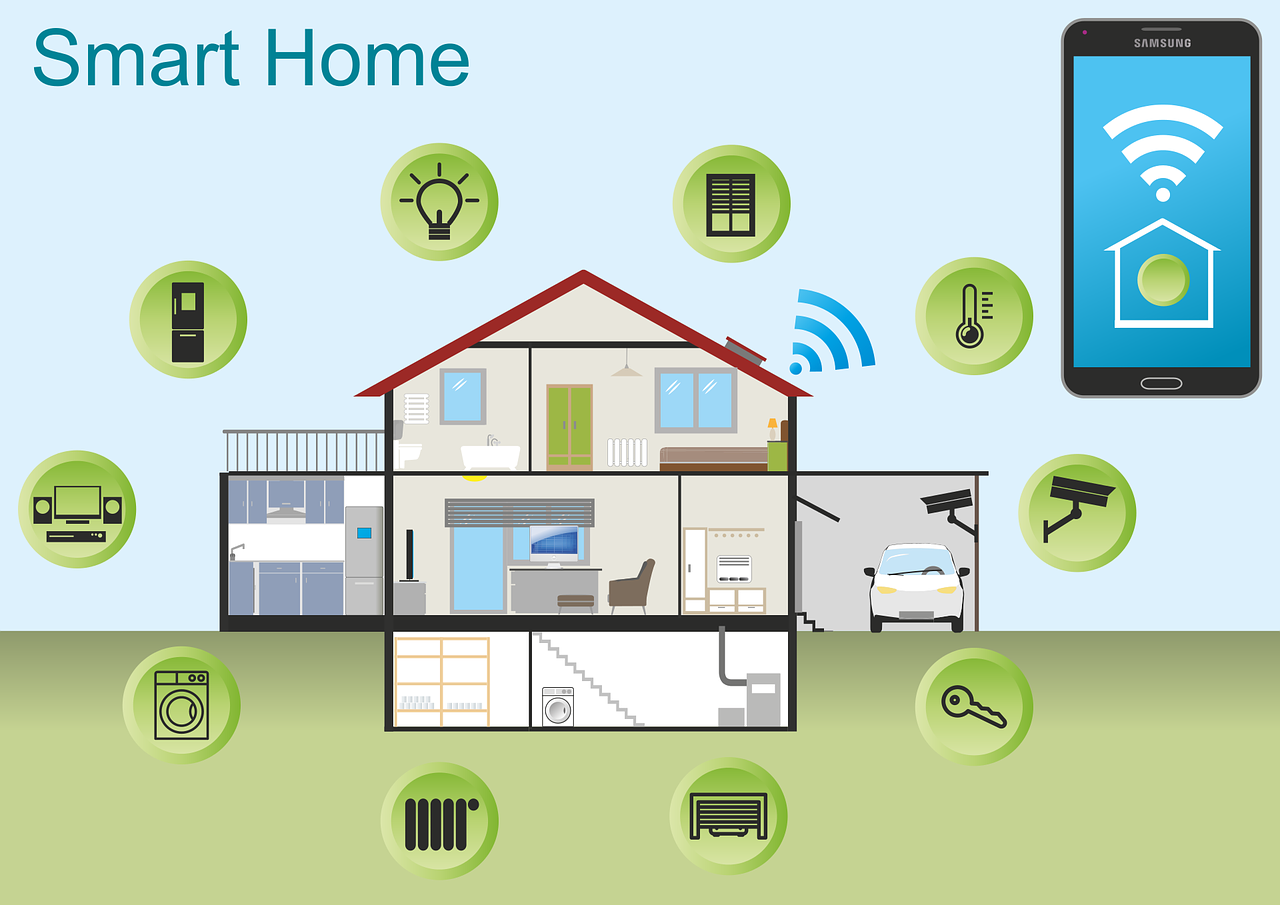
Cloud Computing
The data collected by IoT devices is often sent to the cloud for storage and analysis. This enables remote access and control of smart home systems.
The data journey in the world of IoT is a fascinating one, and understanding how it unfolds sheds light on the immense possibilities and conveniences that IoT brings to smart homes. Here’s a deeper exploration of this idea:
1. Data Collection at the Edge: IoT devices, equipped with an array of sensors, are the first line of data collection. These sensors continuously gather a wealth of information, ranging from temperature and humidity levels to motion detection and energy consumption. At the edge of the network, within the confines of your home, these devices process data locally to make rapid decisions and respond to immediate triggers. For instance, a motion sensor might trigger a smart light to turn on when it detects movement in a room.
2. Local Control and Automation: Many IoT devices are designed to function autonomously within the home environment. Local control hubs or smart controllers, often referred to as smart home hubs, manage these devices. These hubs coordinate the activities of various devices, enabling them to communicate and work together seamlessly. For instance, a smart thermostat can interact with smart blinds to optimize heating and cooling based on the amount of sunlight entering a room.
3. Cloud Connectivity: While local control is essential for real-time responses, cloud connectivity takes IoT to the next level. Data collected by IoT devices is transmitted to cloud servers, where it is stored securely and processed. This cloud-based approach offers several advantages:
Remote Access: Cloud storage allows homeowners to access their smart home systems remotely. Whether you’re at work, on vacation, or simply away from home, you can check the status of your devices, adjust settings, and receive alerts and notifications through smartphone apps or web interfaces.
Data Analysis: The cloud provides a powerful platform for data analysis. Advanced algorithms and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can analyze the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices. This analysis yields valuable insights, such as energy consumption patterns, security alerts, and predictive maintenance information.
Scalability: Cloud storage and processing enable easy scalability. As you expand your smart home ecosystem with additional devices, the cloud can accommodate the growing volume of data and facilitate the integration of new devices seamlessly.
4. Data Security and Privacy: With the transmission of data to the cloud comes a heightened need for security and privacy. Ensuring that data is encrypted during transmission and storage is crucial to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. Additionally, robust authentication mechanisms and user consent protocols are essential to safeguard user privacy in compliance with data protection regulations.
5. User Insights: The data stored in the cloud not only benefits homeowners but also provides valuable insights to device manufacturers and service providers. This data can inform product improvements, troubleshoot issues remotely, and enhance the user experience.
6. Cloud Redundancy: To ensure data integrity and availability, cloud providers implement redundancy measures. Data is often stored across multiple servers and data centers, minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
In essence, the journey of IoT data from collection at the edge to storage and analysis in the cloud is a harmonious blend of real-time responsiveness and the power of data-driven intelligence. It empowers homeowners with convenience, security, and control while fostering innovation and continuous improvement in the realm of smart homes. As IoT technologies continue to evolve, this data journey will pave the way for even more sophisticated and personalized smart home experiences.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …
Convenience
IoT-equipped smart homes offer unparalleled convenience. You can control your lights, thermostats, appliances, and security systems remotely using your smartphone or voice commands. Automated routines, such as turning off all lights and locking doors when you leave, enhance daily life.
The convenience of IoT-enabled smart homes extends beyond remote control; it embraces the art of anticipation. These systems learn your habits and preferences, orchestrating your living environment to perfection. Picture this: your home adjusts the lighting and temperature just as you like it before you even step through the door. It’s a world where technology seamlessly syncs with your lifestyle, making each moment at home a tailored and comfortable experience.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Usage and impact of the internet-of-things-based smart home …

Energy Efficiency
Smart thermostats and lighting systems can adapt to your preferences and schedule, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
In the realm of smart homes powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), devices like smart thermostats and lighting systems have become transformative tools for homeowners. These intelligent devices not only offer convenience but also contribute significantly to energy efficiency, ultimately leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
1. Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats, such as the popular Nest and Ecobee, are prime examples of IoT devices that have revolutionized home heating and cooling management. These devices are designed to learn your temperature preferences over time and create customized heating and cooling schedules. Here’s how they contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings:
Adaptive Learning: Smart thermostats use algorithms and sensors to adapt to your daily routines. They learn when you’re home and when you’re away, as well as your preferred temperature settings for different times of the day.
Remote Control: You can control your thermostat remotely through a smartphone app. This means that if you forget to adjust the temperature before leaving home, you can do so from wherever you are. You can also turn the system off when you’re away and switch it on before returning, reducing unnecessary heating or cooling.
Energy Usage Reports: Many smart thermostats provide detailed reports on your heating and cooling usage. They offer insights into how your habits impact energy consumption and suggest ways to optimize settings for cost savings.
Integration: Smart thermostats often integrate with other IoT devices in your home, such as smart speakers or sensors. For example, they can adjust the temperature based on occupancy detected by motion sensors.
Geofencing: Some thermostats use geofencing technology to detect when you’re approaching or leaving home, allowing them to prepare the temperature accordingly.
All of these features combined can lead to significant energy savings, with estimates suggesting that smart thermostats can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 15%.
2. Smart Lighting Systems: Smart lighting solutions have also made substantial contributions to energy efficiency within smart homes. Here’s how they achieve this:
Energy-Efficient Bulbs: Smart lighting systems often use LED bulbs, which are inherently energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Customized Schedules: Just like smart thermostats, smart lighting systems allow you to create customized lighting schedules. You can set lights to automatically turn off when you leave a room or gradually dim in the evening, reducing energy consumption.
Remote Control: You can control your lights remotely through a smartphone app or voice commands. If you forget to turn off a light when leaving home, you can do so remotely.
Motion Sensors: Some smart lighting systems come with motion sensors that can detect when a room is unoccupied and automatically turn off the lights.
Integration: These systems often integrate with other smart devices, allowing you to create complex automation routines. For example, lights can turn on automatically when a motion sensor detects movement and then turn off when no motion is detected.
The combined effects of these features help reduce electricity bills while making your home more environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, smart thermostats and lighting systems are instrumental in optimizing energy usage in smart homes. Their adaptability, remote control capabilities, and integration with other devices offer homeowners a practical and sustainable way to lower utility bills while enjoying a more comfortable living environment. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, we can expect even more innovations that further enhance energy efficiency and cost savings in our homes.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: A Review of Using IoT for Energy Efficient Buildings and Cities: A …
Security
IoT-powered security cameras, doorbell cameras, and smart locks provide real-time monitoring and alerts, enhancing home security.
“Smart security devices powered by IoT technology usher in a new era of home protection. With real-time monitoring, instant alerts, and remote accessibility, these innovations fortify home security like never before. Whether it’s keeping an eye on the front door, deterring potential intruders, or granting secure access to trusted individuals, IoT-powered security solutions offer peace of mind and an elevated sense of control over one’s living space.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …

Health and Well-being
IoT can be used for health monitoring, allowing individuals to track vital signs and receive medical alerts or reminders. Smart appliances can also promote healthier eating and lifestyle choices.
The fusion of IoT with healthcare and well-being is a transformative synergy that offers individuals unprecedented control over their health and lifestyle. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how IoT is revolutionizing health monitoring and promoting healthier choices:
1. Health Monitoring and Vital Signs Tracking: IoT-enabled wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have become invaluable tools for health-conscious individuals. These devices continuously monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and even sleep patterns. The real-time data collected is not only displayed on the device itself but is often synchronized with smartphone apps and cloud platforms. Users can track their health metrics over time, allowing for proactive health management.
2. Medical Alerts and Reminders: IoT extends its capabilities to medical alert systems, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions or the elderly. Smart sensors and wearable devices can detect falls, sudden changes in heart rate, or abnormal activity patterns. In such cases, automatic alerts can be sent to caregivers or medical professionals, ensuring prompt assistance and intervention when needed. Additionally, IoT-enabled pill dispensers and medication tracking apps send reminders to individuals to take their prescribed medications on time, enhancing medication adherence.
3. Remote Patient Monitoring: For patients recovering at home or managing chronic conditions, IoT provides a lifeline to healthcare providers. Remote patient monitoring devices, such as connected glucometers for diabetes management or spirometers for respiratory conditions, transmit data directly to healthcare professionals. This allows for real-time assessment of a patient’s condition and early intervention if any anomalies are detected, reducing hospital readmissions and improving overall patient outcomes.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Promotion: IoT-driven smart appliances and devices are not limited to healthcare monitoring; they also promote healthier choices in daily life. Here’s how:
Smart Refrigerators: These appliances can monitor food inventory, track expiration dates, and even suggest recipes based on available ingredients. They encourage users to make healthier meal choices by providing nutritional information and meal planning assistance.
Smart Kitchen Gadgets: IoT-powered kitchen gadgets, such as smart scales and blenders, assist users in portion control and healthy meal preparation. They can offer calorie counts, suggest healthier ingredient alternatives, and even provide step-by-step cooking guidance.
Fitness Equipment: Connected fitness equipment like smart treadmills and stationary bikes not only offer personalized workout plans but also track progress and set fitness goals. They motivate users to stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Nutrition Apps: Smartphone apps paired with IoT devices can help users make informed dietary choices. These apps often scan barcodes or use image recognition to provide detailed nutritional information for a wide range of food products.
5. Personalized Health Insights: The data collected from IoT devices is a goldmine of information that can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and lifestyle. Machine learning algorithms can analyze this data to provide personalized health insights, such as dietary recommendations, exercise routines, and even early warnings for potential health risks. This tailored guidance fosters healthier choices and encourages individuals to take a proactive role in their well-being.
In summary, IoT’s integration with health monitoring and lifestyle choices is a game-changer that places individuals in the driver’s seat of their own health and well-being. It offers a holistic approach to health management, from real-time vital signs tracking to personalized health insights and encourages healthier lifestyle choices through smart appliances and devices. As IoT technologies continue to evolve, their impact on healthcare and well-being is poised to grow, promoting a healthier and more empowered society.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: IoT in Smart Cities: A Survey of Technologies, Practices and …

Accessibility
Smart home technology makes living spaces more accessible for individuals with disabilities. Voice-activated controls and IoT-powered assistive devices enhance independence and quality of life.
In the realm of smart homes, accessibility is a cornerstone principle. IoT technology, paired with thoughtful design, opens doors to a world of possibilities for individuals with disabilities. Voice-activated controls, smart sensors, and assistive devices empower people to navigate their living spaces with newfound ease and independence. Whether it’s adjusting room conditions, opening doors, or managing daily tasks, smart homes are transforming accessibility, breaking down barriers, and ensuring that everyone can enjoy a life of greater convenience and autonomy.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …

Future Trends in IoT and Smart Homes
The impact of IoT on smart homes is set to grow even more significant in the future. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
The rapid evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) technology continues to shape the landscape of smart homes, and the impact of IoT is poised to become even more significant in the near future. Here are some emerging trends and developments to keep a close eye on:
1. Increased Device Interoperability: One of the key challenges in the current smart home ecosystem is the fragmentation caused by various manufacturers using different communication protocols. In the future, we can expect a stronger push for device interoperability, allowing devices from different brands to seamlessly communicate and work together. This will enhance the user experience and make it easier to create comprehensive smart home setups.
2. Enhanced Voice Control: Voice-activated assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri have already become integral parts of smart homes. Future developments will likely focus on making these voice interfaces more intuitive and capable of handling a broader range of commands. Additionally, we can expect more devices to feature built-in voice recognition for localized control.
3. AI-Powered Automation: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are becoming more sophisticated in understanding user preferences and behaviors. This will lead to smarter automation within smart homes. For example, AI could anticipate your needs by adjusting lighting, temperature, and even music preferences based on your habits and routines.
4. Edge Computing: While cloud computing has been central to IoT data processing, edge computing is gaining prominence. Edge devices process data locally, reducing latency and enhancing privacy. This trend will likely continue as more processing power is integrated into IoT devices themselves.
5. 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable internet connectivity, which is essential for IoT devices. This will enable real-time communication and streaming, making smart home devices even more responsive and efficient.
6. Enhanced Security Measures: As IoT devices become more integrated into our lives, security will be a paramount concern. Future trends will include improved security measures, such as end-to-end encryption, biometric authentication, and enhanced firewall capabilities, to protect smart homes from cyber threats.
7. Sustainable Solutions: There is a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in smart home technology. Future IoT devices will likely include features that help users reduce their carbon footprint, such as energy-efficient appliances, renewable energy integration, and intelligent water and waste management systems.
8. Healthcare and Wellness: IoT is expanding its role in healthcare and wellness. Smart devices can monitor health metrics, track fitness goals, and even provide remote healthcare services. Expect to see more IoT applications in this space, including personalized health recommendations based on real-time data.
9. Robotics and Automation: Home robotics, from cleaning robots to home security drones, are expected to become more commonplace. These devices will become more intelligent and autonomous, further enhancing the convenience and safety of smart homes.
10. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: AR will play a role in enhancing user interfaces for smart home devices. It could provide interactive guides for DIY installations, immersive control interfaces, or even virtual home tours before making IoT-related purchases.
As IoT technology continues to mature, its integration with smart homes will become increasingly seamless and transformative. These emerging trends represent just a glimpse of the exciting developments we can expect in the world of IoT-powered smart homes, promising more convenience, efficiency, and connectivity for homeowners in the years to come.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is IoT (Internet of Things) and How Does it Work? | Definition …
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster, more reliable connections, enabling even more IoT devices to operate seamlessly.
“The impending arrival of widespread 5G networks heralds a new era for the Internet of Things. With lightning-fast speeds and unparalleled reliability, 5G will facilitate the seamless operation of an ever-expanding array of IoT devices. From smart homes to connected cities, this technology promises to unlock unprecedented possibilities for automation, data exchange, and real-time responsiveness, revolutionizing the way we live and interact with our surroundings.”
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Study and Investigation on 5G Technology: A Systematic Review …

Edge Computing
Processing data locally (at the “edge” of the network) will reduce latency and enhance device response times, critical for applications like autonomous vehicles and real-time monitoring.
Processing data at the edge of the network is a transformative paradigm shift that not only enhances device response times but also redefines the possibilities of real-time applications across various domains. Here’s a deeper exploration of the significance of local data processing at the edge:
1. Ultra-Low Latency: The foremost advantage of local data processing at the edge is the dramatic reduction in latency. In traditional cloud-centric architectures, data must traverse the network to reach remote data centers for processing. This round-trip journey can introduce noticeable delays, which are unacceptable in applications where split-second decisions are critical. By processing data locally on edge devices or edge servers, latency is virtually eliminated, ensuring near-instantaneous response times.
2. Real-Time Decision-Making: Industries that rely on real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, benefit immensely from edge computing. Autonomous vehicles, for instance, need to process sensor data and make split-second decisions about navigation, obstacle avoidance, and safety. Edge computing enables these vehicles to make decisions locally without relying on distant cloud servers, enhancing safety and reliability.
3. Bandwidth Efficiency: Transmitting large volumes of raw data to the cloud for processing can strain network bandwidth and incur significant costs, especially in applications like video surveillance. Edge processing allows devices to preprocess data, extracting relevant information or sending only data that triggers an alert, reducing the burden on network infrastructure and conserving bandwidth.
4. Offline Operation: Edge devices can continue to operate even when disconnected from the cloud or experiencing intermittent connectivity. This is particularly valuable in remote or mission-critical environments where network reliability may be a concern. Local processing ensures that critical functions can continue seamlessly without dependence on external cloud resources.
5. Privacy and Security: Edge computing offers enhanced privacy and security by keeping sensitive data within the local environment. In applications like surveillance or healthcare, where data privacy is paramount, edge processing ensures that sensitive information does not leave the premises, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
6. Scalability and Cost Efficiency: Edge computing architectures are inherently scalable and cost-effective. Instead of relying on a centralized cloud infrastructure, organizations can deploy edge servers or devices as needed. This flexibility allows for more efficient resource allocation and can significantly reduce operational costs.
7. Customization and Adaptability: Edge processing allows for customization and adaptability at the device level. Devices can be tailored to specific use cases and can adapt to changing conditions without the need for frequent updates from a central server. This agility is essential in applications like industrial automation, where production processes may evolve rapidly.
8. Redundancy and Reliability: Local processing enhances redundancy and reliability. Edge devices can be designed with redundancy features to ensure continuous operation, even in the event of hardware failures or network outages. This redundancy is crucial in critical infrastructure and industrial applications where downtime can have severe consequences.
In essence, local data processing at the edge of the network is a transformative approach that empowers devices and applications to operate with unprecedented speed, efficiency, and autonomy. It enables real-time decision-making, reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, enhances privacy and security, and offers scalability and cost-efficiency. As edge computing technologies continue to advance, their impact will extend to a wide range of industries, shaping the future of real-time applications and services.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology …

AI and Machine Learning
IoT devices will become smarter, capable of learning and adapting to user preferences without explicit programming.
The evolution of IoT devices is on a trajectory toward unprecedented intelligence and adaptability. These devices will harness the power of machine learning and artificial intelligence to intuitively understand and cater to user preferences, eliminating the need for explicit programming. Imagine a thermostat that learns your preferred temperature settings or lighting systems that adjust based on your daily routines. With this level of smart technology, IoT devices will seamlessly integrate into our lives, making our environments more personalized, efficient, and user-friendly. The future of IoT promises a world where technology truly works in harmony with our needs and desires.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications – PMC
Interoperability
Efforts are underway to improve the compatibility of different IoT devices and ecosystems, reducing fragmentation and enhancing user experience.
Efforts to improve compatibility and reduce fragmentation in the IoT ecosystem are gaining momentum as the demand for seamless, interconnected smart home experiences continues to grow. Here are some key initiatives and strategies aimed at enhancing the user experience:
1. Industry Standards: Various industry consortiums and standards organizations are working on developing common protocols and standards for IoT devices. For instance, the “Project CHIP” (Connected Home over IP) is a collaborative effort by major tech companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, and others to create an open-source standard for smart home devices. This initiative aims to ensure that devices from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
2. Cross-Platform Integration: Many tech giants are investing in cross-platform integration, allowing their voice assistants (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant) to control a wide range of third-party smart devices. This approach encourages device manufacturers to make their products compatible with major voice assistants, thereby expanding the interoperability of smart home ecosystems.
3. Hub Devices: Smart home hub devices act as intermediaries that can communicate with a variety of IoT devices using different communication protocols and then translate those signals into a common language. These hubs play a critical role in bridging the gap between incompatible devices, enabling them to work together. Companies like Samsung SmartThings and Hubitat have gained popularity in this space.
4. Smart Home Platforms: Major tech companies offer smart home platforms (e.g., Apple HomeKit, Google Smart Home) that provide developers with guidelines and tools to create compatible IoT devices. These platforms encourage manufacturers to follow certain standards and protocols, making their products more likely to work harmoniously within the ecosystem.
5. Firmware Updates: Device manufacturers are increasingly releasing firmware updates that improve compatibility and add new features. These updates can enhance device interoperability by addressing known issues and ensuring devices remain compatible with evolving standards.
6. User Education: Educating users on how to select compatible devices and set up their smart homes effectively is essential. Manufacturers and tech companies often provide resources and guidelines to help users build cohesive ecosystems.
7. Third-Party Apps and Services: Developers are creating third-party apps and services that act as intermediaries between different devices. These apps can provide a unified interface and control for various devices, even if they were not originally designed to work together.
8. Open APIs: Some manufacturers are opening up their APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to allow third-party developers to create integrations and plugins for their devices. This encourages innovation and can lead to more comprehensive device compatibility.
9. Interoperability Certifications: Industry organizations and certification bodies are introducing interoperability certifications for IoT devices. Earning these certifications demonstrates a device’s compatibility with specific standards, which can boost consumer confidence and encourage manufacturers to follow interoperability guidelines.
As these efforts gain traction, consumers can expect a more streamlined and user-friendly experience when setting up and expanding their smart homes. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless IoT ecosystem where devices from different manufacturers work together effortlessly, empowering users to enjoy the full potential of their smart homes without the hassle of compatibility issues.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology …
Conclusion
The impact of IoT on smart homes is transformative, offering unparalleled convenience, efficiency, and security. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications and a seamless integration of IoT into our daily lives. Whether you’re looking to make your home more energy-efficient, secure, or simply more convenient, embracing IoT technology is a step toward a smarter future.
“As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, its transformative impact on smart homes becomes increasingly apparent. The promise of convenience, efficiency, and security that IoT brings to our living spaces is only the beginning. With ongoing technological advancements, we can anticipate even more innovative applications and a seamless integration of IoT into our daily lives. Whether you seek energy efficiency, enhanced security, or sheer convenience, embracing IoT technology is a pivotal step toward building a smarter and more connected future within our homes.”
You can also read more about this here: Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology …
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What Is IoT? Complete Guide to Internet of Things
