Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, safety remains a top priority. Vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology have come to the forefront, offering advanced features and innovations designed to protect drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. This article explores the latest developments in vehicle safety systems, their role in reducing accidents, and the promise they hold for a safer future on the road.
With the rapid advancement of vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology, we are witnessing a revolution in road safety. These cutting-edge innovations are reshaping the way we approach transportation safety, from preventing accidents to mitigating their severity. In this article, we will delve into the remarkable world of vehicle safety systems, exploring how these technologies work, the benefits they bring, and their critical role in safeguarding lives on the road.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Crash Avoidance | NHTSA
Modern vehicles are equipped with a range of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) that use sensors, cameras, and radar to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and provide real-time information to the driver. These systems offer several crucial safety features:
“Furthermore, ADAS technologies continue to evolve, paving the way for more advanced autonomous driving capabilities that have the potential to transform the way we commute and travel in the near future.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here ADAS: Everything You Need to Know
ACC automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. It reduces the need for constant speed adjustments and minimizes the risk of rear-end collisions.
“ACC automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. It reduces the need for constant speed adjustments and minimizes the risk of rear-end collisions. This technology enhances both safety and driving comfort.”
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Impact of adaptive cruise control (ACC) system on fatality and injury …
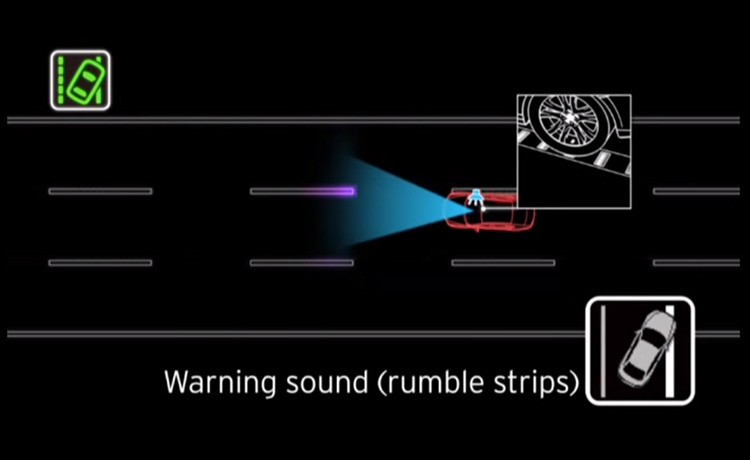
LDW alerts the driver if the vehicle unintentionally drifts out of its lane. LKA goes a step further by actively steering the vehicle back into its lane.
LDW (Lane Departure Warning) and LKA (Lane Keeping Assist) are both advanced driver assistance systems designed to enhance vehicle safety and prevent accidents related to unintentional lane departures. LDW serves as a warning system, alerting the driver when the vehicle drifts out of its lane without the use of turn signals. This alert is usually conveyed through visual or audible cues, such as flashing lights, vibrations, or beeping sounds, depending on the vehicle’s design.
LKA, on the other hand, takes a proactive approach to correct lane deviations. It not only detects when the vehicle is leaving its lane but actively intervenes to guide the vehicle back into the lane. This intervention can be achieved through various means, such as steering input, braking on one side of the vehicle, or adjustments to the power steering. LKA technology uses cameras and sensors to monitor lane markings and the vehicle’s position within them.
Both LDW and LKA systems aim to reduce the risk of accidents caused by lane drifting, which can result from driver distraction, drowsiness, or momentary lapses in attention. By providing warnings or corrective actions, these systems contribute to improved road safety and help drivers stay within their lanes, reducing the likelihood of collisions with other vehicles or objects on the road.
As automotive technology continues to advance, these lane-keeping and warning systems may become even more sophisticated, further enhancing safety on our roads.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Driver Assistance Technologies | NHTSA
BSD uses sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spot and provides warnings to prevent lane-change accidents.
Blind Spot Detection (BSD) has emerged as a lifesaving feature in modern vehicles. Using a network of sensors, typically mounted on the sides and rear of the vehicle, BSD constantly monitors the driver’s blind spots. When another vehicle enters these blind spots, the system triggers a visual or audible alert to warn the driver. This real-time feedback acts as an extra set of eyes, reducing the risk of collisions during lane changes or merging onto highways.
BSD technology primarily relies on radar sensors or cameras to scan the adjacent lanes. These sensors continuously send data to the vehicle’s onboard computer, which analyzes it to detect the presence and relative speed of nearby vehicles. When a potential collision threat is identified, the system promptly notifies the driver.
One of the standout advantages of BSD is its ability to function in various driving conditions, including inclement weather and low visibility. Rain, fog, or darkness doesn’t hinder its performance, making it a reliable safety feature day and night.
Moreover, some advanced BSD systems include Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA) capabilities. RCTA extends the functionality of BSD to provide warnings when a vehicle is approaching from the sides while the driver is reversing, making it invaluable in crowded parking lots and busy intersections.
BSD has proven to be a game-changer in reducing accidents related to lane changes and blind spots. By enhancing driver awareness and assisting in critical decision-making moments, BSD contributes significantly to road safety. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated iterations, further elevating the standard of vehicle safety.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Target Crash Population For Crash Avoidance Technologies in …

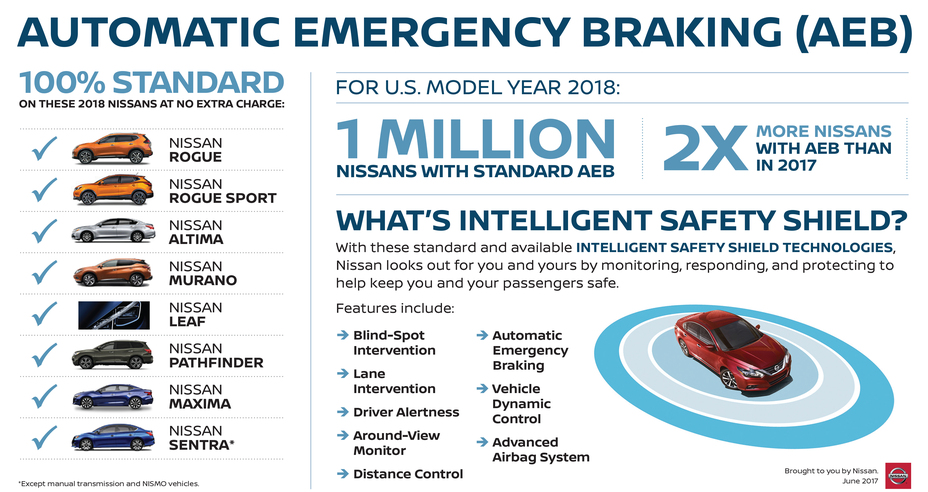
FCW warns the driver of an impending collision, while AEB can automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the severity of a collision.
“In addition to FCW and AEB, many ADAS features include lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and blind-spot monitoring, providing a comprehensive safety net for drivers in various driving conditions.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Effects of forward collision warning and automatic emergency …
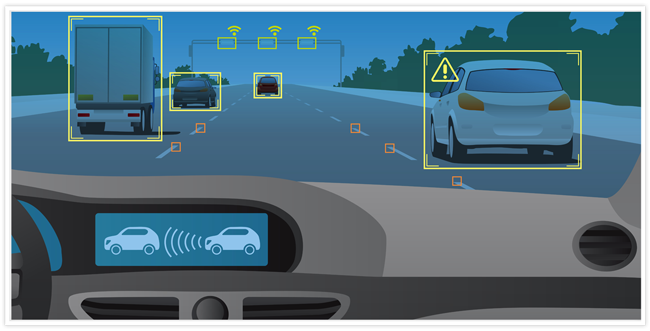
Vehicle safety systems have expanded beyond protecting occupants to safeguarding pedestrians as well. Pedestrian detection systems use cameras and sensors to identify pedestrians in or near the vehicle’s path. If a potential collision is detected, the system can initiate visual and auditory alerts to the driver and, in some cases, apply emergency braking to avoid or reduce the impact.
“Vehicle safety systems have expanded beyond protecting occupants to safeguarding pedestrians as well. Pedestrian detection systems use cameras and sensors to identify pedestrians in or near the vehicle’s path. If a potential collision is detected, the system can initiate visual and auditory alerts to the driver and, in some cases, apply emergency braking to avoid or reduce the impact. This technology plays a crucial role in enhancing road safety for all road users.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Driver Assistance Technologies | NHTSA
Crash avoidance technology aims to prevent accidents before they happen. Key technologies in this category include:
Crash avoidance technology represents a significant leap forward in automotive safety, with a focus on preventing accidents and reducing their severity. Several key technologies are at the forefront of this category, each designed to address specific aspects of road safety:
Forward Collision Warning (FCW): FCW systems use sensors, such as radar and cameras, to monitor the road ahead. When they detect a potential collision with a vehicle or pedestrian, these systems provide the driver with visual or audible warnings. In some cases, FCW can also initiate automatic emergency braking to mitigate or avoid the impending collision.
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AEB takes FCW a step further by actively applying the vehicle’s brakes if the driver does not respond to the collision warning in time. This technology can significantly reduce the severity of collisions or even prevent them altogether, particularly in situations where the driver’s reaction time is limited.
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): BSM systems use sensors to monitor the vehicle’s blind spots, areas that are typically not visible to the driver through mirrors. When a vehicle enters a blind spot, BSM provides visual or audible alerts to warn the driver, preventing unsafe lane changes and potential side collisions.
Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA): RCTA systems are especially useful when backing out of parking spaces or driveways. They detect approaching vehicles or pedestrians from the sides and provide warnings to the driver, reducing the risk of collisions while reversing.
Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA): LDW alerts the driver if the vehicle unintentionally drifts out of its lane without signaling. LKA, on the other hand, actively intervenes by steering the vehicle back into its lane. These systems help prevent accidents caused by lane drifting, drowsiness, or momentary lapses in attention.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC maintains a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead by automatically adjusting the vehicle’s speed. It uses sensors to detect the speed of the vehicle in front and can even bring the vehicle to a complete stop if necessary, reducing the risk of rear-end collisions due to sudden stops.
Pedestrian Detection and Protection: These systems use sensors and cameras to identify pedestrians in or near the vehicle’s path. When a potential collision is detected, the system can activate the brakes or take evasive actions to avoid or mitigate the impact.
By integrating these advanced technologies into modern vehicles, automakers are striving to make our roads safer and reduce the frequency and severity of accidents. These systems provide an additional layer of protection for drivers, passengers, and pedestrians, contributing to improved road safety and overall peace of mind. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated crash avoidance features to become standard in vehicles, further enhancing safety on our roads.
You can also read more about this here: Crash Avoidance | NHTSA
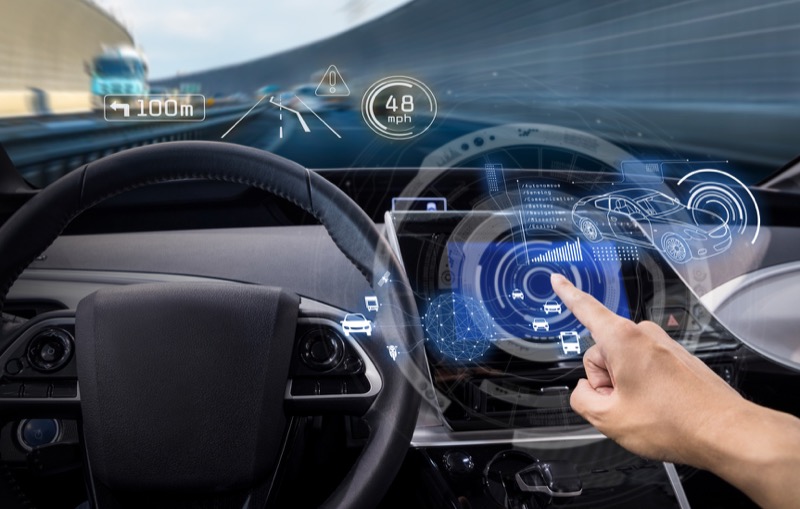

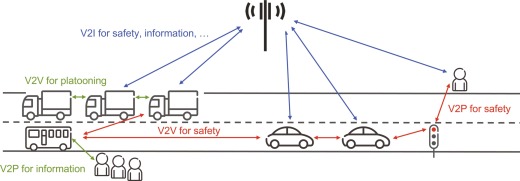
V2V technology enables vehicles to exchange data about their speed, position, and direction. This information helps vehicles predict potential collisions and take evasive actions, such as steering or braking.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication is a revolutionary advancement in vehicle safety technology. It essentially allows vehicles to “talk” to each other, exchanging critical data that can help prevent accidents and improve overall road safety.
At the heart of V2V communication are dedicated short-range radio communication devices installed in vehicles. These devices constantly transmit and receive information to and from nearby vehicles within a certain range. This information includes data about each vehicle’s speed, position, and direction of travel.
The real magic of V2V technology happens when this data is processed and analyzed by each vehicle’s onboard computer system. These computers are equipped with sophisticated algorithms that can predict potential collision scenarios based on the information received from neighboring vehicles. When a collision risk is detected, the system can provide warnings to the driver in various ways, such as visual alerts on the dashboard or audible warnings.
What sets V2V technology apart is its ability to go beyond the capabilities of a single vehicle’s sensors and cameras. While a vehicle’s onboard sensors are excellent at detecting immediate surroundings, they have limitations when it comes to seeing “around corners” or beyond obstacles. V2V communication effectively extends a vehicle’s awareness beyond its line of sight, providing a comprehensive view of the traffic environment.
In practice, V2V technology can be a lifesaver in situations where a collision is imminent but not yet visible to the driver. For example, if a car up ahead suddenly slams on its brakes due to an obstacle, V2V-equipped vehicles trailing behind will instantly receive this information and can begin to react even before the driver has a chance to see the obstruction. This split-second advantage can make all the difference in avoiding a collision.
V2V technology doesn’t just stop at providing warnings; it can also enable vehicles to take evasive actions automatically. Some advanced systems can intervene in the vehicle’s control systems, such as applying the brakes or steering, to help avoid or mitigate a collision.
As more vehicles become equipped with V2V technology and as it becomes a standard feature, we can expect significant reductions in accidents caused by factors like sudden braking, rapid lane changes, or unexpected obstacles on the road. V2V communication is a crucial building block in the development of autonomous vehicles and the creation of safer and more efficient transportation systems.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication | NHTSA
This system uses sensors and cameras to monitor intersections and alert drivers to potential collisions, especially when another vehicle is approaching from a different direction.
“Intersection monitoring systems can significantly enhance safety at crossroads, helping drivers make informed decisions and avoid dangerous situations. By detecting potential collisions and providing timely warnings, these systems contribute to reducing accidents and improving road safety.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Intersection Collision Warning System – FHWA-RD-99-103

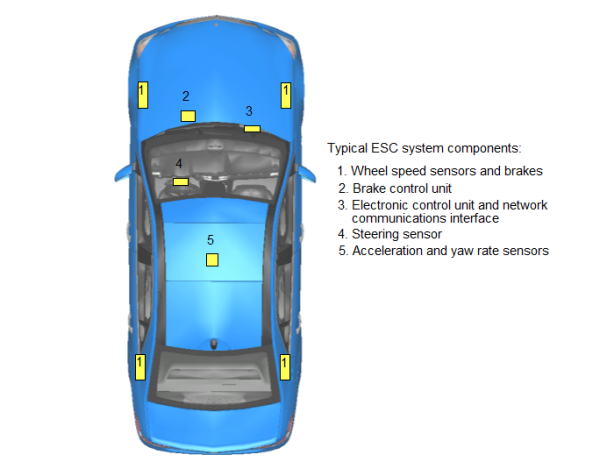
ESC helps prevent skidding and rollovers by applying individual brakes and reducing engine power when a loss of vehicle control is detected.
“ESC, or Electronic Stability Control, is a vital safety feature that helps prevent skidding and rollovers by applying individual brakes and reducing engine power when a loss of vehicle control is detected. By continuously monitoring various parameters, such as steering angle and vehicle speed, ESC acts swiftly to keep the vehicle stable, ensuring safer driving experiences and reducing the risk of accidents.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Electronic Stability Control (ESC) – Publication Topic – CrashStats …
Independent organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) conduct rigorous crash tests to assess vehicle safety. These tests evaluate various aspects, including crashworthiness, crash avoidance technology effectiveness, and pedestrian safety. Vehicle manufacturers strive to achieve high ratings in these tests to demonstrate their commitment to safety.
Independent organizations such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) play a pivotal role in enhancing vehicle safety standards. They conduct comprehensive crash tests and evaluations to rigorously assess the safety performance of vehicles. These tests cover various critical aspects of safety, helping consumers make informed choices and encouraging automakers to prioritize safety innovations. Here are some key areas that these organizations assess:
Crashworthiness: This assessment evaluates how well a vehicle protects its occupants in the event of a crash. It includes frontal, side, and rear impact tests, assessing factors like the structural integrity of the vehicle, airbag effectiveness, and the likelihood of injury to occupants.
Crash Avoidance Technologies: NHTSA and IIHS assess the effectiveness of crash avoidance technologies, such as Forward Collision Warning (FCW), Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), and Lane Departure Warning (LDW). These technologies are tested under various scenarios to determine their ability to prevent or mitigate collisions.
Pedestrian Safety: Ensuring the safety of pedestrians is a crucial aspect of vehicle design. Both organizations conduct tests to assess how well vehicles protect pedestrians in the event of a collision, including evaluations of front-end impact protection and pedestrian detection and protection systems.
Rollover Resistance: Rollover crashes can be particularly dangerous. Testing evaluates a vehicle’s stability and likelihood of rolling over during emergency maneuvers, helping consumers make informed decisions about vehicle safety.
Child Seat Anchors (LATCH): IIHS assesses the ease of use and effectiveness of the Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH) system, which secures child safety seats in vehicles. An easily accessible and user-friendly LATCH system is essential for child safety.
High ratings in these tests are highly sought after by vehicle manufacturers, as they demonstrate a commitment to safety and provide a competitive edge in the market. Consumers can use these ratings as a valuable resource when choosing a vehicle, ensuring they prioritize safety for themselves and their families.
As technology advances and new safety features are developed, the criteria for safety evaluations may evolve to encompass emerging technologies. This ongoing commitment to rigorous testing and evaluation is instrumental in driving continuous improvement in vehicle safety, ultimately making our roads safer for everyone.
You can also read more about this here: IIHS-HLDI

As technology continues to advance, vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology will become more sophisticated. The ultimate goal is to create a future where accidents are rare, and road safety is significantly improved. By integrating these systems into an increasing number of vehicles, we move closer to that vision, making our roads safer for everyone.
The relentless march of technology shows no signs of slowing down, especially when it comes to vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology. As we look to the future, there’s a promising landscape of even more sophisticated and intelligent safety features on the horizon.
One of the key areas where we can expect significant advancements is in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies are poised to transform vehicle safety by enabling systems to learn and adapt in real-time. Imagine a car that not only detects an impending collision but also predicts the most effective way to avoid it based on past data and the current situation. AI can make these split-second decisions even more precise, potentially reducing accident rates to unprecedented lows.
Additionally, we’re likely to see enhanced sensor technologies, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and radar, become more affordable and widely available. These sensors, which are already used in some autonomous vehicles, can provide incredibly detailed and real-time information about a vehicle’s surroundings. As their adoption grows, they’ll contribute to a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of the road environment, further improving safety.
The integration of V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle) and V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure) communication will also play a significant role. As more vehicles and traffic infrastructure become connected, the ability to share critical safety information will expand, reducing the risk of accidents caused by sudden lane changes, red-light runners, or unexpected road conditions. This interconnectedness will create a network of safety that spans entire road systems.
Moreover, automakers and tech companies are investing heavily in research and development to perfect autonomous driving systems. While full autonomy is still on the horizon, even advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are becoming more capable with each iteration. These systems can take over various driving tasks, such as lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and even parking, reducing the risk of human error.
The integration of biometric sensors and advanced driver monitoring systems is another exciting frontier. These technologies can monitor a driver’s alertness and physical state, helping prevent accidents caused by drowsiness or distraction. In some cases, they can also authenticate drivers for added security.
In conclusion, the future of vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology is one of continuous improvement and innovation. With advancements in AI, sensor technology, connectivity, and automation, we are moving ever closer to a world where accidents are rare occurrences, and road safety is significantly enhanced. As these systems become standard in more vehicles, we can look forward to safer roads for everyone.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Safety Features and Technology: Discover Buick

Conclusion
Vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technology represent significant advancements in the automotive industry’s commitment to safety. These technologies not only protect drivers and passengers but also extend their reach to pedestrians and other road users. As these systems continue to evolve and become more widespread, the potential for reducing accidents and saving lives on the road grows, ultimately leading to a safer and more secure transportation environment for all.
“The continuous evolution and integration of vehicle safety systems and crash avoidance technologies are pivotal in creating a safer and more inclusive transportation landscape. These innovations not only prioritize the safety of drivers and passengers but also extend their protective shield to pedestrians and fellow road users. As these technologies become more prevalent, the potential for mitigating accidents and preserving lives on the road expands, promising a future where transportation is safer and more secure for everyone.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Autonomous vehicles: challenges, opportunities, and future …
More links
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Next Wave in Safety Tech: Collision Avoidance Systems
