Introduction
The advent of Web3, an internet built on decentralized principles and blockchain technology, has paved the way for a transformative approach to identity management. At the heart of this paradigm shift is the concept of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), a groundbreaking concept that empowers individuals to have complete control over their digital identities. In this article, we will delve into the world of Web3 and SSI, exploring how this innovative approach is revolutionizing the way we manage and protect our online identities.
The advent of Web3, built on blockchain and decentralized principles, marks a turning point in how we perceive and manage our online identities. At the forefront of this digital revolution lies the concept of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), a transformative idea that grants individuals unprecedented control over their digital personas. As we journey deeper into the realm of Web3 and SSI, we’ll uncover not only the technological intricacies but also the profound societal implications of this innovation, reshaping how we safeguard and wield our online identities.
Web3, in its essence, signifies a shift from centralized authorities and intermediaries to a decentralized, peer-to-peer network. It reimagines the internet as a realm where individuals, not corporations or governments, hold the keys to their digital existence. This shift is particularly pronounced in the realm of identity management.
SSI, as a cornerstone of Web3, empowers individuals with self-sovereignty. It redefines the rules of identity, putting users at the helm of their digital personas. With SSI, individuals can own, control, and selectively share their identity attributes without relying on centralized identity providers. Instead of entrusting their data to third parties, users store their identity information on secure, tamper-proof blockchains. This groundbreaking approach not only safeguards personal information but also enhances privacy and minimizes the risk of data breaches and identity theft.
Furthermore, SSI transcends borders and siloed digital ecosystems. It offers a universal framework for identity that works seamlessly across platforms and services, fostering interoperability and reducing the need for repetitive identity verification processes. This not only simplifies the user experience but also reduces the administrative burden on organizations.
As we delve deeper into the world of SSI within Web3, we’ll explore its applications across various domains. From online authentication and access control to secure voting systems and healthcare data management, SSI is unlocking a myriad of possibilities. It challenges conventional notions of trust, ushering in a new era where individuals are the custodians of their digital reputations.
But the transformation doesn’t stop at the technological level. The advent of SSI in Web3 prompts profound societal questions about identity, trust, and authority. It challenges existing power structures and reimagines the relationship between individuals, institutions, and the digital realm. As we navigate this evolving landscape, we must grapple with issues of consent, ethics, and governance to ensure that SSI remains a tool for empowerment and not exploitation.
In conclusion, Web3 and Self-Sovereign Identity are forging a path toward a digital future where individuals hold the reins of their online identities. It’s a journey that transcends technology, touching upon fundamental questions of autonomy, privacy, and trust in the digital age. As we continue to explore this paradigm shift, we must also consider the responsibilities and ethical considerations that come with wielding such unprecedented control over our digital selves.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) v1.0
Traditional identity management systems are riddled with challenges. Centralized databases, often held by corporations or government entities, store vast amounts of personal information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. Moreover, individuals have little control over how their data is collected, used, and shared, leading to privacy concerns and vulnerabilities.
The shortcomings of traditional identity management systems have paved the way for a profound shift in how we safeguard personal information and uphold privacy. Here’s an in-depth exploration of the challenges and the Web3-inspired solutions on the horizon:
Data Vulnerability: Centralized databases housing personal information have long been attractive targets for hackers and malicious actors. Data breaches, which can compromise millions of identities at once, have become alarmingly common, resulting in financial losses and privacy violations.
- Web3 Solution: Decentralized Identity (DID) solutions distribute personal data across a blockchain network, reducing the appeal of centralized targets. Users retain control over their DID, ensuring that their data remains secure and under their management.
Privacy Erosion: In traditional systems, individuals often have limited say over how their data is collected, used, or shared. This lack of control leads to privacy erosion, as personal information is routinely harvested without consent or understanding.
- Web3 Solution: Web3 empowers individuals to manage their own digital identities and personal data. With self-sovereign identity systems, individuals grant and revoke access to their data as needed, restoring agency over their digital footprint.
Data Monetization: Corporations frequently monetize personal data without adequately compensating individuals. This data commodification raises ethical concerns, as individuals should have the right to profit from the value their data generates.
- Web3 Solution: Through tokenization and smart contracts, Web3 allows individuals to participate in the value exchange of their data. Users can choose to share data in exchange for tokens or benefits, creating a more equitable data economy.
Identity Verification Hassles: Traditional identity verification processes often involve cumbersome procedures, including sharing sensitive documents, enduring lengthy wait times, and managing countless login credentials.
- Web3 Solution: DID solutions streamline identity verification. Users can provide proof of identity in a privacy-preserving manner, eliminating the need for redundant verification processes while enhancing security.
Cross-Border Identification: In a globally connected world, cross-border identification can be a bureaucratic nightmare. Traditional systems struggle to verify identities across different jurisdictions, hindering international transactions and services.
- Web3 Solution: Web3’s borderless nature enables seamless cross-border identity verification. Users can prove their identity digitally, making international interactions and transactions more efficient and secure.
Identity Theft: Identity theft is a persistent threat in traditional systems, as stolen personal information can be easily exploited. Victims often face lengthy battles to reclaim their identities and restore their financial well-being.
- Web3 Solution: DID solutions, built on cryptographic security, make it exceedingly difficult for bad actors to impersonate individuals. This higher level of security reduces the risk of identity theft.
Regulatory Compliance: Traditional identity systems struggle to adhere to evolving data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Compliance challenges can result in hefty fines for organizations.
- Web3 Solution: Web3’s privacy-centric design aligns with many regulatory principles. Decentralized identity solutions provide individuals with greater control over their data, facilitating compliance with data protection laws.
In conclusion, Web3-driven innovations in identity management promise to rectify the shortcomings of traditional systems. These decentralized solutions offer enhanced security, user control, and privacy while fostering a fairer data economy. As the world moves toward Web3-inspired identity systems, individuals will regain sovereignty over their digital identities, personal data, and online interactions, forging a path toward a more secure and privacy-respecting digital landscape.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Embracing Web3: The Next Chapter in KYC Data and Identity …

Self-Sovereign Identity, an essential component of Web3, offers a solution to these problems. At its core, SSI empowers individuals with full control over their digital identities. Here’s how it works:
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) represents a fundamental shift in how we perceive and manage our digital personas within the Web3 landscape. This innovative concept not only addresses the challenges posed by traditional identity management but also introduces a paradigm where individuals become the rightful owners and custodians of their online identities.
The Architecture of SSI
At the heart of Self-Sovereign Identity lies a decentralized architecture facilitated by blockchain technology. Here’s a more detailed look at how it works:
Creation of Digital Identities: In the SSI model, individuals initiate the creation of their digital identities. They generate a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key for sharing and a private key for secure access.
Distributed Ledger: The individual’s identity credentials, such as personal details or attributes, are not stored in a central database but are rather recorded on a distributed ledger, often a blockchain. This ledger ensures the immutability and tamper resistance of the identity data.
Selective Disclosure: One of the fundamental principles of SSI is selective disclosure. It empowers individuals to share specific pieces of identity information with others as needed. For instance, when accessing a service, you can choose to reveal only the necessary attributes without divulging your entire identity.
Verifiable Credentials: SSI relies on verifiable credentials – digitally signed claims – that attest to the authenticity of the information. These credentials can be issued by trusted entities like governments, educational institutions, or banks.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): DIDs are a core component of SSI. They are unique, persistent, and globally resolvable identifiers that are registered on a blockchain or decentralized network. DIDs serve as the foundation for linking verifiable credentials to individuals.
The Benefits of SSI
The introduction of SSI brings a multitude of advantages:
Enhanced Privacy: Individuals can exercise granular control over what information they share, reducing unnecessary exposure of personal data. This privacy-centric approach mitigates the risk of surveillance and data breaches.
Security: The cryptographic security of SSI ensures that only the rightful owner of the private key can access and share their identity information. This robust security mechanism significantly reduces identity theft and fraud.
User-Centric Approach: SSI puts individuals in the driver’s seat, allowing them to manage their digital identities autonomously, independently of centralized authorities.
Interoperability: SSI systems are designed to interoperate seamlessly across various platforms and services. This not only simplifies identity management but also reduces the need for redundant identities on different online services.
SSI in Action
The adoption of Self-Sovereign Identity is already making waves in numerous sectors:
Education: Educational institutions are exploring SSI for issuing digital diplomas and certificates, enhancing the portability and verification of academic credentials.
Healthcare: SSI facilitates secure and portable health records, empowering patients to control access to their medical history and personal health information.
Financial Services: In the financial sector, SSI streamlines identity verification processes, making account openings, loan applications, and financial transactions more efficient and secure.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While Self-Sovereign Identity promises a transformative future, challenges persist. Widespread adoption and standardization are vital to its success, and education is essential to help individuals understand and manage their digital identities effectively.
In conclusion, Self-Sovereign Identity stands as a beacon of individual empowerment and privacy in the evolving landscape of Web3. It reshapes the way we interact online, offering a future where individuals have true ownership and control over their digital selves. As we embrace this exciting paradigm shift, we anticipate a world where digital identities are not only self-sovereign but also universally respected and recognized. The era of SSI has arrived, and it is set to redefine the very essence of identity in the digital age.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Compare and Contrast — Federated Identity vs Self-sovereign …
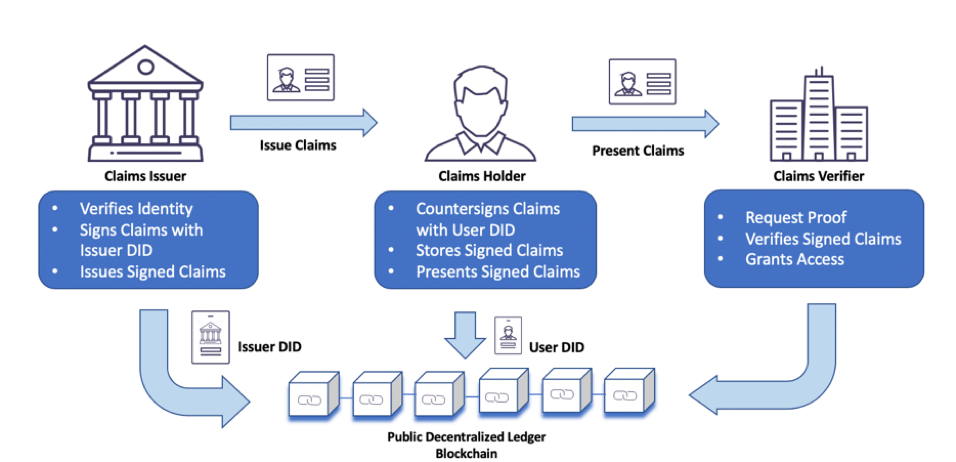
In SSI, individuals are at the center of their identity. They create, own, and manage their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities.
In Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), the individual’s empowerment and control over their digital identity are paramount. Here’s a deeper look at how individuals are central to SSI:
Ownership of Identity: SSI enables individuals to be the sole owners of their digital identities. They have the authority to create, modify, and manage their identity attributes, which may include personal information, credentials, and affiliations.
User-Centric Design: SSI systems are designed with user-centricity in mind. The focus is on making identity management intuitive and accessible to individuals, ensuring that they can easily navigate and control their digital identity.
Decentralization: SSI relies on decentralized and distributed ledger technologies, such as blockchain, to store and secure identity data. This eliminates the need for a central authority to control or verify identity, putting the individual in charge.
Portability: Individuals can carry their digital identities across various applications, services, and platforms. This portability ensures that their identity is not tied to a single provider or ecosystem.
Consent-Based Sharing: SSI emphasizes consent-based data sharing. Individuals have the power to grant or revoke access to their identity attributes, enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of data misuse.
Interoperability: SSI solutions are designed to be interoperable, allowing individuals to use their digital identities seamlessly across different contexts, from healthcare and finance to education and social interactions.
Security and Trust: Individuals benefit from the security features of blockchain technology, which ensures the integrity and immutability of their identity records. This trust in the system enhances confidence in digital interactions.
Reduced Identity Theft: With individuals in control of their digital identities, the risk of identity theft and fraud is mitigated. Unauthorized access to personal data becomes significantly more challenging.
Privacy Preservation: SSI prioritizes privacy by design. Individuals can selectively disclose only the necessary information to complete a transaction or verify their identity, preserving their privacy.
Empowerment: SSI empowers individuals to actively participate in the digital world. They can engage in online activities with confidence, knowing that they have control over their identity and data.
Credential Issuance: Individuals can receive verifiable credentials, such as diplomas or professional certifications, directly from trusted issuers. These credentials are securely stored in their digital identity wallets and can be shared as needed.
Revocation and Updates: Individuals can easily update or revoke outdated credentials or information from their digital identity, ensuring that their identity remains accurate and up to date.
Global Accessibility: SSI is accessible to individuals worldwide, bridging identity gaps and providing a means for those without traditional forms of identification to participate in the digital economy.
In essence, SSI places individuals at the heart of their digital identity, granting them sovereignty, control, and privacy over their personal information. This shift represents a fundamental transformation in the way identity is managed and used in the digital age, empowering individuals to take charge of their online presence and interactions.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: How self-sovereign identity helps users own their data
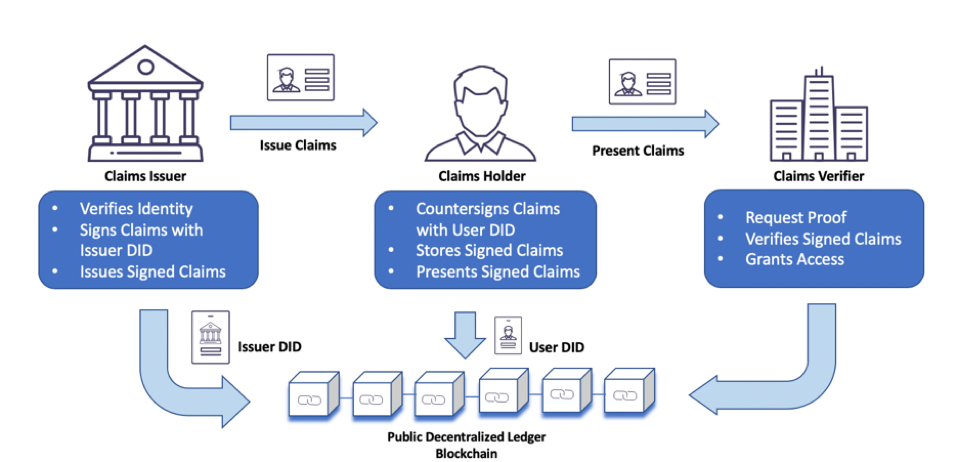
SSI leverages blockchain technology to decentralize identity data. Instead of being stored in a single database, identity credentials are cryptographically secured on a distributed ledger, making them tamper-proof and verifiable.
SSI harnesses the transformative potential of blockchain technology to redefine the very nature of identity management. At its core, SSI operates on the principles of decentralization and cryptographic security, reshaping the way we safeguard and verify our digital identities.
One of the primary tenets of SSI is the decentralization of identity data. In the traditional paradigm, sensitive personal information is typically siloed in centralized databases controlled by various entities, including governments, corporations, and service providers. This centralized model not only raises concerns about data security but also places individuals at the mercy of these custodians for identity verification.
In stark contrast, SSI takes a bold step by dispersing identity credentials across a distributed ledger, often built on blockchain technology. This blockchain-based approach ensures that personal data is not held in a single, vulnerable repository but is instead fragmented and cryptographically secured across a network of nodes. This fundamental shift in data storage and management has several profound implications:
Tamper-Proof Records: Cryptographic hashes and digital signatures are employed to secure identity data on the blockchain. Once recorded, these records become virtually immutable, resistant to unauthorized alterations or deletions. This tamper-proof nature ensures the integrity and reliability of identity information, instilling trust in the system.
User Control: Individuals gain complete control over their identity credentials. They possess the private keys required to access and share their data, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This self-sovereign control empowers users to manage their digital identities with autonomy and consent.
Interoperability: SSI’s decentralized approach fosters interoperability. Users can seamlessly employ their digital identities across various platforms, services, and applications without the need for redundant registrations or fragmented identity verification processes. This universal identity framework streamlines user experiences and reduces administrative overhead for organizations.
Privacy Enhancement: SSI prioritizes user privacy. Identity credentials are selectively disclosed only when necessary, minimizing the exposure of personal data. This granular control enables individuals to share specific attributes without divulging their entire identity, reducing the risk of identity theft and data breaches.
Reduced Dependence on Central Authorities: The decentralized nature of SSI reduces reliance on centralized authorities for identity verification. Individuals no longer need to entrust their data to third parties, mitigating concerns about potential data mishandling or misuse. This shift redistributes authority and places users firmly in charge of their digital reputations.
Global Reach: SSI operates on a global scale, transcending geographical boundaries and jurisdictional limitations. This borderless approach is particularly valuable in a world where digital interactions and services are increasingly cross-border and international.
As SSI continues to gain traction, its potential applications extend far beyond traditional identity verification. It has the capacity to revolutionize industries such as finance, healthcare, education, and more, by offering secure, user-centric identity solutions. However, with this transformative potential also come important discussions about standards, privacy, security, and the responsible implementation of this groundbreaking technology.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Towards Digital Self-Sovereignty: The Web3 Identity Stack …
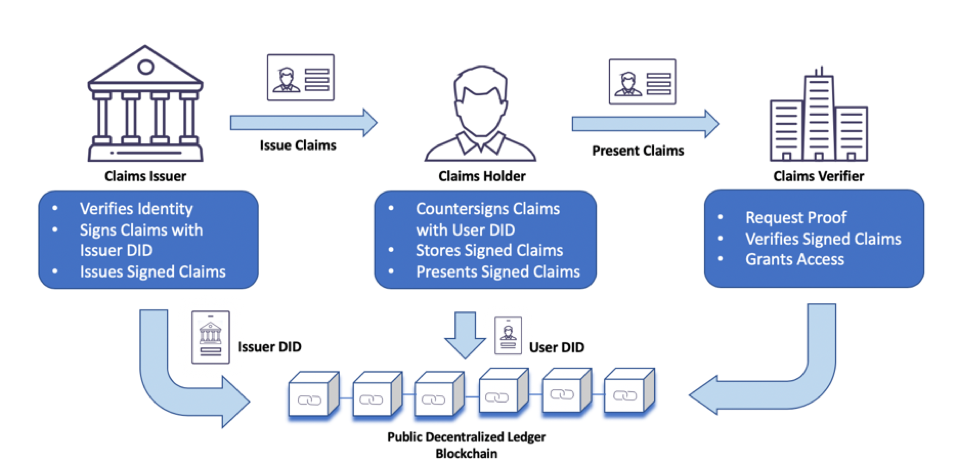
SSI ensures that users only share the minimum necessary information for any given transaction. This minimizes the exposure of personal data and enhances privacy.
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) heralds a fundamental shift in the way we manage and share personal information, with privacy at its core. Here’s a more detailed exploration of how SSI achieves its remarkable privacy enhancements:
Selective Data Disclosure: SSI empowers individuals to selectively disclose only the information needed for a specific transaction or interaction. This “need-to-know” principle minimizes the exposure of sensitive data. For example, when verifying age at a bar, the user need only prove they are over a certain age without revealing their exact birthdate.
Contextual Control: SSI solutions provide users with granular control over their data. They can set context-specific rules for sharing information. This means that even if a piece of data is shared once, it doesn’t grant indefinite access. Users can define when, where, and for how long their data can be accessed.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Advanced cryptographic techniques, such as zero-knowledge proofs, play a pivotal role in SSI. These proofs allow a party to verify the truth of a statement (e.g., verifying someone is of legal drinking age) without requiring the statement itself (e.g., the birthdate). This zero-knowledge approach preserves privacy while enabling verification.
Data Minimization: SSI inherently follows the principle of data minimization. This means that personal data is minimized, both in terms of what is collected and what is shared. This reduces the risk of data exposure and misuse.
Consent-Based Access: SSI relies on user-centric consent models. Individuals must explicitly grant consent before their data is accessed or shared. This not only empowers users but also ensures that data usage adheres to their preferences and intentions.
Revocation and Expiry: Users have the ability to revoke access to their data or set expiration dates for data-sharing permissions. This ensures that data access is not open-ended and can be terminated at any time.
Immutable Records: SSI solutions often use blockchain technology to record identity transactions. These records are immutable, meaning they cannot be altered or deleted. This feature enhances transparency while maintaining data integrity.
Interoperability and Portability: SSI systems are designed to be interoperable, allowing users to carry their digital identities across various services and platforms. This ensures that users retain control and consistency over their data regardless of where they interact.
Reduced Risk of Identity Theft: SSI minimizes the need for individuals to share sensitive personal information, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraudulent activities.
Compliance with Privacy Regulations: SSI aligns with the principles of privacy regulations like GDPR, enabling organizations to meet compliance requirements while respecting user privacy.
In sum, SSI represents a paradigm shift in digital identity management, prioritizing user privacy, control, and data protection. By putting individuals at the center of their digital identities, SSI fosters a more secure and privacy-respecting online environment, where data is shared on users’ terms and privacy is not compromised in the pursuit of digital interactions.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Enabling Patient Data Ownership With Self-Sovereign Identity
SSI systems are designed to work seamlessly across various platforms and services. This interoperability eliminates the need for individuals to create separate identities for different online services.
The concept of interoperability within Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) systems is a game-changer that simplifies and streamlines the way individuals engage with various online services and platforms. It not only enhances user convenience but also strengthens the security and privacy of digital identities.
A Unified Identity Experience
In the traditional online landscape, individuals are often burdened with the task of creating and managing multiple identities across various platforms. Each service, whether it’s a social media platform, a banking app, or an e-commerce website, typically requires users to create a new set of credentials, passwords, and profile information. This fragmented approach not only adds complexity to users’ online experiences but also creates numerous points of vulnerability.
SSI addresses this challenge by offering a unified identity experience. Through the use of Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) and Verifiable Credentials, individuals can assert their identity seamlessly across different services without the need for redundant identity creation. This interoperability is facilitated by a decentralized network or blockchain, which acts as a trust anchor for identity verification.
How Interoperability Works
Imagine a scenario where a user holds a verified credential, such as a driver’s license, issued by a government agency. With SSI’s interoperability, this verified credential can be reused across multiple services. Here’s how it works:
Cross-Service Validation: When the user needs to prove their age for various purposes, such as age-restricted content or alcohol purchase, they can present their verified driver’s license credential.
Credential Verification: The receiving service, let’s say an e-commerce platform, can then verify the authenticity of the credential by checking the cryptographic signature and the issuer’s DID on the blockchain.
Selective Disclosure: Importantly, SSI allows for selective disclosure. In this scenario, the user can choose to disclose only the relevant information—age, in this case—while keeping other personal details hidden.
Efficiency and Trust: This interoperable approach not only saves time and effort for users but also establishes trust between service providers, as they rely on a shared, decentralized infrastructure for identity verification.
Benefits of Interoperability in SSI
Reduced Friction: Interoperability eliminates the need for individuals to remember multiple usernames and passwords, reducing the friction associated with accessing various online services.
Enhanced Security: With decentralized verification, there are fewer centralized repositories of sensitive data, making it harder for malicious actors to target and compromise identities.
User Control: Users have greater control over which aspects of their identity are disclosed, reinforcing the self-sovereign nature of SSI.
Global Access: Interoperability transcends geographical boundaries, allowing individuals to access services across borders with their verified credentials.
Challenges and Future Development
While the concept of interoperable SSI is promising, it is still in its early stages of adoption and standardization. The development of universally recognized standards and protocols for interoperability is a key challenge that the Web3 community is actively working to address.
In conclusion, interoperability is a cornerstone of Self-Sovereign Identity, reshaping the way individuals interact with online services. It brings convenience, security, and user control to the forefront, while also paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient digital world. As SSI systems continue to evolve and gain acceptance, we can anticipate a future where the days of creating countless online identities are replaced with a unified, self-sovereign digital identity that works seamlessly across the web.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Web3 and Self-Sovereign Identity – NamaChain
Individuals have full control over their identity data, deciding when, where, and with whom to share it.
The concept of individuals having full control over their identity data represents a paradigm shift in the way we manage and protect our personal information. Here’s a more detailed exploration of this idea:
Granular Control: Self-sovereign identity (SSI) enables individuals to exercise granular control over their identity attributes. They can choose which specific pieces of information to disclose in different situations, tailoring their identity presentation to match the context.
Informed Consent: Before sharing any identity data, individuals must provide informed consent. This means that they are fully aware of what information is being shared, why it is needed, and how it will be used. This transparency fosters trust in digital interactions.
Revocation of Access: SSI systems allow individuals to revoke access to their identity data at any time. If they no longer wish to share certain information with a particular entity, they can simply withdraw consent, instantly cutting off access.
Data Minimization: SSI encourages the principle of data minimization, where only the minimal necessary information is shared to complete a transaction or verify identity. This practice reduces the exposure of sensitive data.
Selective Disclosure: Individuals can engage in selective disclosure, revealing only the relevant parts of their identity for a specific purpose. For instance, when purchasing age-restricted items online, they can prove their age without revealing their full birthdate.
Temporary Sharing: Temporary or time-bound sharing is possible with SSI. Individuals can grant access to their identity data for a limited duration, after which access is automatically revoked. This is useful for short-term transactions or interactions.
Dynamic Updates: SSI identity data is dynamic. Individuals can update their information in real-time, ensuring that it remains accurate. This is particularly important for attributes like addresses or contact information.
Identity Wallets: Digital identity wallets serve as secure containers for identity data. Individuals have exclusive access to these wallets, safeguarding their information from unauthorized access.
Cross-Context Control: Individuals can maintain control over their identity data across various contexts, whether it’s for financial services, healthcare, social media, or government interactions. This consistency and continuity enhance their online experience.
Protection Against Data Breaches: Since individuals hold their identity data, the risk of large-scale data breaches is significantly reduced. Even if a service provider experiences a breach, the attacker would not gain access to a comprehensive identity dataset.
Privacy Preservation: The ability to selectively share information protects individual privacy. It minimizes the collection of unnecessary data by organizations and limits the potential for profiling and surveillance.
Empowerment: This control empowers individuals to be active participants in the digital world. They can confidently engage in online activities, knowing they have the authority to manage their digital identity.
Reduced Identity Theft: The decentralized nature of SSI makes it challenging for identity thieves to exploit centralized databases. Even if one aspect of an individual’s identity is compromised, the attacker cannot easily access the rest.
In summary, the concept of individuals having full control over their identity data in the realm of SSI embodies a fundamental shift towards user-centric, privacy-preserving, and secure identity management. It places individuals in the driver’s seat, allowing them to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and control, while also reducing the risks associated with identity theft and data breaches.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Web3 Identity Evolution, Use Cases & Self-Sovereign Identity
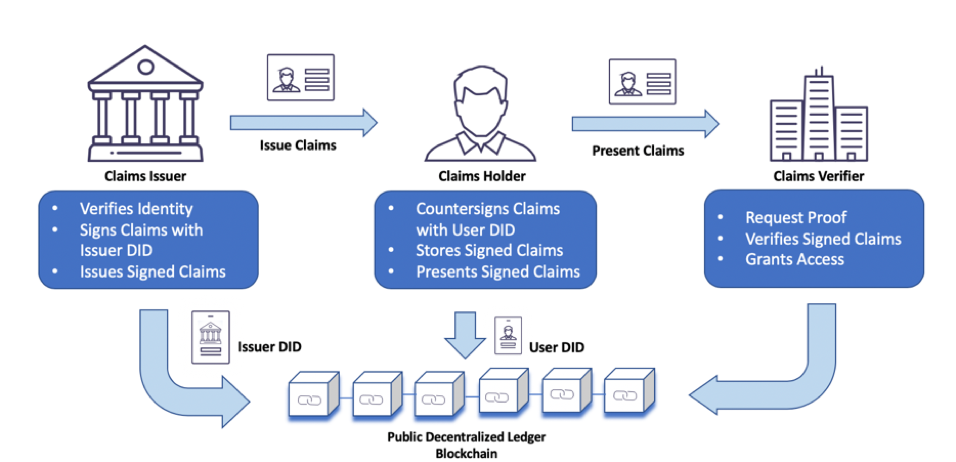
Blockchain-based SSI systems are highly secure, making it incredibly difficult for unauthorized parties to access or manipulate identity information.
Blockchain-based Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) systems stand as a paragon of security in the digital realm, setting new standards for safeguarding identity information. The robust security measures they employ make it exceedingly challenging for unauthorized parties to gain access to, let alone manipulate, sensitive identity data. Here’s an in-depth exploration of why blockchain-based SSI systems are synonymous with security:
Immutability and Tamper Resistance: On the blockchain, once data is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it becomes virtually immutable. Cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms ensure that altering or deleting information from the blockchain is computationally infeasible. This tamper-resistant nature makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with identity credentials.
Cryptographic Encryption: Blockchain-based SSI systems leverage cryptographic encryption extensively. Private keys, public keys, and digital signatures are integral components of the cryptographic infrastructure. Private keys are securely held by the identity owner and used to sign transactions, providing a unique and secure means of identity verification. Unauthorized access to these private keys is extremely challenging, as they are protected by robust encryption techniques.
Decentralization: Traditional identity systems are vulnerable to breaches because they rely on centralized databases. In contrast, blockchain-based SSI distributes identity data across a network of nodes. For an attacker to compromise identity information, they would need to gain control of a significant portion of the network, a feat that is computationally and economically unfeasible in well-established blockchain networks.
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks employ consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and secure the network. These mechanisms require participants to expend significant computational resources or stake assets, adding an additional layer of security. Manipulating the blockchain would require an attacker to overpower the network’s consensus, a task that becomes increasingly challenging as the network grows.
Selective Disclosure: Blockchain-based SSI systems are designed with privacy in mind. Individuals have the ability to selectively disclose identity attributes, sharing only the information necessary for a specific transaction or interaction. This minimizes the exposure of sensitive data, reducing the potential attack surface for malicious actors.
Secure Wallets: Identity owners store their digital identity credentials in secure digital wallets. These wallets are often protected with strong encryption and are designed to resist hacking attempts. Even if a wallet is compromised, the attacker would still need to access the private keys stored within it, a formidable challenge given modern encryption standards.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Some SSI systems incorporate zero-knowledge proofs, allowing parties to verify the accuracy of a statement without revealing the underlying data. This cryptographic technique enhances privacy and security by ensuring that sensitive identity information remains hidden even during verification processes.
In summary, blockchain-based SSI systems offer an unparalleled level of security, underpinned by immutability, cryptography, decentralization, and consensus mechanisms. These layers of protection create a formidable fortress around identity data, making it exceptionally challenging for unauthorized parties to breach or manipulate. As the world increasingly embraces digital identities, the security and trustworthiness of blockchain-based SSI systems will continue to drive their adoption in various sectors, setting new benchmarks for digital identity protection.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Self-Sovereign Identity: The Ultimate Guide 2023
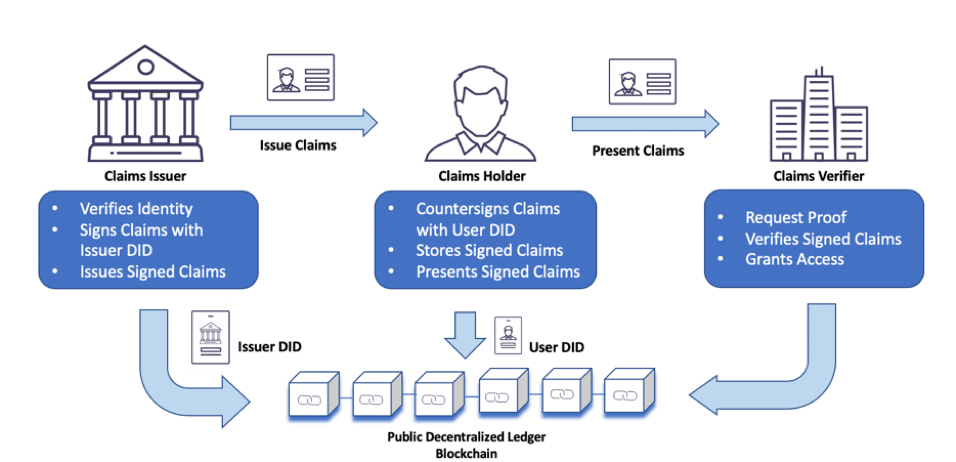
The decentralized nature of SSI makes it significantly harder for malicious actors to steal personal information or commit identity fraud.
The decentralized architecture of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) stands as a formidable bulwark against the relentless tide of identity theft and cybercrime. Here’s a closer examination of how SSI’s decentralized nature fortifies digital identity against malicious actors:
Eliminating Centralized Data Stores: Traditional identity systems rely on centralized databases and repositories that house vast troves of personal information. These central points of vulnerability have long been prime targets for hackers and data breaches. SSI, in stark contrast, decentralizes identity data, scattering it across a network of nodes. This dispersion minimizes the appeal of single targets for cybercriminals, making it substantially more challenging for them to access large volumes of data in one fell swoop.
User-Controlled Data: SSI flips the script on data ownership and control. In a decentralized SSI ecosystem, individuals become the custodians of their own data. This user-centric approach means that malicious actors cannot infiltrate a single entity to harvest scores of personal information. Instead, they must compromise multiple individuals, each safeguarding their own data.
Cryptography and Secure Transactions: SSI leverages robust cryptographic techniques to secure identity transactions. Immutable records on a blockchain or decentralized ledger ensure that any changes or tampering with data are immediately detectable. This cryptographic layer adds another barrier to entry for cybercriminals attempting to manipulate or exploit identity data.
Consent-Based Access: In SSI, data access is contingent on explicit user consent. Without the user’s agreement, malicious actors cannot access personal information, even if they manage to infiltrate a transaction or service. This consent-driven model erects a formidable barrier to unauthorized data access.
Revocation and Expiry: SSI users have the power to revoke access permissions or set expiration dates for data sharing. Even if an attacker gains access to certain data, it may only remain accessible for a limited time. This dynamic control minimizes the window of opportunity for malicious actors.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Zero-knowledge proofs, a cryptographic tool used in SSI, enable one party to prove a fact (e.g., verifying age) without revealing the underlying data (e.g., the birthdate). This means that even when data is shared, it is done so in a privacy-preserving manner, significantly reducing the potential for misuse.
Immutable Audit Trails: Transaction records in SSI systems, often maintained on blockchains, are immutable. This means that any unauthorized access or tampering attempts are recorded indelibly. Malicious actors attempting to cover their tracks face a near-impossible task in altering these records.
Interoperability Challenges for Attackers: SSI’s interoperability model means that individuals can use their digital identities across various services and platforms. This inherent diversity creates a fragmented landscape for cybercriminals, as each service may operate on a different technology stack or blockchain network.
In essence, the decentralized nature of SSI transforms the identity theft and identity fraud landscape from an inviting playground for malicious actors into a formidable fortress. By returning control of digital identities to individuals, reducing centralized data targets, and leveraging cutting-edge cryptographic techniques, SSI creates an environment where the cost and complexity of cybercrime rise significantly, discouraging potential attackers and enhancing the overall security of digital identity.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Web3 Identity: Beginner’s Guide 2023

SSI simplifies identity verification, reducing the need for extensive paperwork and manual verification processes.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is a technological marvel that not only empowers individuals but also transforms the way identity verification is conducted. One of its most compelling advantages lies in simplifying and streamlining the identity verification process, effectively reducing the reliance on extensive paperwork and manual procedures.
A Paperless Identity Ecosystem
In traditional identity verification scenarios, whether it’s opening a bank account, applying for a job, or accessing healthcare services, individuals are often required to provide physical documents, fill out numerous forms, and undergo manual verification processes. This cumbersome and time-consuming approach is not only inefficient but also prone to human errors and fraud.
SSI disrupts this antiquated paradigm by introducing a paperless identity ecosystem. Here’s how:
Digital Identity Credentials: With SSI, individuals possess digital identity credentials that are cryptographically secure and verifiable on a blockchain or decentralized ledger. These credentials replace the need for physical documents like passports, driver’s licenses, or utility bills.
Remote Verification: SSI allows for remote identity verification, eliminating the need for individuals to physically present themselves at verification centers. This is particularly relevant in the digital age, where remote interactions are increasingly common.
Selective Disclosure: When individuals need to prove their identity or specific attributes, they can digitally present their verifiable credentials. Importantly, SSI enables selective disclosure, meaning users can choose to reveal only the necessary information while keeping the rest confidential.
Instant Verification: The verification process becomes near-instantaneous as it relies on cryptographic proofs and the trustworthiness of the blockchain. This expedites access to services, reducing wait times and administrative overhead.
Enhanced Security: The digital nature of SSI credentials enhances security by significantly reducing the risk of document forgery, identity theft, or tampering. Immutable records on the blockchain further bolster trust.
Real-World Applications
The impact of SSI on reducing paperwork and manual verification processes is already evident in various sectors:
Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions are exploring SSI for customer onboarding and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, making account openings and loan applications more efficient.
Employment: SSI simplifies the job application process, allowing candidates to share their verified credentials with potential employers, streamlining background checks and reducing hiring times.
Healthcare: Patients can securely share their health records with healthcare providers without the need for physical copies or extensive paperwork.
Education: Educational institutions are adopting SSI for issuing and verifying digital diplomas and transcripts, eliminating the need for manual verification of academic credentials.
The Future of Paperless Identity
As SSI continues to evolve and gain acceptance, the future of identity verification promises to be paperless, efficient, and user-centric. The elimination of extensive paperwork and manual processes not only saves time and resources but also enhances security and privacy, aligning perfectly with the principles of self-sovereign identity.
In conclusion, Self-Sovereign Identity stands as a beacon of progress in simplifying identity verification. It empowers individuals with digital credentials that can be selectively disclosed, making paperwork-intensive processes a relic of the past. As we move toward a digital-first society, SSI is a catalyst for transforming the way we prove and protect our identities in an increasingly interconnected world.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: 7 Ways How Digital Identities Could Transform Our Lives

Web3 and SSI are already making waves in various industries:
The impact of Web3 and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is undeniable, as they are already revolutionizing numerous industries across the globe. Here’s a closer look at how these technologies are making waves in various sectors:
Finance and Banking:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Web3 has given rise to decentralized financial services, enabling users to access lending, borrowing, and trading platforms without intermediaries.
- Identity Verification: SSI is transforming KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, allowing individuals to securely verify their identities without exposing sensitive information.
Healthcare:
- Patient Records: SSI ensures secure and interoperable management of electronic health records, enhancing patient data security and streamlining healthcare interactions.
- Drug Traceability: Blockchain-based solutions are improving the transparency and traceability of pharmaceutical supply chains, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs.
Art and Collectibles:
- NFTs: Web3’s NFTs have disrupted the art world, allowing artists to tokenize their digital creations and sell them directly to collectors, thereby reshaping the art market.
- Provenance Tracking: Blockchain ensures the provenance and authenticity of artworks, reducing the risk of art fraud.
Supply Chain Management:
- Transparency and Traceability: Web3 and blockchain enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud and ensuring the authenticity of products.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing smart contracts automate supply chain processes, reducing errors and inefficiencies.
Education:
- Digital Credentials: SSI is revolutionizing education by providing secure and verifiable digital credentials, making it easier for learners to share their achievements and qualifications.
- Decentralized Learning Platforms: Web3 is fostering the development of decentralized learning environments that empower learners and educators.
Governance:
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Web3 governance models are empowering individuals to participate in decision-making processes across organizations, protocols, and communities.
- Transparency and Accountability: Blockchain ensures transparency and immutability in governance, reducing corruption and inefficiencies.
Gaming:
- Ownership of In-Game Assets: Web3 enables true ownership of in-game assets as NFTs, allowing players to buy, sell, and trade digital items across games.
- Play-to-Earn: Decentralized gaming platforms are introducing play-to-earn models, where gamers can earn real value through their in-game activities.
Real Estate:
- Tokenization: Traditional assets like real estate are being tokenized on blockchain, enabling fractional ownership and enhancing liquidity in the market.
- Property Records: SSI ensures the integrity of property records, reducing fraud and disputes.
Legal:
- Smart Contracts: Web3’s smart contracts are being utilized for automated execution of legal agreements, streamlining processes and reducing the need for intermediaries.
- E-Notarization: SSI is transforming notarization processes, making them more efficient and secure.
Charity and Nonprofits:
- Transparent Donations: Blockchain-based donations provide transparency in charitable giving, allowing donors to track the impact of their contributions.
- Decentralized Governance: DAOs are being used for decentralized decision-making in nonprofit organizations.
These are just a few examples of how Web3 and SSI are already disrupting traditional models and creating innovative solutions across industries. As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact is expected to grow, reshaping the way we conduct business, interact, and engage with various sectors of the economy.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Concordium Web3 ID: Zero-Knowledge Based Identity Infrastructure …
Educational institutions and employers are adopting SSI for issuing and verifying digital diplomas, certificates, and credentials.
The adoption of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) in educational and professional spheres represents a transformative leap in the way we handle academic and career achievements. Both educational institutions and employers are recognizing the immense potential of SSI for issuing, verifying, and managing digital diplomas, certificates, and credentials. Here’s how this innovative approach is revolutionizing the realms of education and employment:
Immutable Academic Records: Educational institutions are utilizing SSI to issue digital diplomas and certificates on the blockchain. These records, once stored, become tamper-proof and immutable. This ensures the long-term integrity of academic achievements, eliminating concerns about fraudulent credentials.
Enhanced Verification: Employers and educational institutions alike benefit from the secure and straightforward verification process enabled by SSI. With digital credentials anchored on the blockchain, verification can be executed swiftly and with confidence. Employers can efficiently confirm the authenticity of applicants’ qualifications, reducing hiring risks.
Reduction of Credential Fraud: Traditional paper-based diplomas and certificates are susceptible to forgery and fraud. SSI’s cryptographic security measures make it exceedingly difficult for individuals to counterfeit or misrepresent their credentials. This reduction in credential fraud is a significant win for both educational institutions and employers.
Privacy and Control: SSI places individuals in control of their digital credentials. Graduates and job applicants can selectively share their academic records with employers and institutions, without exposing unnecessary personal information. This privacy-conscious approach aligns with evolving data protection regulations.
Streamlined Onboarding: SSI simplifies the onboarding process for employers. With digital credentials that can be quickly and securely verified, employers can expedite the hiring process. This benefits both parties, reducing administrative burdens and enabling faster access to opportunities for job seekers.
Global Recognition: SSI transcends international boundaries, making it easier for educational credentials to be recognized globally. This is particularly advantageous for students and professionals seeking opportunities abroad, as their digital credentials are readily verifiable, regardless of their home country’s accreditation standards.
Continual Learning and Professional Development: SSI extends beyond traditional diplomas to encompass a wide range of educational achievements, including micro-credentials and badges. This flexibility enables professionals to showcase their continual learning and skill development, enhancing their marketability in a dynamic job landscape.
Standardization and Interoperability: Efforts are underway to establish standards and interoperability frameworks for SSI in education and employment. These initiatives aim to ensure that digital credentials can be seamlessly recognized and accepted across various platforms and institutions, further enhancing their utility.
Reduced Administrative Costs: Adopting digital credentials can lead to significant cost savings for educational institutions. The elimination of physical certificate production and mailing, as well as streamlined verification processes, reduces administrative overhead.
Environmental Impact: Going digital with credentials aligns with sustainability goals. It reduces the need for paper-based records, thereby minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact.
In conclusion, the integration of SSI into education and employment represents a paradigm shift in how we manage and verify academic and professional achievements. It offers unparalleled security, efficiency, and control to individuals while simplifying processes for educational institutions and employers. As SSI adoption continues to grow, we can anticipate a future where digital credentials are the norm, and trust in academic and professional achievements is fortified by blockchain-powered verification.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Self-Sovereign Identity: Decentralized digital identity … – Amazon.com
Patients can have secure, portable health records that they control and share as needed, enhancing healthcare data management.
The transformation brought about by Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) extends its profound impact to the realm of healthcare, revolutionizing the way patient data is managed and shared. Here’s a closer look at how SSI empowers patients with secure, portable health records and reshapes healthcare data management:
Patient-Centric Control: In traditional healthcare systems, patients often have limited control over their medical records. These records are typically held by healthcare providers, and patients must request access or updates. With SSI, patients gain full control over their health records. They become the custodians, deciding who can access their data and under what conditions. This patient-centric approach ensures that individuals have the final say in how their health information is managed.
Secure and Tamper-Proof Records: SSI leverages blockchain technology to maintain immutable records of health data transactions. This means that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus. This cryptographic security provides patients with assurance that their medical records are tamper-proof, reducing the risk of fraudulent changes or unauthorized access.
Interoperability: SSI’s interoperable nature ensures that patients can carry their health records across different healthcare providers, clinics, and even borders. This seamless interoperability streamlines healthcare data exchange, allowing medical professionals to access critical patient information quickly, whether during emergencies or routine care.
Selective Data Sharing: SSI enables patients to selectively share specific health information with healthcare providers, specialists, or researchers. For example, a patient can share their entire medical history with their primary care physician while only sharing relevant allergy information with an allergist. This granularity enhances patient privacy and data security.
Consent-Driven Access: Before any healthcare provider can access a patient’s data, explicit consent is required. Patients grant access on a case-by-case basis, ensuring that their data is only accessible when needed for diagnosis, treatment, or research. This consent-driven model aligns with privacy regulations and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Reduced Redundancy: Traditional healthcare systems often involve redundant data collection, with patients providing the same information to multiple providers. SSI eliminates this redundancy by allowing patients to share verified data, reducing the burden of repetitive paperwork and improving data accuracy.
Empowering Research Participation: Patients can choose to participate in medical research initiatives by sharing their health data securely. SSI enables individuals to contribute to scientific advancements while maintaining control over their data and ensuring that it is used for ethical and research-approved purposes.
Enhanced Portability: Patients can access their health records anytime, anywhere, using a digital wallet or identity app. This portability is particularly valuable during travel or when seeking care from different providers. It ensures that critical health information is readily available when needed.
Emergency Medical Response: During emergencies, immediate access to accurate medical records can be a matter of life and death. SSI facilitates rapid access to critical health information, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions quickly.
Data Security: With patients in control of their health data, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access is significantly reduced. Data remains under the patient’s encryption and protection, minimizing the appeal of healthcare data as a target for cyberattacks.
In essence, SSI’s integration into healthcare data management empowers patients with secure, portable, and privacy-respecting health records. Patients become active participants in their healthcare journey, seamlessly sharing data with trusted providers and researchers while retaining sovereignty over their medical information. This transformative shift not only enhances data security but also improves the overall quality of care and patient experience in the healthcare ecosystem.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Self-Sovereign Identity
SSI enables secure, instant identity verification for financial transactions, simplifying account openings and reducing fraud.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) not only simplifies identity verification but also brings a new level of security and efficiency to financial transactions. Whether it’s opening a bank account, applying for a loan, or conducting digital payments, SSI introduces several advantages that enhance the overall financial experience.
1. Streamlined Account Openings
In the traditional banking sector, opening a new account often involves a laborious process. Customers are required to visit a physical branch, provide multiple forms of identification, and fill out extensive paperwork. With SSI, this process becomes significantly more efficient:
Digital Credentials: Individuals can present their digital identity credentials, which are stored securely on a blockchain or decentralized network. These credentials contain verified personal information, making the onboarding process faster and more convenient.
Remote Verification: SSI allows for remote identity verification, eliminating the need for customers to physically visit a bank branch. This is especially relevant in today’s digital age, where remote interactions are preferred.
Selective Disclosure: When opening an account, individuals can selectively disclose specific attributes from their digital credentials, such as proof of age or address, without revealing unnecessary personal information. This enhances privacy and security.
2. Reduced Fraud
Financial institutions face a constant battle against identity theft and fraudulent account openings. SSI provides a robust defense against these challenges:
Cryptographic Security: SSI relies on cryptographic keys and decentralized ledgers, making it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to forge or manipulate identity credentials.
Immutable Records: Information recorded on the blockchain is immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with. This ensures the integrity of identity data and reduces the risk of fraud.
Biometric Authentication: SSI systems can incorporate biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for added security. These biometric data points are stored securely and can only be accessed with the user’s consent.
3. Digital Payments and Transactions
In the realm of digital payments, SSI offers a frictionless experience:
Cryptocurrency Transactions: When conducting cryptocurrency transactions, users can verify their identity and authorization with their SSI credentials, ensuring that only the rightful owner can initiate payments.
Cross-Border Transactions: SSI’s global interoperability makes cross-border transactions more efficient. Users can securely prove their identity and comply with international regulations without cumbersome paperwork.
Smart Contracts: SSI can be integrated with smart contract platforms, automating financial agreements based on identity verification. This reduces the need for intermediaries in financial transactions.
4. Enhanced User Control
SSI empowers individuals with control over their financial identity. They can choose when and how to disclose their credentials, ensuring that their personal information is not unnecessarily exposed.
The Road Ahead
As the adoption of Self-Sovereign Identity continues to grow, the financial sector stands to benefit significantly. SSI promises to revolutionize account openings, reduce fraud, and enhance the overall security and efficiency of financial transactions. With the integration of this innovative identity management approach, the financial industry is poised to enter a new era of customer-centric, secure, and streamlined services.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Self-Sovereign Identity | What You Need To Know
While Self-Sovereign Identity is promising, it is not without challenges. Adoption and standardization are ongoing concerns, as is the need to educate users about the benefits and responsibilities of managing their digital identities.
Indeed, the promise of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) comes with its share of challenges and complexities that need to be addressed. Here are some of the key challenges associated with the adoption of SSI:
Adoption Hurdles:
Awareness and Education: Many individuals are not yet familiar with the concept of SSI and may not fully understand the benefits and responsibilities it entails. Education and awareness campaigns are crucial to drive adoption.
Resistance to Change: People are accustomed to centralized identity systems, and shifting to a new paradigm can be met with resistance. Overcoming the inertia of the status quo is a significant challenge.
Interoperability: Achieving interoperability among different SSI solutions and platforms is a complex task. Without interoperability, the benefits of SSI may be limited.
Standardization:
Lack of Global Standards: The absence of universally accepted standards for SSI poses a challenge. Standardization is crucial to ensure compatibility, security, and widespread adoption.
Fragmented Ecosystem: The SSI ecosystem is still fragmented, with various providers, protocols, and platforms vying for dominance. This fragmentation can hinder the development of cohesive, standardized solutions.
Security and Privacy:
Key Management: Individuals are responsible for managing their cryptographic keys, which can be complex and prone to errors. Ensuring secure key management is essential to prevent identity theft.
Privacy Concerns: While SSI is designed to enhance privacy, it also raises concerns about how identity data is handled and shared. Striking the right balance between privacy and usability is a challenge.
Trust in Issuers: Trust in the organizations that issue verifiable credentials is essential. Ensuring the authenticity of issuers and their credentials is crucial to prevent fraudulent claims.
Regulatory Compliance:
Legal Frameworks: SSI operates in a legal and regulatory environment that is still evolving. Adhering to local and international laws while maintaining the principles of SSI is a complex task.
Identity Verification: Regulatory requirements for identity verification may vary across regions and industries. SSI solutions need to be adaptable to different compliance standards.
User Experience:
Usability: SSI solutions must offer user-friendly experiences that are as seamless as traditional identity verification methods. Complex user interfaces can deter adoption.
Recovery Mechanisms: Designing effective recovery mechanisms for individuals who lose access to their digital identity or keys is a challenge. Balancing security with user accessibility is crucial.
Scalability:
- Scalability Issues: As the adoption of SSI grows, scalability becomes a concern. Ensuring that SSI systems can handle a large number of users and transactions is essential.
Cost and Infrastructure:
- Infrastructure Costs: Developing and maintaining the necessary blockchain infrastructure can be costly. These costs may be a barrier to entry for some organizations and individuals.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of SSI are compelling. As the technology matures and stakeholders work together to address these issues, the path to widespread adoption becomes clearer. Collaboration among industry players, standardization efforts, and continuous education are crucial in overcoming these challenges and realizing the vision of self-sovereign identity.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) v1.0
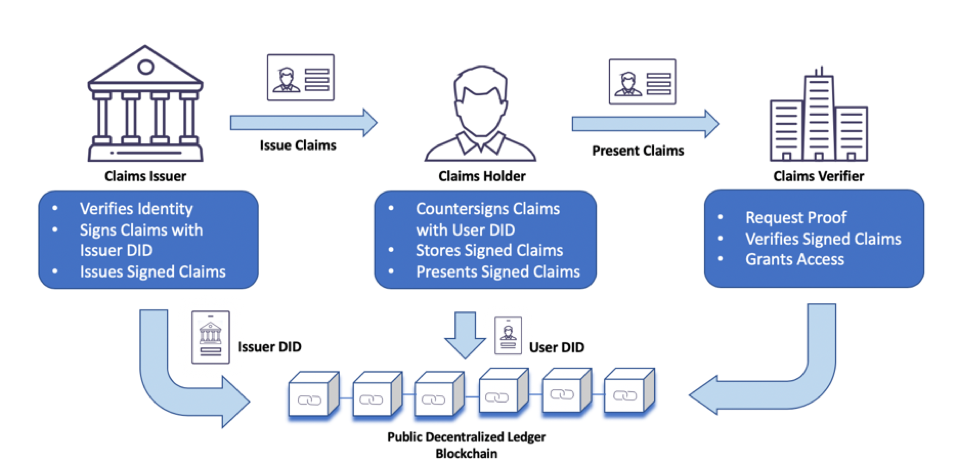
Conclusion
Web3, with its focus on decentralization and individual empowerment, is ushering in a new era of identity management through Self-Sovereign Identity. This innovative approach gives individuals the keys to their digital identities, offering enhanced privacy, security, and control. As SSI continues to evolve and gain acceptance, it has the potential to transform how we interact online, ensuring that individuals, not institutions, hold the keys to their digital selves. The era of Self-Sovereign Identity is upon us, heralding a future where digital identities are truly owned and managed by their rightful owners.
Web3, driven by its core principles of decentralization, trustlessness, and individual empowerment, stands as a harbinger of a profound transformation in the realm of identity management. At its heart lies the concept of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), an innovative paradigm that bestows upon individuals the unprecedented ability to govern their digital identities with unparalleled privacy, security, and autonomy. As we delve deeper into the realm of SSI, its potential to revolutionize online interactions and redefine our digital existence becomes increasingly apparent.
SSI, in essence, reframes the narrative of digital identity. It grants individuals the keys to their digital personas, offering a level of control that was previously inconceivable in traditional identity systems. This control extends not only to the creation and management of digital credentials but also to the selective disclosure of personal information. Users have the prerogative to share only the necessary attributes for specific transactions or interactions, minimizing the exposure of sensitive data and preserving their privacy.
Privacy and security are the bedrock of SSI. Cryptographic encryption, blockchain’s immutable ledger, and user-centricity work in concert to safeguard identity information. SSI’s cryptographic infrastructure ensures that personal data remains secure, with private keys serving as the gatekeepers to access and share this information. The blockchain’s tamper-proof nature makes data breaches and identity theft exceedingly rare occurrences, instilling trust in the system.
Furthermore, SSI transcends the boundaries of centralized institutions and intermediaries. It envisions a world where individuals, rather than institutions, hold the keys to their digital selves. This shift empowers users to control their online reputations, reducing their reliance on centralized authorities for identity verification. It represents a democratization of identity, placing the individual at the epicenter of their digital existence.
As SSI continues to evolve and gain acceptance, its implications extend far beyond personal control. It holds the potential to reshape various aspects of our online interactions, from streamlined and secure login processes to the facilitation of seamless cross-border transactions. The technology is poised to underpin a wide array of applications, including secure access to digital services, robust authentication for financial transactions, and even the prevention of online identity fraud.
The era of Self-Sovereign Identity has undeniably arrived, heralding a future where digital identities are truly owned and managed by their rightful owners—individuals. This evolution aligns seamlessly with the ethos of Web3, which seeks to shift the balance of power from centralized entities to the individual. As SSI continues to mature and garner widespread acceptance, it not only promises a more secure and privacy-conscious online world but also signifies a fundamental reimagining of the relationship between individuals and their digital identities. In this new era, the keys to our digital selves are firmly in our hands, ushering in an age where autonomy, control, and empowerment reign supreme.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Gaia-X secure and trustworthy ecosystems with Self Sovereign Identity
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Web3 and Self-Sovereign Identity – NamaChain