Introduction
As the automotive industry becomes increasingly connected and reliant on advanced technology, the issue of vehicle cybersecurity has gained paramount importance. Modern vehicles are equipped with intricate computer systems, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks and hacking attempts. In this article, we will delve into the world of vehicle cybersecurity, exploring the risks, challenges, and the crucial anti-hacking measures that are essential to safeguarding the future of automotive technology.
As the automotive industry becomes increasingly connected and reliant on advanced technology, the issue of vehicle cybersecurity has gained paramount importance, shaping the landscape of modern transportation. Modern vehicles are equipped with intricate computer systems, turning them into highly sophisticated mobile computers on wheels. While this technological leap has brought about numerous conveniences and innovations, it has also exposed vehicles to new and evolving risks—cyberattacks and hacking attempts that can potentially compromise safety, privacy, and the functionality of the vehicle.
The Growing Complexity of Automotive Technology: Today’s automobiles are marvels of engineering, featuring a complex network of interconnected systems that control everything from engine performance and safety features to infotainment systems and autonomous driving capabilities. This interconnectedness, while providing a seamless driving experience, opens up multiple entry points for cyber threats. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in various systems, potentially gaining access to critical vehicle functions.
Cybersecurity Risks in the Automotive Industry: The risks associated with vehicle cybersecurity are diverse and alarming. Unauthorized access to a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) can lead to dangerous scenarios, such as remote manipulation of braking systems, acceleration, or steering. Privacy breaches are another concern, as personal data collected by modern vehicles can be a target for malicious actors.
Additionally, cyberattacks on the automotive supply chain can affect vehicle safety and functionality. A breach at a component manufacturer or a software supplier can have far-reaching consequences, impacting multiple vehicle models.
Challenges in Ensuring Vehicle Cybersecurity: Securing modern vehicles is a complex and evolving challenge. The automotive industry must grapple with issues such as:
Rapid Technological Advancement: Vehicle technology evolves quickly, and cybersecurity measures must keep pace with these advancements.
Interconnected Ecosystems: Modern vehicles are part of a broader ecosystem that includes cloud-based services, mobile apps, and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication. Securing this entire ecosystem is essential.
Legacy Systems: Many vehicles on the road today have outdated software and hardware that may lack the necessary security features, posing challenges for retrofitting cybersecurity measures.
Crucial Anti-Hacking Measures: To safeguard the future of automotive technology, a multi-faceted approach to vehicle cybersecurity is necessary. This includes:
Encryption and Authentication: Implementing robust encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect data and ensure that only authorized users can access critical systems.
Regular Software Updates: Providing over-the-air (OTA) software updates allows manufacturers to patch vulnerabilities promptly and improve cybersecurity.
Intrusion Detection Systems: Equipping vehicles with intrusion detection systems that monitor for abnormal behavior and patterns, helping to identify and respond to potential cyber threats.
Education and Training: Raising awareness and educating both manufacturers and consumers about cybersecurity best practices is essential. Users should be encouraged to update their vehicle software regularly and practice safe digital habits.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in setting cybersecurity standards and requirements for the automotive industry.
In conclusion, as the automotive industry continues its transformation into a tech-driven sector, vehicle cybersecurity stands as a critical pillar of innovation and safety. Addressing the risks and challenges associated with cybersecurity is essential to ensuring the continued advancement of automotive technology and providing consumers with vehicles that are not only smart and connected but also secure and resilient to the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Automated Vehicle Safety | NHTSA
With the advent of smart cars and the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), vehicles have become sophisticated computing platforms on wheels. While this connectivity offers numerous benefits, including enhanced safety and convenience, it also exposes vehicles to cyber threats that were once unthinkable. The potential consequences of vehicle cyberattacks range from data breaches and privacy infringements to life-threatening situations if the vehicle’s control systems are compromised.
With the advent of smart cars and the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), vehicles have become sophisticated computing platforms on wheels. While this connectivity offers numerous benefits, including enhanced safety and convenience, it also exposes vehicles to cyber threats that were once unthinkable. The potential consequences of vehicle cyberattacks range from data breaches and privacy infringements to life-threatening situations if the vehicle’s control systems are compromised.
In this era of connected vehicles, where cars can communicate with each other and with infrastructure to optimize traffic flow and provide real-time navigation, the concept of cybersecurity has taken center stage. Here are some key points to consider:
Data Privacy Concerns: The wealth of data generated by smart cars, including location, driving behavior, and even personal preferences, is a goldmine for potential attackers. Ensuring robust data encryption and strict privacy controls is paramount to protect individuals from unauthorized access to their personal information.
Remote Hacking: Cybercriminals could potentially gain control over a vehicle’s critical systems, such as brakes and steering, through remote hacking. This frightening scenario could lead to accidents and loss of life. To counter this threat, automakers must implement stringent security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access to the car’s control systems.
Software Vulnerabilities: Modern vehicles rely heavily on software to manage various functions, from engine performance to entertainment systems. Vulnerabilities in this software can be exploited by cybercriminals. Regular software updates and patches, as well as rigorous testing and validation processes, are essential to mitigate these risks.
Supply Chain Security: The automotive industry involves complex supply chains, with numerous components and software from various sources. Ensuring the security of these components and their integration into the vehicle is crucial to prevent potential entry points for cyberattacks.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulatory bodies are recognizing the importance of cybersecurity in the automotive industry and are working on establishing guidelines and regulations. These frameworks aim to ensure that automakers implement robust cybersecurity measures and respond effectively to incidents.
Collaboration and Threat Sharing: Automakers, technology companies, and cybersecurity experts must collaborate to stay ahead of emerging threats. Sharing information about vulnerabilities and attack patterns can help the industry collectively strengthen its defenses.
Education and Awareness: Vehicle owners must also be educated about cybersecurity risks and best practices. They should be encouraged to update their vehicle’s software regularly, use strong, unique passwords, and be cautious about connecting to unsecured networks.
In summary, as vehicles become increasingly connected and reliant on software-driven technologies, the need for robust cybersecurity measures in the automotive industry becomes paramount. While the benefits of smart cars and IoT integration are vast, addressing the associated cybersecurity challenges is essential to ensure the safety, privacy, and security of both vehicle occupants and the broader transportation ecosystem.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Cybersecurity | Homeland Security

Cybercriminals may gain unauthorized access to a vehicle’s systems, allowing them to manipulate various functions, from door locks and windows to the engine and brakes.
The increasing integration of technology in modern vehicles has brought with it a concerning new dimension of security vulnerabilities. In today’s interconnected world, cybercriminals have the potential to exploit these vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to a vehicle’s systems, opening the door to a range of dangerous manipulations:
Remote Vehicle Control: Once cybercriminals infiltrate a vehicle’s systems, they can potentially assume control over various critical functions. This includes not only basic features like door locks and windows but also more critical components such as the engine and brakes. With this level of access, they can remotely start or stop the engine, apply brakes unexpectedly, or even disable the vehicle entirely, posing significant safety risks.
Data Theft and Privacy Invasion: Beyond physical control, unauthorized access can lead to the theft of sensitive data stored within the vehicle’s systems. This could include personal information, navigation history, or even financial details if the vehicle is linked to apps or services. Such data breaches can have severe consequences for individuals’ privacy and security.
Ransom Attacks: Cybercriminals might use the gained control over a vehicle to initiate ransom attacks. They could lock the owner out of their own vehicle and demand a ransom for its release, causing significant inconvenience and financial strain.
Tracking and Surveillance: Unauthorized access can enable the constant tracking and surveillance of a vehicle’s location, which is a severe violation of privacy. This can have implications for personal safety, as cybercriminals could use this information for nefarious purposes.
Unauthorized Modifications: In some cases, cybercriminals may tamper with a vehicle’s software or settings to make unauthorized modifications. These changes could affect the vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, or emissions, potentially leading to regulatory violations or costly repairs.
Safety Compromises: By manipulating the vehicle’s critical systems like brakes or steering, cybercriminals can directly endanger the lives of occupants and other road users. This potential for harm underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures in the automotive industry.
To counter these emerging threats, automotive manufacturers, technology companies, and cybersecurity experts are working diligently to develop and implement advanced security protocols and measures. These may include robust encryption, intrusion detection systems, over-the-air software updates, and multi-factor authentication for vehicle access.
As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, cybersecurity will remain a top priority to ensure the safety and privacy of vehicle owners and passengers. The evolving nature of cyber threats demands ongoing vigilance and innovation in securing the vehicles of the future against the potentially devastating consequences of unauthorized access and manipulation.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Vehicle Cybersecurity | NHTSA

Vehicles store a wealth of sensitive data, such as personal information and location history. A breach could lead to identity theft or compromise user privacy.
In our increasingly interconnected world, vehicles have evolved into more than just modes of transportation; they are now rolling data centers on wheels. This transformation, while bringing convenience and innovation, also presents significant cybersecurity challenges. Understanding the potential risks and consequences is essential:
Data Proliferation: Modern vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors, cameras, and communication systems. They continuously collect data about the vehicle’s surroundings, performance, and even driver behavior. This wealth of information includes not only technical data related to the vehicle but also personal information like contact details, navigation history, and even biometric data if the vehicle incorporates driver monitoring systems.
Identity Theft: A breach in a vehicle’s data systems could expose sensitive personal information, making owners and passengers vulnerable to identity theft. This information may include names, addresses, phone numbers, and more, all of which can be exploited by malicious actors for fraudulent activities.
Location Privacy: The constant tracking of a vehicle’s location history can reveal a lot about an individual’s habits and routines. Unauthorized access to this data could compromise user privacy, putting them at risk of stalking or other invasive actions.
Financial Implications: Beyond the personal impact, data breaches involving vehicles can have financial consequences. Stolen vehicle data could be used to commit vehicle-related fraud, such as altering vehicle ownership records or even stealing the vehicle itself.
Safety Risks: In the context of autonomous vehicles, data breaches become a matter of life and death. If hackers gain control of autonomous systems, they could potentially manipulate vehicle behavior, leading to accidents or other safety hazards.
Reputation Damage: For automakers and technology providers, a data breach can lead to severe damage to their reputation and brand trust. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the security of their data, and any breach can erode the trust between customers and manufacturers.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments and regulatory bodies are taking a keen interest in the cybersecurity of connected vehicles. They are implementing strict regulations to ensure that automakers and tech companies prioritize cybersecurity in their designs and operations. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to legal consequences and fines.
To mitigate these risks, the automotive industry is actively investing in cybersecurity measures, including robust encryption, intrusion detection systems, and over-the-air software updates to patch vulnerabilities. Additionally, consumer awareness about the importance of cybersecurity in vehicles is growing, pushing manufacturers to prioritize this aspect in their designs.
As vehicles continue to evolve into complex data-driven machines, safeguarding the sensitive data they collect and transmit is paramount. The potential consequences of data breaches in vehicles are far-reaching, affecting individuals’ personal lives, financial well-being, and even public safety. Therefore, the ongoing efforts to secure connected vehicles are critical for ensuring a safer and more private driving experience in the digital age.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Cybersecurity | Homeland Security

In extreme cases, hackers can remotely control a vehicle’s critical functions, endangering the safety of occupants and other road users.
In today’s interconnected world, the vulnerability of vehicles to cyberattacks represents a pressing concern that transcends the realm of mere inconvenience. The scenario of hackers gaining remote control over a vehicle’s essential functions is not merely a theoretical concept; it is a real and growing threat with far-reaching implications:
Safety Compromised: When hackers gain control over a vehicle’s critical functions, the consequences can be catastrophic. They can manipulate steering, acceleration, and braking systems, directly endangering the lives of the vehicle’s occupants and others on the road. This type of intrusion can result in accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
Privacy Invasion: Beyond the immediate safety risks, vehicle hacking also raises concerns about privacy invasion. Hackers can access personal data stored in the vehicle, such as location history, contact information, and even voice recordings. The breach of this sensitive information can have severe consequences for individuals and their families.
Financial Implications: Vehicle hacking can result in substantial financial losses. In addition to the potential costs associated with accidents or damage caused by a compromised vehicle, there may be expenses related to repairing or replacing hacked systems, insurance claims, and legal actions.
Reputation Damage: Automakers and technology companies that provide vehicle connectivity services can suffer significant damage to their reputation if their products are associated with hacking incidents. Consumers may lose trust in these companies, impacting their market share and future sales.
Regulatory Responses: As vehicle hacking incidents become more prevalent, governments and regulatory bodies are likely to respond with stricter cybersecurity standards and regulations. Compliance with these regulations can impose additional costs on the automotive industry, which may be passed on to consumers.
Continuous Innovation: To combat the evolving tactics of hackers, the automotive industry must invest heavily in cybersecurity measures. This ongoing battle for security can drive up research and development costs, which may again impact vehicle pricing.
Global Implications: The interconnected nature of the automotive industry means that hacking incidents can have international repercussions. Vehicles manufactured in one country may be sold and driven in another, making it crucial for cybersecurity standards to be harmonized across borders.
Ransomware Threat: In addition to taking control of a vehicle’s functions, hackers can deploy ransomware attacks that demand payment in exchange for restoring control to the owner. Such attacks can have severe financial and emotional consequences for victims.
In conclusion, the threat of hackers remotely controlling a vehicle’s critical functions extends far beyond the realm of cybersecurity; it has tangible and severe real-world consequences. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, addressing this threat becomes paramount. Automakers, technology companies, governments, and consumers must collaborate to develop and implement robust cybersecurity measures to ensure the safety, privacy, and security of our increasingly interconnected vehicles.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: A comprehensive review study of cyber-attacks and cyber security …

To combat these risks and ensure the safety and security of connected vehicles, automakers and cybersecurity experts are implementing a range of measures:
To combat these risks and ensure the safety and security of connected vehicles, automakers and cybersecurity experts are implementing a range of measures. These measures represent a collaborative effort to address the growing concerns associated with the increasing connectivity of vehicles in today’s digital age. Here’s an extended overview of the strategies and initiatives being employed:
Advanced Encryption and Authentication Protocols: Automakers are investing in robust encryption and authentication systems to secure the data transmitted within and to and from vehicles. These protocols ensure that only authorized entities can access and interact with critical vehicle systems, safeguarding against unauthorized access and tampering.
Intrusion Detection Systems: Intrusion detection systems continuously monitor a vehicle’s network for unusual or suspicious activities. When anomalies are detected, these systems can trigger alarms, initiate protective measures, or alert vehicle owners and manufacturers, allowing for swift responses to potential cyberattacks.
Regular Software Updates: Frequent software updates are essential to address vulnerabilities and patch security flaws. Automakers are increasingly adopting over-the-air (OTA) updates, which enable them to remotely and quickly deliver security patches and software improvements to connected vehicles, bolstering their defense against emerging threats.
Secure Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: V2X communication is central to the future of connected and autonomous vehicles. Ensuring the security of these communication channels is paramount. Automakers are working on implementing secure V2X protocols and encryption methods to protect the integrity of data exchanged between vehicles, infrastructure, and other road users.
Cybersecurity Training and Awareness: Education is a fundamental component of cybersecurity. Automakers are investing in training programs for their employees, suppliers, and customers to raise awareness of potential risks and promote best practices for staying safe online and while driving connected vehicles.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: The automotive industry is collaborating with cybersecurity organizations, governmental agencies, and other stakeholders to share threat intelligence and best practices. This collaborative approach helps in staying ahead of emerging threats and creating a more robust defense ecosystem.
Redundancy and Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Automakers are incorporating redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms into vehicle systems to ensure that critical functions, such as braking and steering, remain operational even in the event of a cyberattack. These measures provide an added layer of protection and safety.
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing: To proactively identify vulnerabilities, some automakers engage ethical hackers and security experts to conduct penetration testing. These experts attempt to uncover weaknesses in vehicle systems and communication networks, allowing manufacturers to address potential issues before malicious actors can exploit them.
Regulatory Compliance: Automakers are closely monitoring and adhering to evolving cybersecurity regulations and standards set by governments and industry bodies. Compliance with these standards helps ensure that vehicles meet a minimum level of security and privacy protection.
In conclusion, the automotive industry recognizes the critical importance of cybersecurity in the era of connected vehicles. By implementing these comprehensive measures, automakers are actively working to mitigate risks, protect consumer trust, and ensure that the future of transportation remains safe, secure, and technologically advanced.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Vehicle Cybersecurity | NHTSA
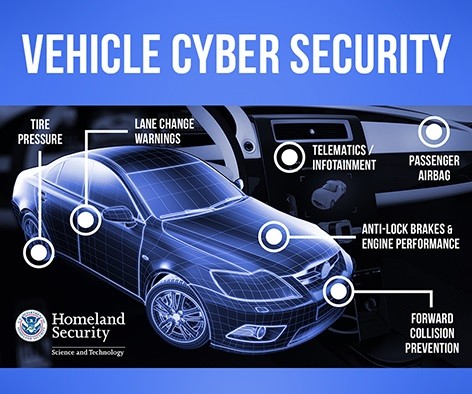
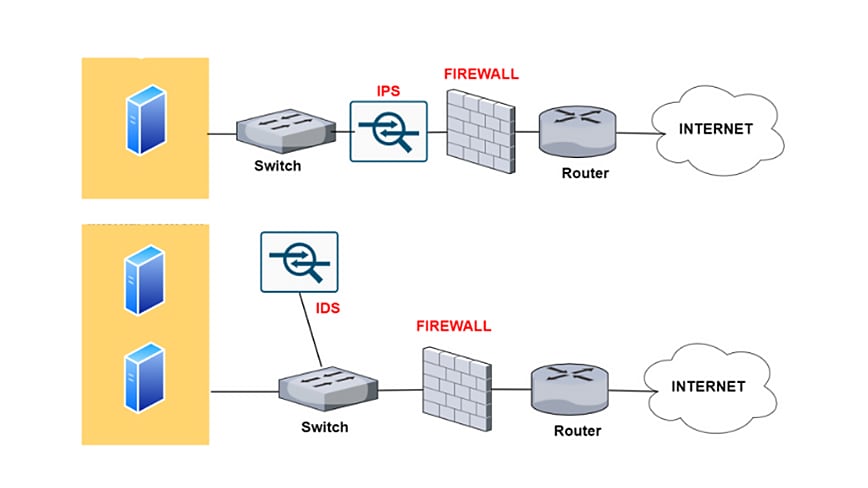
Equipping vehicles with firewalls and intrusion detection systems can help monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and block unauthorized access.
Equipping vehicles with firewalls and intrusion detection systems represents a critical step in fortifying the digital defenses of modern automobiles. These cybersecurity measures act as a virtual shield, continuously monitoring the intricate web of networks and systems within a vehicle to detect and thwart potential cyber threats.
Proactive Threat Detection: Intrusion detection systems employ sophisticated algorithms and pattern recognition techniques to analyze network traffic and system behavior. They can identify irregularities or anomalies that may indicate a cyberattack, such as unauthorized access attempts or unusual data transmissions. This proactive approach allows for the early detection of potential threats, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
Real-Time Response: When suspicious activity is detected, these systems can initiate real-time responses to mitigate the threat. For instance, they can isolate compromised components or disconnect from external networks to prevent further unauthorized access. This rapid response capability is essential in preventing cyberattacks from escalating and causing significant harm.
Adaptive Security: As cyber threats continue to evolve, intrusion detection systems can adapt and learn from new attack patterns. Machine learning algorithms enable these systems to become more adept at identifying emerging threats, making them a valuable asset in the ongoing battle against cybercriminals.
Enhanced User Privacy: Intrusion detection systems also play a vital role in safeguarding user privacy. By monitoring data flows and access attempts, they can prevent unauthorized data collection or transmission, ensuring that sensitive user information remains confidential.
Comprehensive Network Protection: Modern vehicles are essentially rolling networks, with multiple interconnected systems. Equipping them with firewalls ensures that all entry points, including infotainment systems, telematics, and communication interfaces, are well-protected. This comprehensive approach minimizes vulnerabilities across the entire vehicle ecosystem.
Regulatory Compliance: In an era where data protection regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, intrusion detection systems help automakers and fleet operators meet compliance requirements. They demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding user data and maintaining cybersecurity standards.
User Confidence: Perhaps most importantly, the presence of robust cybersecurity measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems instills confidence in consumers. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, consumers need assurance that their safety and privacy are a top priority for automakers.
In summary, the integration of firewalls and intrusion detection systems into vehicles represents a pivotal advancement in vehicle cybersecurity. These measures not only protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats but also contribute to user privacy, regulatory compliance, and overall consumer trust. As the automotive industry continues to embrace digitalization, these cybersecurity technologies will remain essential components of safe and secure connected vehicles.
You can also read more about this here: What is an intrusion detection system (IDS)? Definition from …
Ensuring that software updates and patches are secure is critical. Automakers are working on secure over-the-air (OTA) update mechanisms to protect against unauthorized modifications.
Ensuring that software updates and patches are secure is not only critical but has become increasingly essential in our interconnected world. Automakers, in particular, are at the forefront of this effort, recognizing the significance of secure software management in modern vehicles. To address this challenge, they are actively developing and implementing secure over-the-air (OTA) update mechanisms. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Enhancing Vehicle Safety: With the proliferation of software-driven features in today’s vehicles, including advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous capabilities, software updates are a means to enhance vehicle safety and performance continuously. Secure OTA updates allow automakers to deploy critical safety improvements swiftly. This agility can address emerging threats or vulnerabilities, ensuring that vehicles remain safe throughout their lifespan.
Protecting Against Cybersecurity Threats: Modern vehicles are complex computer networks on wheels, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Secure OTA updates are a crucial defense against these threats. By encrypting and authenticating software updates, automakers can protect against unauthorized modifications and ensure that only trusted, verified updates are installed.
Cost-Effective Maintenance: OTA updates can significantly reduce maintenance costs for automakers and vehicle owners. Traditional recalls and service campaigns can be costly and time-consuming. Secure OTA updates enable remote diagnostics and repairs, reducing the need for physical visits to service centers. This not only saves money but also minimizes inconvenience for vehicle owners.
Minimizing Downtime: For fleet operators and commercial vehicle owners, minimizing downtime is of paramount importance. Secure OTA updates can be scheduled during non-operational hours, ensuring that vehicles are on the road when needed. This efficiency is especially critical for industries like logistics and transportation, where downtime translates to revenue loss.
Customization and Feature Enhancements: Secure OTA updates also open the door to customization and feature enhancements. Automakers can offer new features or performance improvements to customers, enhancing the overall ownership experience. This flexibility helps in retaining customer loyalty and adapting to evolving consumer preferences.
Data Security and Privacy: Secure OTA updates are not just about protecting the vehicle’s physical systems but also safeguarding sensitive data. Many modern vehicles collect and transmit data related to driver behavior, location, and more. Secure updates ensure that this data remains confidential and is not susceptible to breaches or tampering.
Regulatory Compliance: As regulations and industry standards evolve, automakers must ensure that their vehicles comply with the latest cybersecurity and data protection requirements. Secure OTA updates enable manufacturers to stay compliant with changing regulations without the need for costly hardware changes.
Continuous Improvement: Secure OTA updates empower automakers to adopt an agile approach to software development. They can collect real-world data from their vehicles, identify issues or opportunities for improvement, and then deploy updates rapidly. This continuous improvement cycle can result in safer, more efficient, and more reliable vehicles over time.
Consumer Confidence: Building trust with consumers is crucial in the automotive industry. Secure OTA updates demonstrate a commitment to customer safety and satisfaction. When consumers trust that their vehicles are protected against cybersecurity threats and that they can enjoy the latest features hassle-free, it enhances their confidence in the brand.
Collaboration and Industry Standards: The development of secure OTA update mechanisms often involves collaboration across the automotive industry. Standardizing secure update protocols and practices ensures interoperability and enhances the overall security posture of the entire sector.
In conclusion, secure OTA updates represent a pivotal shift in the automotive industry’s approach to software management. They not only enhance vehicle safety and performance but also offer cost savings, convenience, and the ability to adapt to an ever-changing technological landscape. As automakers continue to invest in these technologies, the future of automotive software management looks poised to be more secure, efficient, and consumer-friendly.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Protect Your Computer From Viruses, Hackers, and Spies | State of …

Encrypting data both at rest and in transit helps protect sensitive information from being intercepted or tampered with.
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is a fundamental practice in modern information security, serving as a powerful shield against the ever-present threats of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Data at Rest Encryption: When data is said to be “at rest,” it means that it is stored on a physical or digital storage medium, such as hard drives, databases, or cloud storage, rather than actively being transmitted between systems. Encrypting data at rest involves converting this data into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key.
This security measure is crucial for protecting sensitive information, as it prevents unauthorized access to data even if the storage medium is physically stolen or compromised. In the event of a breach, encrypted data remains essentially useless to unauthorized parties, significantly reducing the potential impact of a security incident.
Data in Transit Encryption: Data in transit refers to information actively moving between two or more systems over a network or communication channel. Encrypting data in transit involves scrambling the data so that it cannot be intercepted or understood by unauthorized entities during transmission. This protection is especially critical when data travels over the internet or untrusted networks.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols are commonly used to establish secure, encrypted connections for activities like online banking, e-commerce transactions, and secure email communication. These encryption methods ensure that sensitive data, such as login credentials, financial information, and personal details, remains confidential during transmission.
Comprehensive Data Protection: The combination of encrypting data both at rest and in transit creates a comprehensive defense against various security threats:
Confidentiality: Encryption safeguards the confidentiality of sensitive information, ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access and understand the data.
Integrity: Encryption helps maintain data integrity by detecting any unauthorized alterations during transmission or while at rest. If any tampering is detected, the decryption process will fail, alerting security teams to potential breaches.
Compliance: Many industries and regulations mandate the use of encryption to protect sensitive data. Compliance with these requirements is essential for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining trust with customers.
Risk Mitigation: In the unfortunate event of a data breach, encrypted data limits the exposure of sensitive information, reducing the potential financial and reputational damage to organizations.
User Trust: Encrypting data at rest and in transit demonstrates a commitment to data security, enhancing user trust and confidence, which is especially important in sectors that handle sensitive customer data.
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats are ever-present and sophisticated, data encryption serves as a foundational pillar of cybersecurity. It not only helps protect sensitive information but also contributes to a safer and more secure digital ecosystem, safeguarding the privacy and trust of individuals, organizations, and institutions alike.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris Administration Delivers on …

Implementing strong authentication and authorization protocols ensures that only authorized individuals can access and control vehicle systems.
Implementing strong authentication and authorization protocols ensures that only authorized individuals can access and control vehicle systems. This critical aspect of vehicle cybersecurity is akin to safeguarding the digital “keys” to a modern car’s functionality and data. Let’s explore how robust authentication and authorization mechanisms contribute to vehicle security and privacy:
1. Biometric Authentication: One of the most advanced methods for ensuring the right person is behind the wheel involves biometric authentication. Features such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, or even retina scans can be integrated into vehicles. These biometric identifiers are unique to each individual, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized users to gain access to the vehicle’s systems. Biometric authentication also provides a seamless and convenient user experience, as drivers simply need to provide their biometric data to unlock and start the vehicle.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more types of identification before accessing vehicle systems. This could involve a combination of something the user knows (like a password or PIN) with something the user has (such as a physical key fob or a smartphone app). MFA significantly enhances security by making it more challenging for attackers to breach the authentication process.
3. User Profiles and Permissions: Assigning different user profiles with varying levels of access and permissions is another crucial aspect of authorization. For instance, a car owner may have full control over all vehicle functions, while a guest driver might have limited access. This way, individuals can share the vehicle without compromising its security. Additionally, these profiles can be customized to restrict certain functions when, for example, a teenager is using the car.
4. Secure Key Management: The secure storage and management of cryptographic keys used for authentication and encryption are fundamental to protecting vehicle systems from unauthorized access. Manufacturers must implement robust key management practices to prevent key exposure, theft, or tampering.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Anomaly Detection: Real-time monitoring of user interactions with vehicle systems, coupled with anomaly detection algorithms, can help identify suspicious behavior. If an unauthorized access attempt or unusual activity is detected, the system can trigger alerts and take preventive measures to mitigate the threat.
6. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Manufacturers can leverage OTA software updates to patch vulnerabilities and strengthen authentication and authorization mechanisms. Regular updates ensure that the vehicle’s cybersecurity remains up-to-date and adaptive to emerging threats.
7. User Education: Vehicle owners and users should be educated about the importance of strong authentication and authorization practices. This includes using unique, complex passwords or PINs, safeguarding their biometric data, and understanding the security features of their vehicles.
In an era where vehicles are becoming increasingly connected and reliant on digital technologies, the implementation of robust authentication and authorization protocols is not only a matter of convenience but also a vital component of ensuring the safety, security, and privacy of both drivers and passengers. As technology continues to advance, so too must the cybersecurity measures that protect our vehicles from potential threats.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Authentication vs. Authorization: What’s the Difference? | OneLogin

Advanced machine learning algorithms can detect abnormal behavior in a vehicle’s systems, allowing for early identification of potential cyber threats.
In the era of increasingly connected vehicles, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. To safeguard both the vehicle and its occupants from potential cyber threats, advanced machine learning algorithms play a pivotal role. These algorithms have the capacity to not only detect but also respond to abnormal behavior in a vehicle’s systems, ushering in a new era of proactive cybersecurity:
Behavioral Anomaly Detection: Advanced machine learning algorithms can continuously monitor the vast array of data generated by a vehicle’s systems. By establishing a baseline of normal behavior, these algorithms can quickly identify deviations that may signal a cyber threat. For instance, unexpected fluctuations in sensor readings, unusual software activity, or unauthorized access attempts can trigger alerts, prompting immediate investigation and action.
Predictive Analysis: Machine learning goes beyond just identifying anomalies; it can also predict potential threats based on historical data and patterns. By analyzing past cybersecurity incidents and vulnerabilities, these algorithms can forecast potential future attacks and vulnerabilities, allowing manufacturers to proactively address and patch them before they can be exploited.
Real-time Response: One of the most significant advantages of machine learning algorithms is their ability to respond in real-time. When an anomaly is detected, these algorithms can trigger immediate countermeasures. This might involve isolating the affected system, updating software, or alerting the vehicle owner and manufacturer to take corrective action.
Adaptive Security: Machine learning models are dynamic and adaptive. They can continuously learn from new data and evolve their threat detection capabilities. As cyber threats evolve, these algorithms can adapt to recognize new attack patterns and vulnerabilities, providing an ever-improving line of defense.
Reduced False Positives: Advanced machine learning algorithms excel at reducing false positives, which can be a significant challenge in traditional cybersecurity methods. Their ability to differentiate between genuine threats and benign anomalies minimizes unnecessary alarms, allowing for more efficient use of resources and minimizing disruption for vehicle owners.
Cloud-Based Updates: Many vehicles are now equipped with over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can facilitate the secure delivery of OTA security patches and updates, ensuring that vehicles stay protected against the latest threats without requiring a physical visit to a dealership.
Collaborative Threat Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms can contribute to a collective pool of threat intelligence. Data from one vehicle’s threat detection can be anonymized and shared within a network, providing valuable insights into emerging cyber threats and attack trends across different vehicle models and manufacturers.
In summary, advanced machine learning algorithms represent a crucial component of modern vehicle cybersecurity. Their ability to autonomously detect and respond to abnormal behavior enhances the security posture of connected vehicles, safeguarding not only the vehicle itself but also the safety and privacy of its occupants. As the automotive industry continues to embrace technology and connectivity, the role of machine learning in cybersecurity will become increasingly indispensable in countering the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Vehicle Cybersecurity | NHTSA

Educating both consumers and automotive professionals about the risks and best practices for cybersecurity is essential in building a culture of awareness and vigilance.
Building a culture of cybersecurity awareness and vigilance within the automotive industry and among consumers is a proactive and crucial step in safeguarding the digital integrity of vehicles and the privacy of those who drive them. This educational effort can take several forms and have far-reaching benefits:
Cybersecurity Training: Providing comprehensive cybersecurity training programs for automotive professionals, from engineers and developers to service technicians, ensures that they understand the potential threats and vulnerabilities. This knowledge equips them to design, develop, and maintain secure systems and respond effectively to emerging threats.
Consumer Education: For vehicle owners and users, raising awareness about cybersecurity risks and best practices is essential. Automakers can provide user-friendly guides, online resources, and in-vehicle notifications to inform consumers about the importance of keeping software up to date, using strong and unique passwords, and being cautious with third-party devices or apps that connect to the vehicle.
Simulated Attacks: Conducting simulated cyberattacks, also known as penetration testing, can be an eye-opening experience for both automotive professionals and consumers. These exercises demonstrate the vulnerabilities that exist within vehicle systems and emphasize the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Industry Standards and Certification: The automotive industry can establish cybersecurity standards and certification programs, similar to those in other sectors like information technology and healthcare. Compliance with these standards can be a mark of trust for consumers, reassuring them that their vehicles meet rigorous cybersecurity criteria.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Encouraging collaboration between automakers, government agencies, cybersecurity experts, and academia can foster an environment of shared knowledge and resources. Information sharing about threats and vulnerabilities can lead to faster and more effective responses to emerging cybersecurity challenges.
Legislation and Regulation: Governments can play a pivotal role in promoting cybersecurity awareness by implementing legislation and regulations that require automakers to adhere to cybersecurity standards and disclose data breach incidents. These laws can incentivize proactive cybersecurity measures and hold companies accountable for breaches.
Ethical Hacking: Encouraging ethical hacking or bug bounty programs can incentivize cybersecurity experts to identify vulnerabilities and report them responsibly. Offering rewards for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities can strengthen a vehicle’s security.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Automakers should prioritize continuous monitoring of their vehicle fleets and providing regular software updates. Consumers should be educated on the importance of promptly installing these updates to patch known vulnerabilities.
Transparency: Building trust with consumers involves transparency about how data is collected, stored, and used in connected vehicles. Clear and concise privacy policies should be made available, and consumers should have the ability to control their data-sharing preferences.
Community Engagement: Hosting workshops, webinars, and community outreach events can engage both automotive professionals and consumers in discussions about cybersecurity. These forums provide opportunities for questions, shared experiences, and collaborative problem-solving.
In conclusion, the journey to a safer and more secure automotive ecosystem begins with education and awareness. By equipping automotive professionals and consumers with the knowledge and tools to understand and mitigate cybersecurity risks, the industry can take a significant stride toward preventing cyberattacks, safeguarding personal information, and ensuring the trust and safety of connected vehicles. As technology continues to advance, a proactive approach to cybersecurity education remains essential for the digital age of transportation.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Online Cyber Security Master’s | University of North Dakota

The automotive industry is increasingly collaborating with cybersecurity organizations and government agencies to share threat intelligence and develop best practices for cybersecurity.
The collaborative efforts between the automotive industry, cybersecurity organizations, and government agencies to enhance vehicle cybersecurity are essential steps in addressing the growing challenges posed by cyber threats. Here’s an in-depth exploration of the significance and potential outcomes of these partnerships:
Knowledge Sharing: Collaboration allows for the exchange of valuable threat intelligence and information regarding emerging cybersecurity risks. This shared knowledge enables the industry to stay ahead of potential threats by understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures used by malicious actors.
Rapid Response: In the event of a cybersecurity breach or vulnerability discovery, these partnerships facilitate swift response and mitigation efforts. The combined expertise of cybersecurity experts and government agencies can help automakers and technology providers quickly address and resolve issues to minimize potential harm.
Standardization and Regulation: Collaborative efforts can contribute to the development of industry standards and regulations related to vehicle cybersecurity. Establishing common practices and guidelines helps ensure a consistent level of security across the automotive sector, benefiting both manufacturers and consumers.
Public Awareness: Through collaboration, industry stakeholders can collectively raise awareness about the importance of vehicle cybersecurity. This increased awareness can empower consumers to make informed choices when purchasing connected vehicles and encourage them to follow best practices for securing their vehicles.
Threat Assessment and Risk Management: Cybersecurity organizations and government agencies can assist in assessing the evolving threat landscape. By analyzing emerging risks, they can work together with automakers to implement effective risk management strategies that protect vehicles throughout their lifecycle.
Testing and Certification: Collaboration can lead to the establishment of testing and certification processes for vehicle cybersecurity. This ensures that vehicles meet specific security standards before they are released to the market, providing consumers with greater confidence in the security of their vehicles.
Global Coordination: Given the global nature of the automotive industry, international cooperation is crucial. Collaborative efforts help align cybersecurity practices and regulations across different regions, preventing fragmentation and ensuring a consistent approach to cybersecurity worldwide.
Innovation and Research: These partnerships foster innovation in the field of automotive cybersecurity. With access to shared research and development resources, the industry can continuously evolve its security measures to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Incident Response Planning: Collaborative initiatives often involve the development of incident response plans. These plans outline how the industry and government agencies will coordinate their actions in the event of a cybersecurity incident, ensuring a more efficient and effective response.
In summary, the collaboration between the automotive industry, cybersecurity organizations, and government agencies is a proactive and crucial response to the growing cybersecurity challenges in the automotive sector. These partnerships not only enhance vehicle security but also contribute to the overall safety and resilience of connected and autonomous vehicles, ultimately benefiting consumers and the future of mobility.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Vehicle Cybersecurity | NHTSA
The battle against vehicle cyber threats is ongoing, as hackers continually adapt and evolve their tactics. As a result, vehicle cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment to staying ahead of potential risks. Automakers, regulators, and cybersecurity experts must work collaboratively to establish and enforce robust cybersecurity standards.
The battle against vehicle cyber threats is an ever-evolving challenge, as hackers continually adapt and evolve their tactics. This dynamic landscape underscores the fact that vehicle cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but rather an ongoing commitment to staying ahead of potential risks. To address this pressing issue effectively, a multifaceted approach is necessary, involving collaboration among automakers, regulators, and cybersecurity experts. Here, we’ll delve deeper into why this collaborative and continuous effort is vital:
Rapid Technological Advancements: The automotive industry is witnessing rapid technological advancements, including increased connectivity, automation, and data sharing. With each innovation comes the potential for new vulnerabilities. This necessitates a continuous commitment to research, development, and adaptation to evolving threats.
Sophisticated Threat Actors: Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it essential to keep pace with their tactics. They employ advanced techniques to breach vehicle systems, steal sensitive data, or disrupt critical functions. An ongoing commitment to cybersecurity ensures that automakers are ready to counter these threats effectively.
Constant Connectivity: Modern vehicles are more connected than ever before, with features like infotainment systems, over-the-air updates, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. While these advancements offer convenience and innovation, they also introduce more entry points for cyberattacks. Continuous monitoring and security updates are essential to safeguard these connections.
Regulatory Landscape: Governments around the world are recognizing the importance of vehicle cybersecurity. As a result, they are introducing regulations and standards to ensure that automakers prioritize cybersecurity. Staying compliant with evolving regulations requires ongoing diligence and adaptation.
Consumer Trust: Maintaining consumer trust is paramount. Any cybersecurity breach can erode confidence in connected vehicles and the automotive industry as a whole. An ongoing commitment to cybersecurity demonstrates to consumers that their safety and data privacy remain top priorities.
Cross-Industry Collaboration: Cybersecurity threats often transcend industry boundaries. Collaboration between automakers, cybersecurity experts, and other industries, such as technology and telecommunications, is crucial for sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and research findings. This collaborative effort helps in developing comprehensive cybersecurity solutions.
Continuous Education and Training: The landscape of cybersecurity is complex and ever-changing. Automakers need to invest in continuous education and training for their workforce to ensure that they are well-equipped to identify, address, and prevent cyber threats effectively.
Redundancy and Resilience: An ongoing commitment to cybersecurity includes the development of redundancy and resilience within vehicle systems. This ensures that even if a breach occurs, vehicles can continue to operate safely and securely.
Ethical Hacking and Red Teaming: Automakers should regularly engage in ethical hacking and red teaming exercises to identify vulnerabilities proactively. These exercises simulate real-world cyberattacks, helping to uncover weaknesses that need immediate attention.
In conclusion, the battle against vehicle cyber threats is an ongoing and multifaceted endeavor. A continuous commitment to research, development, collaboration, education, and compliance is essential to protect vehicles and their passengers from evolving cybersecurity risks. By working together, automakers, regulators, and cybersecurity experts can create a safer and more secure future for connected vehicles and the broader transportation ecosystem.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Automated Vehicle Safety | NHTSA

Conclusion
As vehicles continue to evolve into highly connected and autonomous platforms, the importance of vehicle cybersecurity cannot be overstated. The industry’s dedication to implementing anti-hacking measures will be integral in ensuring that the benefits of smart and connected vehicles are enjoyed without compromising safety, privacy, or security. In the ever-expanding digital landscape of the automotive sector, cybersecurity is a fundamental component that will shape the future of mobility.
The future of mobility is undeniably intertwined with the continued evolution of highly connected and autonomous vehicles. This transformative shift promises to revolutionize transportation, offering enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience. However, it also brings with it an unprecedented level of complexity and digital integration, elevating the importance of vehicle cybersecurity to a paramount position.
Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles, with their reliance on extensive sensor arrays, high-speed data networks, and complex algorithms, are particularly vulnerable to cyber threats. Any compromise in the software or data integrity of an autonomous vehicle could have severe consequences, making robust cybersecurity measures indispensable.
Privacy Concerns: With vehicles becoming increasingly connected to the internet, the potential for data breaches and privacy infringements grows. Protecting the personal data of vehicle occupants, including location history, personal preferences, and biometric data, becomes a critical aspect of cybersecurity.
Safety: Beyond data privacy, the physical safety of occupants is at stake. Cyberattacks on a vehicle’s control systems can lead to catastrophic consequences, including accidents and loss of life. Ensuring the safety and integrity of these systems is non-negotiable.
Supply Chain Security: Vehicle manufacturing involves a complex global supply chain. Ensuring the security of components and software from suppliers is vital. Cyberattacks on components sourced from third parties can compromise the entire vehicle’s cybersecurity.
Legislation and Regulation: As the significance of vehicle cybersecurity continues to grow, governments and regulatory bodies are drafting legislation and standards to ensure minimum cybersecurity requirements. Compliance with these regulations will become a necessity for automakers.
Collaboration and Threat Sharing: The automotive industry recognizes that cybersecurity is not a competitive differentiator but a collective challenge. Collaboration between automakers, cybersecurity firms, and government agencies in sharing threat intelligence and best practices will be essential to stay ahead of cyber threats.
Continuous Adaptation: Cyber threats evolve rapidly, requiring a continuous commitment to adaptation and improvement in cybersecurity measures. Regular updates, threat assessments, and penetration testing are all part of a proactive strategy to protect vehicles from emerging threats.
Consumer Trust: Ultimately, the success of smart and connected vehicles hinges on consumer trust. To encourage widespread adoption, automakers must convey a clear commitment to cybersecurity, offering transparency about the measures in place to protect their customers’ safety, privacy, and security.
In conclusion, vehicle cybersecurity is not merely a component of automotive technology; it is a linchpin in the future of mobility. The industry’s dedication to implementing anti-hacking measures is instrumental in ensuring that the promises of smart and connected vehicles are realized without compromise. As vehicles become increasingly intertwined with the digital landscape, cybersecurity will remain a fundamental and dynamic component, shaping the trajectory of the automotive sector and its contribution to safer, more efficient, and more secure transportation for all.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Automated Vehicle Safety | NHTSA
More links
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Automotive Cybersecurity for ECUs & In-Vehicle Networks …
