Introduction
The world of supply chain management is undergoing a profound transformation, thanks to the integration of Web3 technologies, particularly blockchain. In an era where consumers demand transparency, sustainability, and ethical practices, blockchain offers an innovative solution to enhance visibility and traceability across the supply chain. In this article, we’ll explore how Web3, powered by blockchain, is revolutionizing supply chain management, ensuring transparency, and fostering trust in the global marketplace.
The ongoing transformation of supply chain management is not merely a technological shift; it’s a response to the evolving expectations of consumers and stakeholders. In an era marked by growing awareness of environmental, social, and ethical concerns, traditional supply chain practices are being scrutinized more than ever before. Here’s a deeper look at how Web3 and blockchain technology are driving this transformative process:
Consumer Empowerment: Today’s consumers are increasingly conscientious about the products they purchase. They want to know where their goods come from, how they were produced, and whether the practices involved align with their values. This demand for transparency is a driving force behind the integration of blockchain into supply chains. With blockchain, consumers can access real-time data about a product’s journey, from raw materials to the store shelf, fostering trust and empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices: Sustainability has become a paramount concern in the supply chain. Companies are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize waste, and engage in ethical sourcing. Blockchain supports these initiatives by enabling the tracking of sustainable and ethical practices throughout the supply chain. It allows for the verification of certifications, such as Fair Trade or organic, and the monitoring of eco-friendly production processes.
Globalization Challenges: The global nature of modern supply chains presents both opportunities and challenges. While globalization allows for access to diverse markets and resources, it also makes it difficult to monitor and control every aspect of the supply chain. Blockchain bridges this gap by providing a unified platform for stakeholders across borders to share information securely and efficiently.
Resilience and Risk Mitigation: Supply chain disruptions, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, or unexpected market shifts (as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic), highlight the need for resilient supply chain practices. Blockchain’s transparency and traceability can help identify vulnerabilities and enhance risk management. When an issue arises, stakeholders can quickly trace the affected products, reducing the scope of recalls and minimizing financial losses.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with various regulations, from food safety standards to labor practices, is a critical aspect of supply chain management. Blockchain’s immutable ledger can serve as a tamper-proof record of compliance, simplifying audits and reducing the risk of legal penalties.
Collaborative Networks: Blockchain fosters collaboration among supply chain participants. It encourages shared ownership of data and incentivizes all parties to contribute accurate and timely information. This collaboration improves communication, reduces disputes, and streamlines operations.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: With blockchain, supply chain data becomes a valuable asset. Machine learning and data analytics can be applied to this data, providing insights that drive optimization, cost reduction, and strategic decision-making.
In conclusion, the integration of Web3 technologies, particularly blockchain, into supply chain management is a response to the changing landscape of consumer expectations, sustainability demands, and globalization challenges. Blockchain brings transparency, traceability, and trust to supply chains, empowering consumers, enhancing ethical practices, and enabling businesses to operate more efficiently and responsibly. As Web3 continues to evolve, it will drive further innovations in supply chain management, ushering in a new era of transparency and accountability. The supply chains of tomorrow will be resilient, sustainable, and built on the foundations of Web3 technologies.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: What is Blockchain Technology? – IBM Blockchain | IBM
Traditional supply chains often suffer from opacity, inefficiency, and a lack of accountability. These challenges can lead to issues such as counterfeit products, delays, fraud, and unsustainable practices. Fortunately, Web3 technologies, with blockchain at the forefront, present a game-changing approach to address these concerns.
The traditional supply chain landscape has long been plagued by inherent issues that hinder transparency, efficiency, and accountability. These challenges ripple across industries, resulting in problems like counterfeit products, supply chain delays, fraud, and unsustainable practices. The arrival of Web3 technologies, with blockchain taking the lead, offers a transformative approach to confront and resolve these issues. Here’s how Web3 is poised to reshape supply chains:
Transparency and Traceability: Web3, underpinned by blockchain’s immutable ledger, brings unprecedented transparency to supply chains. Every transaction, from the production of raw materials to the delivery of final products, can be recorded and traced in real-time. This transparency not only prevents fraud but also allows consumers to verify the authenticity and origins of products.
Immutable Records: Blockchain’s tamper-resistant nature ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus. This immutability safeguards supply chain records against fraud and manipulation, enhancing the integrity of the entire ecosystem.
Smart Contracts: Web3 introduces smart contracts, self-executing agreements that automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are met. These contracts can streamline supply chain processes by automating tasks like payments, quality checks, and delivery confirmations, reducing delays and human error.
Decentralized Data Sharing: Traditional supply chains often involve multiple stakeholders with varying degrees of access to information. Web3 enables decentralized data sharing, allowing all authorized parties to access and update data in real-time, eliminating bottlenecks and enhancing collaboration.
Counterfeit Prevention: Blockchain’s ability to verify the authenticity of products is a powerful tool against counterfeiting. Each product can be assigned a unique digital identity on the blockchain, making it easy to track its journey from manufacturer to consumer.
Ethical Sourcing: Web3 technologies empower consumers to make informed choices by providing insights into the ethical and environmental practices of suppliers. This transparency promotes responsible sourcing and encourages sustainable practices.
Efficient Auditing and Compliance: Supply chain audits and compliance checks become more efficient and accurate with blockchain. Auditors can access a transparent and verifiable record of operations, reducing the time and resources required for audits.
Reduction in Middlemen: Smart contracts and decentralized platforms can reduce the need for intermediaries in supply chains. This not only cuts costs but also enhances the speed and efficiency of transactions.
Environmental Impact Tracking: For industries concerned with sustainability, Web3 can enable the tracking of environmental impact throughout the supply chain. This data can inform eco-friendly decisions and support companies’ commitment to sustainability goals.
Consumer Empowerment: Web3 technologies empower consumers to make more informed choices by providing access to real-time data on product origins, quality, and ethical considerations. This can drive demand for products produced with transparency and ethical practices.
In summary, Web3 technologies, particularly blockchain, are poised to revolutionize traditional supply chains by ushering in a new era of transparency, efficiency, and accountability. The benefits extend from preventing counterfeiting and fraud to enhancing sustainability and empowering consumers. As Web3 adoption continues to grow, supply chains stand to become more resilient, responsible, and responsive to the evolving demands of the modern world.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Blockchain for Supply Chain: Track and Trace
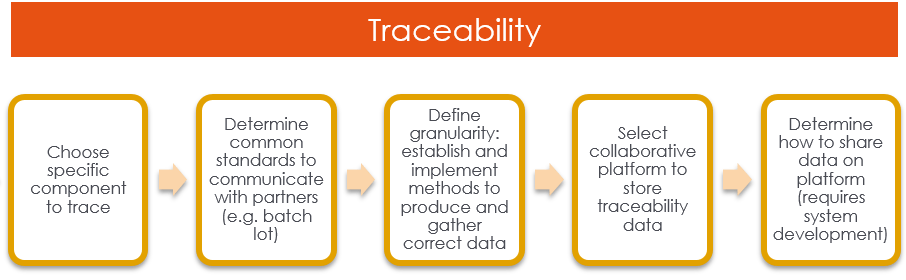
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone of Web3 and plays a pivotal role in transforming supply chain management:
Blockchain technology, as the cornerstone of Web3, is orchestrating a profound revolution in the realm of supply chain management. Its impact goes beyond efficiency gains; it fundamentally reshapes how businesses track, verify, and optimize their supply chains. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how blockchain is catalyzing this transformation:
Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain’s distributed ledger offers unparalleled transparency. Every transaction and movement of goods is recorded in an immutable and tamper-proof manner. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders, from manufacturers to consumers, as they can trace the journey of products from source to destination.
Immutable Records: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that once data is added to the ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted. This eliminates the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, or unauthorized changes in supply chain records. Suppliers and customers can have full confidence in the integrity of the data.
Real-time Tracking: With blockchain, supply chain participants gain access to real-time updates on inventory levels, shipments, and product status. This visibility allows for more accurate demand forecasting, reduced stockouts, and optimized inventory management.
Streamlined Compliance: Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of supply chain management. Blockchain automates compliance by recording every step of the process. This simplifies auditing and reporting, reducing administrative burdens and the risk of non-compliance.
Efficient Payments and Settlements: Blockchain can facilitate smart contracts for automated payment processing. This means that when predefined conditions are met (e.g., goods delivered and verified), payments are triggered automatically, reducing delays and disputes.
Supply Chain Financing: Blockchain enables supply chain financing by providing a transparent and verifiable record of transactions. This allows businesses to access financing options based on their supply chain data, unlocking working capital and improving cash flow.
Provenance and Quality Assurance: In industries like agriculture and luxury goods, blockchain can provide provenance information. Consumers can verify the authenticity and quality of products, fostering trust and brand loyalty.
Reduced Waste and Environmental Impact: Through improved tracking and data analytics, blockchain helps in reducing waste by optimizing processes and minimizing overproduction. This sustainability aspect aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly and responsible supply chains.
Cross-border Trade: Blockchain facilitates smoother cross-border trade by automating customs documentation and reducing the risk of errors. This is particularly beneficial in international supply chains, where compliance and paperwork complexities can be daunting.
Data Security: Supply chain data is highly sensitive, and protecting it from cyber threats is paramount. Blockchain’s cryptographic security measures safeguard data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks, enhancing overall supply chain cybersecurity.
Global Collaboration: Blockchain fosters collaboration across the global supply chain network. It enables diverse stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, to work together seamlessly, improving coordination and efficiency.
Resilience: Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes supply chains more resilient to disruptions, such as natural disasters or global crises. Data redundancy across nodes ensures that critical information remains accessible even during adverse circumstances.
In conclusion, blockchain technology’s pivotal role in supply chain management goes beyond optimizing processes; it signifies a paradigm shift towards transparency, trust, and sustainability. By leveraging blockchain’s capabilities, businesses can create more efficient, secure, and responsible supply chains that benefit both their bottom line and the global community. This transformation promises a future where supply chains are not just efficient but ethical and eco-conscious, ushering in a new era of responsible commerce.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Using Blockchain to Drive Supply Chain Transparency and …
Blockchain’s impact on supply chain management is already evident in various industries:
Blockchain’s transformative impact on supply chain management reverberates across diverse industries, unveiling a host of benefits and reshaping long-established practices:
Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain brings unparalleled transparency to supply chains. Every transaction, movement, or alteration of goods is recorded in an immutable ledger accessible to all authorized parties. This transparency minimizes the risk of fraud, counterfeit goods, and discrepancies in supply chain data.
Immutable Records: The inherent immutability of blockchain records ensures the integrity of supply chain data. Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without consensus, eliminating the potential for tampering or data manipulation.
Real-time Tracking: Blockchain-powered supply chain platforms offer real-time tracking of goods. This level of visibility allows stakeholders to pinpoint the exact location and status of products, streamlining logistics, and reducing delays.
Efficient Auditing: Auditing and compliance processes become more efficient and less labor-intensive with blockchain. Auditors can quickly access the complete history of products and transactions, reducing the time and resources required for audits.
Reduced Counterfeiting: Counterfeit goods cost industries billions of dollars annually. Blockchain’s ability to verify the authenticity and provenance of products at every stage of the supply chain is a powerful deterrent to counterfeiters.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, automated self-executing agreements on the blockchain, streamline supply chain operations. They can trigger actions automatically when predefined conditions are met, such as releasing payment upon successful delivery.
Improved Traceability: The traceability of products is crucial, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Blockchain allows for precise traceability, enabling swift identification and recall of products in case of contamination or safety concerns.
Supplier Accountability: Blockchain promotes supplier accountability. Suppliers can be held to predefined quality and compliance standards, and deviations can trigger alerts and actions automatically.
Data Security: Supply chain data is sensitive and valuable. Blockchain’s cryptographic security ensures that data remains confidential and is only accessible to authorized participants.
Cost Reduction: Blockchain reduces costs associated with paperwork, intermediaries, and reconciliation efforts. It streamlines processes, minimizes errors, and leads to cost savings throughout the supply chain.
Cross-border Trade: International trade benefits from blockchain’s ability to simplify customs and border procedures. Digital documentation on the blockchain accelerates the movement of goods across borders.
Eco-friendliness: By optimizing supply chain processes and reducing inefficiencies, blockchain contributes to sustainability efforts. It minimizes the environmental impact associated with unnecessary transportation and waste.
Global Collaboration: Blockchain facilitates global collaboration among supply chain partners. It standardizes processes, data formats, and communication, making it easier for partners across the world to work together seamlessly.
While blockchain’s influence on supply chain management is evident and promising, widespread adoption is still unfolding. Challenges related to interoperability, scalability, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed. Nevertheless, blockchain’s profound impact on supply chains is set to reshape industries, driving efficiency, trust, and innovation across the global supply chain landscape.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Using Blockchain to Drive Supply Chain Transparency and …

Conclusion
Web3 technologies, particularly blockchain, are ushering in a new era of transparency and traceability in supply chain management. As consumers increasingly prioritize ethical and sustainable products, the ability to provide verifiable information about the journey of products becomes a competitive advantage. The adoption of blockchain in supply chains not only enhances transparency but also fosters trust and accountability among all stakeholders. As Web3 continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations in supply chain management, resulting in more sustainable, secure, and efficient global supply chains. The future of supply chain is decentralized, transparent, and built on the foundation of Web3 technologies.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Blockchain in Agriculture: How It Can Help the Industry
More links
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Web3 Supply Chain: The Road to Transparency
